New Citizenship between knowledge and solidarity
advertisement

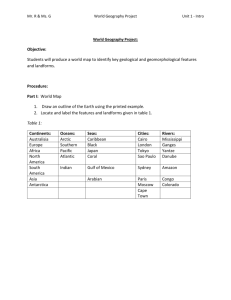
New Citizenship between knowledge and solidarity Citizenship in a global city Literature: Human Geography 5th Edition, Landscapes of Human Activities, Jerome (university of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign) Fellmann. Arthur Getis (San Diego State University). Judith Getis, pg 33-92 How the forces of cooperation and conflict among people influence the division and culture of the earth’s surface. Now this gives the opportunity to mention to you the solidarity part. We know that solidarity is defined as a pattern that allows a group of people in society to come together to either support what they feel strongly about to advance its social impact or destroy what they do not like to be specific the solidarity social movement that was happening in Poland to support the right to work for people. Ukraine Christabel Mwango Chanda 9/12/2013 Mwangochristabel33@gmail.com C onsidering the new world order that countries are forming, becoming a new citizen in another country has tests and trials for ones solidarity to both the new ground and the former so as not to be clothed with unknown espionage terms that will be difficult to understand. So knowledge of laws of citizenry and Solidarity between Experiences In the globalized cities will be the only weapon one can use to stand the ground, to defend himself, to proclaim what one believes in and better still use it to remain loyal to both actions. solidarity can not be without knowledge and knowledge may derive from solidarity. Global citizenship is grounded on knowledge which promotes the commitment for solidarity to a new dignity and meanings. Certainly there is a strong relationship between ctizenship and solidarity. In a successful society, city, and or country, for example one would suspect that, the demands on citizens, if they are good citizens, comes from some common ground of understanding values thus would seem to create a sense of solidarity or unity among the members of society, more so if the common values are strongly held among the members of the group,perhaps less so in a society that is more diverse without such a clear, single set of values and practices. Human Geography deals with the I will begin by exploring the roots world as it is and what the world and meaning of culture, as it might be made to be,litigous establishing the observed ground and non litigous , free and not so rules and laws os spatial behaviour free, discovered and exploited and and examine the areal varriations not yet exploited and discovered. in patterns of population It places emphasis on people, distribution and population what they are, where they are , change. These set the stage for the how they interact over space and following separate discussions of what kind of landscapes of human spatail patterns of language and use they erect upon the natural religion, ethnic distinction, folk and land they occupy popular culture. These are the principle expression of unity and diversity and of areal differention among the peoples and societies of the earth’s surface. The meaning of culture is big and by that I mean it is transmitted within a society to succeeding generations by immitations, instructions, examples and so on. In short we are simply saying culture is not biological it is something we all learn , it has nothing to do with instincts or genes and it can also be broken if there is no persistent and per petual figure to simulate and immulate and this I mean, now, we have terms like westernised culture and or english culture which means that, some people are willing to forsake their own way of life to adapt to their new homes as new citizens in other countries. As members of a social group, individuals acquire sets of behavior patterns,environmental and social perceptions and knowledge of existing technologies, of neccesity each of us learns the culture in which we are born and reared but we need not indeed, cannot learn its totality. Age ,sex, status and occupation may dictate the aspects of the cultural whole in which an individual becomes fully indoctrinated. With the entrance of a new ‘evil’ of globalism, new values, new ideas, norms and strange but acceptable behavious are introduced in to society. To some extent this is mitigated to the 2 extent of the new players who are willing to modify the existing behavoirs and also accomodate the local expectation, but such accommodation cannot be complete, and often (maybe always the global interloppers) bring new things or institutions a vivid example is the springing up of ‘McDonalds’that the locals have to deal with. Therefore depending on the basis of the belief system that underlies the recieving societies norms, the insertion of these new things can be of anything or lets just say is welcomed in anyway they want, that is interestingly, curiously, and at times mildly annoying all the way to being heretical and morally reprehensive. For example in the middle of last year 2012 the General Secretary of the United Nations Mr Ban Kimon was in my home country to talk about the now much talked about LGTB and I have to bring to your attenton that this issue was largely critised, politicized and at the end of his tour, his left with no succees at all, because my home country has different belief system and anything that disturbs the conservativeness of its welfare is not welcomed nicely. In every case though by introducing new ideas, globalism must to an extent threaten solidarity of the previously insular society. Understanding their spatial patterns and interactions goes far beyond and towards the providing of the world views of citizenship is my prime objective, although our focus will shift to the economic and organizational landscapes that the humans have created. We will look at economic geography in a global city and also economic development, urban systems and structures and patterns of a political system or political culture that influences the laws that govern the understanding the knowledge of citizenary and finally we will return to the underlying concern of all geographical studies of citizenship in a global city which is the relationship between human geographic patterns of processes for both the present conditions and future prospects of physical and cultural environments we have chosen to occupy , to create and try to modify. Before we go any further I would also like to define this human geography in my own way, it deals with the world as it is and what the world as it might be made to be,litigous and non litigous , free and not so free, discovered and exploited and not yet exploited and discovered. It places emphasis on people, what they are, where they are , how they interact over space and what kind of landscapes of human use they erect upon the natural land they occupy. It encompasses all those interests and topics of geography that are not directly concerned with physical environment or like cartography are technical in orientation. I would give an example of the Middle East parts of the world, citizenry is marked by alot of constrains that are both ridiculous,unimaginable and not easy to understand. Its contents provides integretion for all the social sciences. It also draws the attention to analyses of identified subfields such as behaviour, political, social and economic geography etc. Now lets look at some of these terms I have introduced with concrete examples of real citizens. -Behaviour geography deals with psychology and economics, just try and imagine the French. French people are mostly known to be very good in cooking and so they know it and they behave like it, they add a mark to their custom that is known world wide, its psychological. -political geography deals with political science, political culture, public policy, government patterns etc. The political culture of a nation influences the citizens that live in it for example we all know that the USA is a democratic country and so every citizen is oriented in such a way that you can not just trample him or her down because they know their laws, they have studied their constitution in fact they learn the document from the very tender age so as to protect themselves in their country and outside. Another example is the islamic 3 nation, the culture is engraved in people so much because they learn it from child hood which makes their solidarity strong to break. -social geography deals with social things, languages of communication, religous studies etc. I would give an example in my home counry, Zambia our social geography is so define that even though there are 72 tribes spoken in this nation each tribe live together in one location and even some churches are attributed to certain tribe and so on and so forth . -economic geography deals with regional economies, national economies and the economy of the global city. This is the interesting part, we have very rich countries in the world that it is very difficult to go to these locations as a new citizen because they have standards for example Switzerland its a small country but rich. -population geography deals with demography, statistics, urbanization rural-urbanization and globalization at large knowing this part of geography is very important because it gives you knowledge as to which countries are densely populated or the opposit it makes you choose your new location wisely. -cultural geography deals with anthropology,sociology and history of the landscape occupied by the humans. Another vital aspect is as a citizen you just need to know the history of certain things. In this one case I would give an example of myself, I have been livivng in another country which is rich in history and cultural heritage at times its annoying. But the primary thing is I had to learn their history, I had to know things because it makes life easier to flow with if you understand where people are coming from. Its also very easy to misjudge their deeds, culture, food, dressing and the like if you do not take time time to learn about their way of life and and before. • social geography • economic geography • political geography experience knowledge citizenship solidarity • cultural geography Human geography admirably serves the objective of a liberal education abroad knowledge that every good citizen whose solidarity is to stand should know. Because one has to make comparisons between the new order of things here and there. It helps us to understand the world we occupy and to appreciate the circumstances affecting peoples and countries over their own land for example the Bible land (Syria and Israel). It clarifies the contrasts in societies and cultures in the landscapes they have created in different regions of the world. Its models and explanations of how things are interacted in earth space give us a clearer understanding of the economies, socials and political systems within which we live and 4 operate. its analyses of those spatial systems make us more aware of the reactions and the prospects of our own society in an increasingly troubled and competitive world. The study of human geography there fore can help us make better knowledgeable decisions at persoanl, city, national and global level. More able to understand the important issues facing our communities and our countries and better prepared to contribute to their solutions. During my research of finding out what makes a citizen a good one I came accross 18 (Eighteen) comprehensive but not exhaustive standards that a very good citizen should be able to know and understand. Some will sound ridiculous but just remember that they are helpful at one point or another. How to use maps and other geographical tools and technologies to acquire, process and deduce and also report information from a simple spatial perspective. How to use mental maps to organize information about people, places and environments in a spatial context How to analyze the spatial organization of people, places and environments of earths space The physical characteristic of human places, diferrentiating the non occupied and the occupied . That people create regions to intepret earths complexity. Demarcating continents from each other at the least How culture and experience influences the peoples perceptions of places and regions. The physical processes that shape the patterns of the earth’s surface. For example you need to know that there are places that are prone to tsunamis, floods, volcanic eruptions, landslides etc The characteristics of spatial distribution of ecosystems on the earth, by now we all know that there are many human factors that are not in good favor of protecting the ecosystem to be specific China has been named the most dangerous country in the producing of greenn houses gases that are polluting the earths environment thus destroying the ecosystem, as a result theres a lot of money going in trying to counter attack these activities and also in the education of people about the importance of ecosystem in our lives. The characteristics and distribution causes of migration of human population which can also be due to some of the reasons I have described above. The characteristic distribution and complexity of cultural mossaics The patterns and networks of economic interdependence on the earths surface The process patterns and functions of human settlement How the forces of cooperations and conflict among people influnce the division and culture of the earth’s surface. Now this gives me the opportunity to mention to you the solidarity part. We know that solidarity is defined as a pattern that allows a group of people in society to come come together to either support what they feel strongly about to advance its social impact or destroy what they do not like to be specific the solidarity social movement that was happening in Poland to support the right to work for people. These processes made so much history, as so many people were killed in the struggle for standing up to what they wanted to achieve and the good news is even when the govern at that time tried to break the solidarity they simply failed and ended up negotiating with the ring leaders of the movement in giving the people what they wanted. How human actions modify the physical environment. How the physical systems affect human system meaning that were the land scape seems viable for production, people will find a way of settling there and erecting cities, making 5 rules and laws of how to take care of that space they have created and occupied. Another example is the physical presence of conflict among each other such civil wars affect people as well. The changes that occur in the meaning, use, distribution and importance of resources. How to apply geography to interpret the past, present and future. As illustrated by the map below. How to apply geography to interpret the present and future. CONCLUSION I hypothesize that this clash of globalism and societal solidarity is worst in countries where the social system is based on strongly held unwavering religious beliefs and teachings. It is somewhat less difficult where the norms are more cultural and superstitious, but more moderate than religion, for example in ukrainian culture it is not allowed to pass items to another accross a threshold nor whistling while in the house, and less problematic in countries that tend to support diversity already although I would contend that even though these are not as open to new ideas as they like to think that way. I wish I had the perfect way of explaining the topic ‘the new citizenship between knowledge and solidarity. Rwanda Northern Ireland , the middle East do not give much hope so far that solidarity and globalism are compatible concepts, unless one society can dominate the world and impose its new world rules, laws, regulations and standards on each and everyone which is far from becoming anything a reality. In a global/city solidarity can not be without knowledge and knowledge may only bw gotten from solidarity of held belief and experiences. Global citizenship is grounded on knowing some of the few things I have writen though not conclusive which promotes the commitment for solidarity to a new dignity and meaning. New Citizenship in between knowledge and solidarity in a global city. Writen by Mwango Christabel Chanda Volyn National University im lesya Ukrainka (Eastern European National University) Faculty of International Relations Lutsk city Vinnichenka 22 Volynska Oblast Ukraine 6