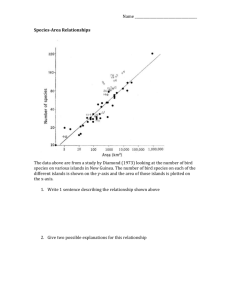
Name: AP Environmental Science Biodiversity Loss and Species
advertisement
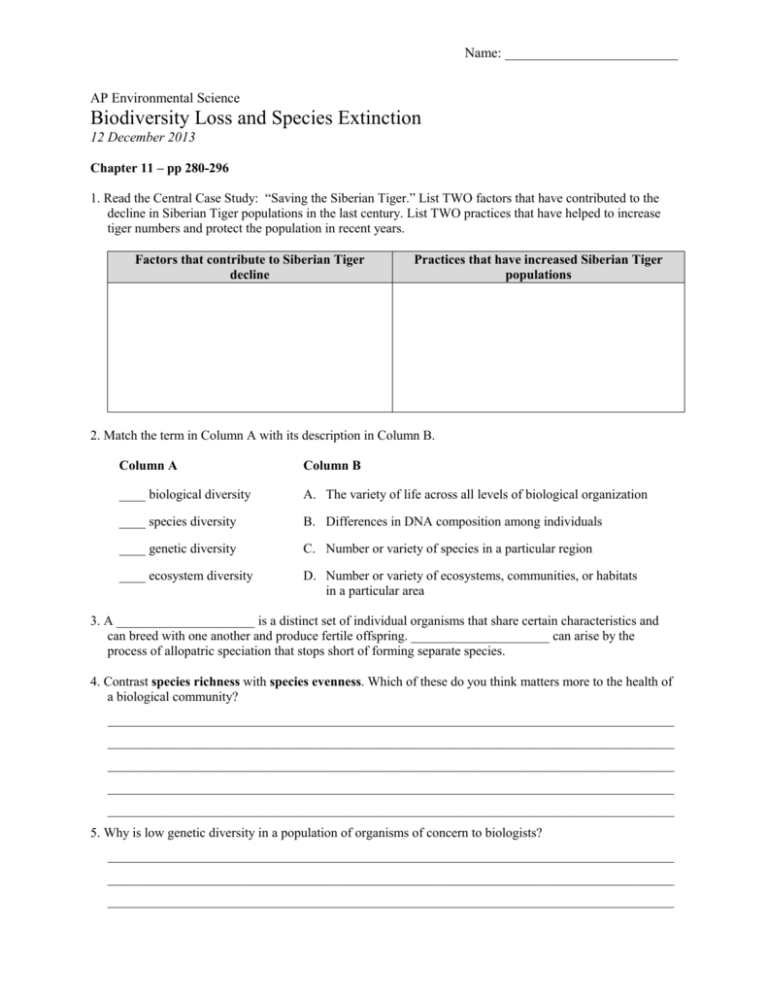
Name: _________________________ AP Environmental Science Biodiversity Loss and Species Extinction 12 December 2013 Chapter 11 – pp 280-296 1. Read the Central Case Study: “Saving the Siberian Tiger.” List TWO factors that have contributed to the decline in Siberian Tiger populations in the last century. List TWO practices that have helped to increase tiger numbers and protect the population in recent years. Factors that contribute to Siberian Tiger decline Practices that have increased Siberian Tiger populations 2. Match the term in Column A with its description in Column B. Column A Column B ____ biological diversity A. The variety of life across all levels of biological organization ____ species diversity B. Differences in DNA composition among individuals ____ genetic diversity C. Number or variety of species in a particular region ____ ecosystem diversity D. Number or variety of ecosystems, communities, or habitats in a particular area 3. A _____________________ is a distinct set of individual organisms that share certain characteristics and can breed with one another and produce fertile offspring. _____________________ can arise by the process of allopatric speciation that stops short of forming separate species. 4. Contrast species richness with species evenness. Which of these do you think matters more to the health of a biological community? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Why is low genetic diversity in a population of organisms of concern to biologists? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Assessment Key: Know why measuring biodiversity is difficult. 6. List THREE reasons why estimating the actual number of species on our planet is difficult and remains incomplete. i. _______________________________________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________________________________ iii. _______________________________________________________________________________ Assessment Key: Understand the factors that contribute to the apparent latitudinal gradient of species diversity that exists on the Earth. _____ 7. The number of species in an ecosystem generally increases as one travels from the poles to the equator. Which of the following does NOT support this latitudinal gradient in species richness? A. B. C. D. E. Terrestrial plant productivity, which supports food webs, is typically higher in tropical latitudes. Climates are more stable in tropical latitudes which favor specialist species. Previous glaciation events repeatedly displaced numerous species from higher latitudes. Variable climates in temperate biomes favor more tolerant and more competitive generalists. Habitats that are more structurally diverse or that exist in a patchwork have more ecotones that favor greater local species diversity. 8. Explain the difference between extinction and extirpation. ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Read each statement. Mark it with ‘T’ if the statement is true. Mark it with ‘F‘ if the statement is false. _____ a. Most extinctions in the past have occurred gradually one by one at a pace scientists call the background rate of extinction. _____ b. Mass extinctions are regular occurrences, happening approximately every 1,000 years or so. _____ c. Scientists estimate that our planet has experienced five major mass extinction events over the past 440 million years. _____ d. Dinosaurs perished during the most recent mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, 65 million years ago. _____ e. Many agree that our planet is poised to see the next, or sixth, mass extinction and that it has been brought about by humans. Assessment Key: Know the significance of the IUCN Red List and the Living Planet Index. 10. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) maintains a ______________________, an updated list of all species facing high risks of extinction. 11. What is the general trend in the United Nations Environment Programme’s Living Planet Index? Why is this of concern? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Assessment Key: Know the FIVE primary causes of population decline and species extinction. Be able to give examples of each. 12. List the FIVE primary causes of population decline and species extinction. Define each. i. _______________________________________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________________________________ iii. _______________________________________________________________________________ iv. _______________________________________________________________________________ v. _______________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the single greatest cause of biodiversity loss today? ___________________________________ 14. Sudden elimination of habitat is uncommon; however, _______________ ______________________ is far too routine as farming, logging, road building, and development gradually degrade habitats piecemeal. 15. Place the following steps of habitat degradation in order. _____ a. A few, small isolated fragments of habitat remain; any species that cannot tolerate this patchy distribution has been eliminated. _____ b. As development proceeds, developed areas increase in size, gaps between original habitat widen, and additional species are displaced. _____ c. A continuous forest is home to a variety of plants and animals. _____ d. Development and human land use form gaps that fragment the forest into smaller pieces; animals and plants adapted to unbroken forest will be eliminated. 16. Your text mentions a number of severe and concerning pollution related impacts; however, it also notes that pollution ‘tends to be less significant than public perception holds it to be.’ Why might this be so? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why are K-selected species more vulnerable to overharvesting than many other organisms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 18. List THREE methods being employed to combat overharvesting. i. _______________________________________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________________________________ iii. _______________________________________________________________________________