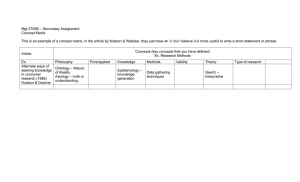
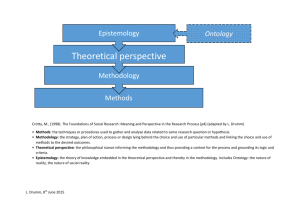
QLMMC L1 Research paradigm – set of views and beliefs that researchers use to guide their work; intellectual map…; … Four principles of Qualitative Research 1. Meaning-making (not numbers like quanti) 2. Embraces complexity (not causal relationships) Observe phenomenon in natural context Comprehensive view not causal explanation that can be generalized 3. Micro insights (not macro picture) 4. Different epistemological, ontological, and methodological positions (applying our views to the world/color what we see) Epistemology – how we know the world; understanding how the world exists (knowledge) o Positivist epistemology – quanti research – … o Constructivist epistemology – quali research – … Role of the research is crucial (background) Ontology – how do we exist in the world, nature of existence; what is the world Different epistemologies + ontologies lead to different approaches to the research process = paradigm (all are paradigms) Ontology (what) Epistemology (how) Methodology and Methods (how we study them) Two views of communication Message transmission o Focus on effects on audiences (media effects) o Messages: explicit, denotative meaning Communication as ritual o Focus on meaning-making as an active participation drawing upon cultural familiarity o Language: implicit, connotative Methodology VS methods Methodology – beliefs related to how to study the social world; how we gain knowledge about the world Method – concrete way of studying the social world o Method of data collection o Method of data analysis Methodological section in paper/thesis o … o … o … Dominant Media and Communication Paradigms Predictive: o Positivism o Post-positivism Descriptive o … o … o … T1 Data collection … Data analysis … Reflexivity – … Small t Big T Falsefication Ethics = morality