Social Research Foundations: Epistemology & Methods
advertisement
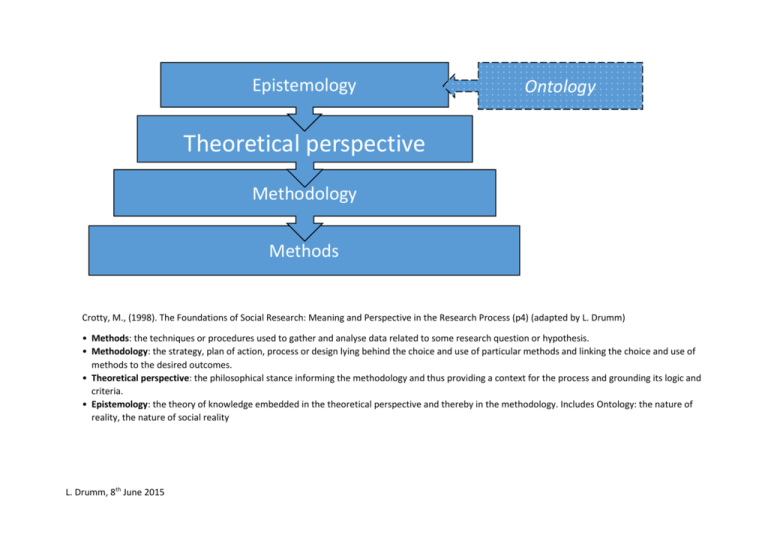
Epistemology Ontology Theoretical perspective Methodology Methods Crotty, M., (1998). The Foundations of Social Research: Meaning and Perspective in the Research Process (p4) (adapted by L. Drumm) • Methods: the techniques or procedures used to gather and analyse data related to some research question or hypothesis. • Methodology: the strategy, plan of action, process or design lying behind the choice and use of particular methods and linking the choice and use of methods to the desired outcomes. • Theoretical perspective: the philosophical stance informing the methodology and thus providing a context for the process and grounding its logic and criteria. • Epistemology: the theory of knowledge embedded in the theoretical perspective and thereby in the methodology. Includes Ontology: the nature of reality, the nature of social reality L. Drumm, 8th June 2015 Epistemology Objectivism Constructionism Subjectivism (and their variants) L. Drumm, 8th June 2015 Theoretical perspective Positivism (and post-positivism) Interpretivism • Symbolic interactionism • Phenomenology • Hermeneutics Critical inquiry Feminism Postmodernism etc. Methodology Experimental research Survey research Ethnography Phenomenological research Grounded theory Heuristic inquiry Action research Discourse analysis Feminist standpoint research etc. Methods Sampling Measurement and scaling Questionnaire Observation • participant • non-participant Interview Focus group Case study Life history Narrative etc. Visual ethnographic methods Statistical analysis Data reduction Theme identification Comparative analysis Cognitive mapping Interpretative methods Document analysis Content analysis Conversation analysis etc.











