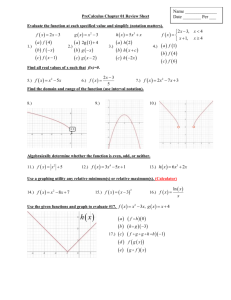
What are Finite State Automata (FSA)
advertisement

CPSC 562 – Programming Project Spring 2013 Description: As discussed in the syllabus, the class programming project will be the construction of a functional calculator. Calculator Requirements: For each computation, accept the expression from an input file (*.inp). All output must be written to a file of the same name (*.out). Upon completion of each computational statement, echo the statement to the file and print out the name of each statement variable and its numerical value. Detect and report expression errors in an accurate and understandable fashion. The calculator must be written in either C (++, #) or Java. The calculator must support the operations show in the below table. Operator X+Y X–Y X*Y X/Y X^Y MOD(X,Y) DIV(X,Y) Description Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division X to the Yth power (XY) Returns remainder of X/Y. Returns divisor of X/Y Approach: Your calculator must have the following components: Grammar – Provides a blueprint for expression parsing Lexical Analyzer – To identify tokens Parser – Creates tree to interpret each line of computation Symbol Table -- To track variables and their values as they change with each computation Conventions: All statements end with semicolons. Variables must begin with a letter, but may be some combination of letters and numbers thereafter. Variable names are limited to ten characters. The calculator enforce proper operator precedence and associatively. This must be done with or without the use of parenthesis. Expressions may be nested through the use of left and right parenthesis. You may assume the nesting level will not exceed 20. If a variable is not explicitly initialized, assume its value is zero. Character case is only relevant for variables. For example, the calculator should treat x1 and X1 as different variables, if both are declared. o Computations are cumulative; that is later computations are based on the results of earlier computations. CPSC 562 – Programming Project Spring 2013 Caveats: Use the Gold Parse Builder (GPB) to design your lexical analyzer and parser. To get you started, I am providing a sample file that allows it to process input for a simple Clike language (Tiny-DFA.GRM). If you use the GPB, use its Test capability to make sure the input is being tokenized correctly. You will need to process the XML output from GPB, which encodes the tables you will need for lexical analysis and parsing. I will provide the code that will allow you to import the XML into a program data structure (tree) and search it. To help you, I will upload a set of project resources to D2L. You must upload your materials to D2L in a zipped file per the below schedule. Testing: Full disclosure—I will evaluate both how well your calculator works, as well as, to what extent it doesn’t work. I will not publish my test files. If you wish, however, I can review your test files. Students may exchange input files for the purposes of testing only. In fact, this would be a smart thing to do. Documentation: When you upload your final project, you must also turn in the following documentation as part of the Zip file: Description of project (3-4 pages): o Approach (finite state machine, parsing method, etc), Summary of important data structures (e.g., symbol table), o Lessons learned Usage Instructions for Calculator software List of known errata or bugs (hopefully, this is short or non-existent). Partial credit will be given based on the degree of working functionality. Final grammar for calculator in BNF form. Full source code listing (well commented). Executable file and any other files necessary for compilation (e.g., project file). Test directory (test cases and corresponding output). Any GPB input files utilized (specify version). Due Dates: Date 28 Feb 2013 14 Mar 2013 9 Apr 2013 10 May 2011 Deliverable Grammar for Lexical Analysis Lexical Analyzer – Given an input file, generates an output file of labeled tokens. Full Grammar (tested on GPB) Completed Project – Inclusive of all project materials CPSC 562 – Programming Project Spring 2013 Sample Input File Contents: x1 = 2; x2 = 10.0; x3 = x1*x2; x4 = x3/(x2/x1); x5 = 0.5; x6 = ((2^x2)/(x4^4))^x5; x7 = div(x3,x4); x8 = mod(x2,x4); x9 = div(mod(x2,x3),div(x6*4,x8)); x10 = mod(div(x3,x8),mod(1,x4));