Stoichiometry Notesheets
advertisement
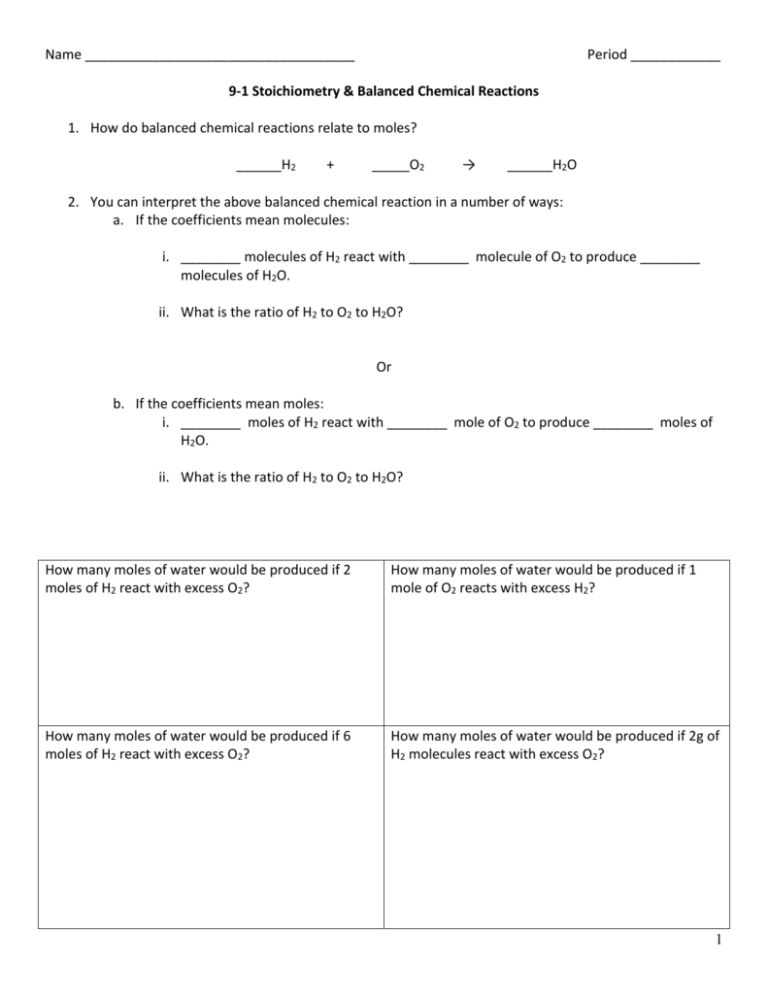
Name ____________________________________ Period ____________ 9-1 Stoichiometry & Balanced Chemical Reactions 1. How do balanced chemical reactions relate to moles? ______H2 + _____O2 → ______H2O 2. You can interpret the above balanced chemical reaction in a number of ways: a. If the coefficients mean molecules: i. ________ molecules of H2 react with ________ molecule of O2 to produce ________ molecules of H2O. ii. What is the ratio of H2 to O2 to H2O? Or b. If the coefficients mean moles: i. ________ moles of H2 react with ________ mole of O2 to produce ________ moles of H2O. ii. What is the ratio of H2 to O2 to H2O? How many moles of water would be produced if 2 moles of H2 react with excess O2? How many moles of water would be produced if 1 mole of O2 reacts with excess H2? How many moles of water would be produced if 6 moles of H2 react with excess O2? How many moles of water would be produced if 2g of H2 molecules react with excess O2? 1 1. What is Stoichiometry? a. Stoichiometry – b. Why do we care about Stoichiometry? 2. How do you sole a Stoichiometry problem? a. Mole-Mole Problems require 3 steps to solve i. ii. iii. Ammonium nitrate decomposes into dinitrogen monoxide and water. How many moles of products are produced from 2.25 moles of reactants? Equation: Ratio: Dimensional Analyses: Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. How many moles of HCl are needed to react with 2.3 moles of Zn? Equation: Ratio: Dimensional Analyses: 2 10-2 Stoichiometry Problems 1. Things to remember when doing Stoichiometry Problems: a. A balanced equation represents a chemical reaction that conforms to the Law conservation of matter b. Subscripts can NEVER be changed to balance a chemical equation. c. The total atoms of the reactants is the same as the total atoms of the products. d. Coefficients in a balanced equation relate moles of substances in the reaction. e. Coefficients are used in constructing the molar ratio for a stoichiometric problem. f. Grams of the known must first be converted to moles, then use the molar ratio to relate the 2 substances, finally convert the moles of the unknown to grams or whatever. 2. How to do Mass-Mass Stoichiometry Problems: What mass of Al2O3 can be prepared by the reaction of 67.5 g of Al according to the equation below? 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3 Glucose is used as an energy source by the human body. Calculate the number of grams of O2 needed to combust 12.5 g of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. 3 During WWII Germany used a method called the Haber Process to produce ammonia for explosives. Today a similar process is used to make fertilizers. If an excess of nitrogen is reacted with 1.71 mol of hydrogen, how many grams of ammonia can be produced? Iron will react with oxygen gas to produce iron (III) oxide. How many grams of iron (III) oxide will be produced if 0.18 mol of iron reacts? 1. How to do Mass-Volume Stoichiometry Problems: Airbags contain a powder called sodium azide (NaN3). When exposed to a spark the sodium azide quickly decomposes into sodium and nitrogen gas. If an uninflated airbag contains 125 g of NaN3, what volume in liters of nitrogen gas will be produced at STP? 2. How to do Mass-Volume Stoichiometry Problems: What volume in liters of hydrogen gas is needed to react completely with 15.5 L of nitrogen gas to produce ammonia gas at STP? 3. How to do Mass-Particle Stoichiometry Problems: How many particles of barium hydroxide are produced from the single replacement reaction of barium and 9.54 g of water? 4 4. How to do Volume-Particle Stoichiometry Problems: How many liters of hydrogen gas are produced from the single replacement reaction of calcium with 6.09x1023 molecules of hydrochloric acid? 10-3 % Yield 1. No chemical reaction actually takes all the reactants and converts them to products. 2. Usually dirty glassware and impurities in the reactants causes chemical reaction to yield less products than the Stoichiometry predicts 3. Because chemical reactions don’t ever go to completion it is necessary to tell the % yield of a chemical reaction a. Expected Yield (Theoretical Yield) - Amount of product that should be produced based on Stoichiometric calculation. b. Actual Yield -Amount of product actually obtained in the lab. c. % Yield – a way of qualitatively describing the efficiency of a chemical reaction by relating the actual yield to the expected yield Actual yield: Expected yield: % Yield is the opposite of % Error: % error = expected - actual x 100% = expected 5 % 𝑌𝑖𝑒𝑙𝑑 = 𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑥 100% = 𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 Lauren burned 4.9 g of Magnesium in oxygen gas. The actual yield obtained was 6.5 g of MgO. What is the % yield and the % error? • write and balance the equation. • calculate the expected yield from the equation. • calculate the % yield and % error from the above data. 6








