Differentiable manifold: Orthogonal curvilinear coordinates
advertisement

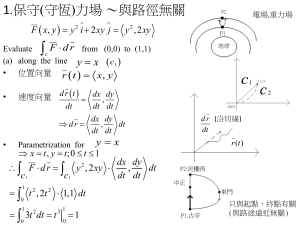
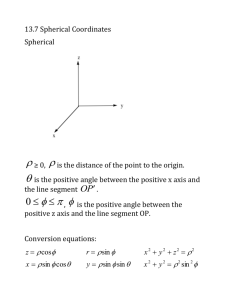
Differentiable manifold: Orthogonal curvilinear coordinates, cylindrical and spherical A differentiable manifold has a differential operator (del operator) xˆ yˆ zˆ x y z eˆ eˆ1 eˆ 2 3 h1 u1 h2 u 2 h3 u 3 In which h1, h2, h3 are scale factors for the given (orthogonal) curvilinear coordinate system as defined by a volume in space dV h1 h2 h3 du 1 du 2 du 3 The scaling relationship is defined by change of position r r r dr du1 du 2 du 3 u1 u 2 u 3 r r For which magnitude ds dr dr du i du j u i u j i, j 2 dr dr g ij du i du j i, j r r where gij is defined as the metric of the (u1, u2, u3) coordinates u i u j If the coordinates are orthogonal then gij r r =0 u i u j for i j ds 2 g 11du12 g 22 du 22 g 33 du 32 and length (squared) is and then ds1 g11 du1 h1 du1 ds 2 g 22 du 2 h2 du 2 ds3 g 33 du 3 h3 du 3 And this is how the scale factors h1, h2, h3 for the coordinate system can be realized, since position is also defined by r xxˆ yyˆ zzˆ = fixed reference basis coordinate system, which allows the ui scaling metric to be determined relative to the fixed reference (x,y,z) coordinates by i.e. x k g i k u 2 ii 2 from which we can get the (h1, h2, h3) scale factors Example: Cylindrical coordinates (r,,z) may be related to the fixed (x,y,z) frame by x r cos y r sin y x z g r r r 2 2 2 cos 2 sin 2 0 2 11 2 2 g 2 22 x y z g 2 133 y x z z z z 2 2 z=z =1 2 r 2 sin 2 r 2 cos 2 0 = r2 2 =1 For which the scale factors are then (h1, h2, h3) = (1, r, 1) Other coordinate system relationships are Spherical: x = R cossin For which the scale factors are Hyperbolic: z = R cos (h1, h2, h3) = (1, R, Rsin ) x = b cossinh For which the scale factors are y = R cossin y = b sin sinh (h1, h2, h3) = z = c cosh a2 + b2 = c2 The vector space derivatives in orthogonal fixed and curvilinear coordinates (cylindrical and spherical) are then 1. Divergence F i F Fy Fz F x x y z 1 h1 h2 h3 i F h1 h2 h3 u i hi 1 R 2 FR 1 sin F 1 F 2 R R sin R sin R 1 rFr 1 F Fz r r r z 2. Curl eˆi ijk hi hk F k j h h h u i , j ,k 1 2 3 F rˆ 1 r r Fr rˆ rF zˆ z Fz xˆ F x Fx Rˆ 1 2 R sin R Fr Rˆ RF yˆ y Fy zˆ z Fz R sin ˆ R sin F 3. Laplacian 2 g i 1 h1 h2 h3 g h1 h2 h3 u i hi2 u i 2 g 2g 2g 2g x 2 y 2 z 2 1 g 1 2 g 2 g r r r r r 2 2 z 2 g 2g 1 2 g 1 1 R sin R R 2 sin R 2 sin 2 2 R 2 R