Gradients in Complexity Rubric
advertisement

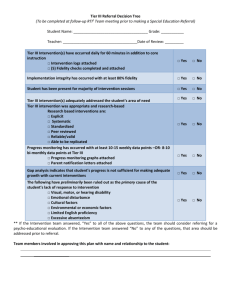
Informational Text Complexity Rubric Title/Author: Source: Type of Text: Lexile: Text Feature Layout Simple Text (Value 1) Consistent placement of text, regular word and line spacing, often large plain font Somewhat Complex Text (Value 2) May have longer passages of uninterrupted text, often plain font Graphics and pictures that directly support and help interpret the written text Table of contents, simple indexes, glossaries Graphs, pictures, tables, charts that directly support the text Types of Writing (e.g. argument, expository, opinion, narrative) Structure One type of writing is evident: (Specify style: _____________) May include different types of writing The organization of the text Is clear or chronological and/or easy to predict Connections among events or ideas are explicit and clear Language Features Mainly simple sentences Vocabulary is mostly familiar Mostly Tier One Words Informational Knowledge Demands General topic is familiar, with details known by reader Complex Text (Value 3) Longer passages of uninterrupted text may include columns or other variations in layout, often smaller more elaborate font Essential integrated graphics, tables, charts, formula (necessary to make meaning of text) Quotes, concluding appendices, table of contents, indexes, glossaries, bibliography Includes smaller sections that utilize different types of writing of varying complexity Very Complex Text (Value 4) Very long passages of uninterrupted text that may include columns or other variations in layout, often small densely packed print Extensive, intricate, essential integrated tables, charts, formulas necessary to make meaning of text Abstracts, footnotes, citations and detailed indexes, appendices, table of contents, bibliography Includes sustained sections that utilize different types of writing and/or hybrid or non-linear texts The organization of the text may include a thesis or reasoned explanation in addition to facts Connections among events or ideas are sometimes implicit or subtle The organization of the text may contain multiple pathways and/or more than one thesis Connections among events or ideas are often implicit or subtle Simple and compound sentences with some more complex constructions Vocabulary includes some unfamiliar, context-dependent words. Some Tier Two Words Many complex sentences, increased subordinate phrases and clauses or transition words Includes much academic vocabulary and some domain specific (content) vocabulary. Mostly Tier Two Words with some Tier Three Words. General topic is somewhat familiar but with many details unknown to reader The organization of the text is intricate or specialized for a particular discipline Connections among events or ideas are implicit or subtle throughout the text Mainly complex sentences, often containing multiple concepts Table of contents, indexes, glossaries, occasional quotes, references General topic is familiar, with some details new to reader Adapted from NYCSLS 2011-2012 from Gradients in Complexity: Informational Texts 2/2013 Includes extensive academic and domain specific (content) vocabulary. Mostly Tier Three Words General topic is mostly unfamiliar with most details unknown to reader Reader & Task Simple, concrete ideas Both simple and more complicated, abstract ideas A range of recognizable ideas and challenging abstract concepts Level of student interaction with the text is simple Level of student interaction with the text is slightly complex Level of student interaction with the text is complex Many new ideas and/or complex, challenging, abstract and theoretical concepts Level of student interaction with the text is highly complex Content is at or below most students’ reading ability Content is at or slightly above most students’ reading ability Content is above most students’ reading ability Content is above all students’ reading ability Notes: Additional Considerations ACTIVATE BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE: What essential/stimulating questions promote inquiry, deduction, and transfer of learning? DIFFERENTIATION: How will you adapt content to meet the needs of all learners? Glossary Narrative Writing: Creative writing, short stories, generally fiction Persuasive Writing: argument writing, to convince reader of a viewpoint Descriptive Writing: describe a person, place or thing; intended to make reader feel or visualize Tier One Words: basic words commonly used that do not require instruction Tier Three Words: high level academic vocabulary; sometimes subject specific Adapted from NYCSLS 2011-2012 from Gradients in Complexity: Informational Texts 2/2013 Expository Writing: to inform, describe, explain; generally used for research Tier Two Words: used commonly by more advanced students; struggling readers or students with limited vocabulary may require support or instruction