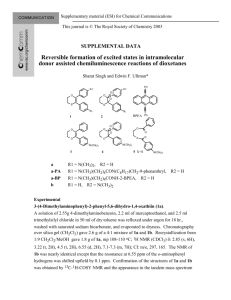
Synthesis of new substituted N-sulfonyl pyrrolidine-2,5
advertisement

S1 Synthesis of new substituted N-sulfonyl pyrrolidine-2,5-dione using Dawson type heteropolyacid as catalyst. Chafika BOUGHELOUM, Robila BELGHICHE, Abdelrani MESSALHI LSC, Sciences Faculty, Chemistry Department, Badji Mokhtar-Annaba University, BP 12 El Hadjar, 23000, Algeria E-mail: c_bougheloum@yahoo.fr Supplemental Materials General procedure for the synthesis of carboxylsulfamides (1a-h) ………….…S 2 Selected spectra data ……………..……………………..………………….….… S 2-3 General procedure for the synthesis of deprotected sulfamides (2a-h) ….……...S 3 Selected spectroscopic data ...................................................................................S 3-4 Supplemental data of compounds (3a-h) .………………...……………………S 5-10 S2 General procedure for the synthesis of carboxylsulfamides[24] (1a-h): To a stirred solution of chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI) (1.62 g, 11.44 mmol) in (10 mL) of anhydrous dichloromethane at 0 °C was added (1.47 g, 11.39 mmol) of t-butanol in the same solvent. After a period of 30 min, the resulting solution and (1.75 mL, 1.1 equiv) of triethylamine was slowly added into a solution containing 1 equiv of primary or secondary amine in (10 mL) of dichloromethane. The reaction did not rise above 5 °C. The resulting reaction solution was allowed to warm up to room temperature for over 2 h. The reaction mixture diluted with 30 mL of dichloromethane, washed with HCl 0.1 N and water. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuum to give the crude product. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (CH2Cl2/ MeOH: 9.9/0.1) to give a carboxylsulfamides in good yields. Selected spectroscopic data N -(butyl)-N'-(tert-butoxycarbonyl) sulfamide (1b): Yield: 88%, Rf = 0.80(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 0.88(t, J=5.02Hz, 3H, CH3), 1.32 ( m, 2H, CH2), 1.42 ( s, 9H, tBu), 1.49(m, 2H, CH2), 2.99 (m, 2H, CH2), 5.05 ( t, J=5.4Hz, 1H, NH), 7.32 ( s, 1H, NH-Boc). 13C NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm ): 13.6, 19.7, 27.9, 30.9, 43.5, 83.6, 150.4. N-(benzyl)-N'-(tert-butoxycarbonyl) sulfamide (1e): Yield: 75%, Rf = 0.84(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (CDCl3, δppm): 1.40(s, 9H, tBu), 4.16 (s, 2 H, CH2-N), 7.25-7.36 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 10.5 (s, 1H, NH). MS (ESI+ 70 eV m/z): 105.98 (30%), 304.00 ([M+NH4]+, 100%). S3 N-(3, 4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)-N'(tert-butoxycarbonyl) sulfamide (1g): Yield: 82%, Rf = 0.86(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 1.5 (s,9H, tBu), 2.90 (t, J = 5.70 Hz, 2H, CH2-Ph), 3.30 (t, J =6.02 Hz, 2H, CH2-N), 4.50 (s, 2H, Ph-CH2-N), 7.1-7.6(m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.8 (s, 1H, NH-Boc). MS (ESI+ 70 eV m/z): 131.93 (17%), 212.95 (32%), 229.91(27%), 273.94 (62%), 330.01 ([M+NH4]+, 100%). General procedure for the Synthesis of deprotected sulfamides[25] (2a-h): The sulfonamides was prepared from carboxylsulfamides (1 mmol) in water and stirred at reflux temperature. After 15 min the resulting reaction solution was extracted by ethyl acetate. The organic layer is dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. Selected spectroscopic data N -(3-butyl) sulfamide (2b): Yield: 75%, Rf = 0.55(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (CDCl3 , δ ppm): 0.88(t, J=5.02Hz, 3H, CH3), 1.32 ( m, 2H, CH2), 1.49(m, 2H, CH2), 2.99 (m, 2H, CH2). 13C NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 13.6, 19.7, 30.9, 43.5. MS (ESI+ 70 eV m/z): 72.02 (5 %), 153.01 ([M+1]+, 100 %). N-Benzylsulfamide (2e): Yield: 76%, Rf = 0.43(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δppm): 4.16 (s, 2 H, CH2-ph), 7.10-7.33(m, 5H, H-Ar). 13C RMN (DMSO-d6, δ en ppm): 44.2, 126.2, 126.9, 128.6, 142.3. MS (ESI+ 70 eV m/z): 105.98 (8%), 187.01 ([M+1]+, 5%), 204.00 ([M+NH4]+, 100%). S4 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-sulfonamide (2g): Yield: 78%, Rf = 0.62(CH2Cl2/MeOH, 9/1), 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.90 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H, CH2-Ph), 3.25 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H, CH2-N), 4.25 (s, 2H, Ph-CH2-N), 6.90-7.25 (m, 4H, ArH). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 28.2, 43.9, 47.2, 126.1, 126.2, 126.3, 128.6, 131.6, 133.4. MS (ESI+ 70 eV m/z): 103.97 (4%), 131.05 (7 %), 213.02 ([M+1]+, 52 %), 230.01 ([M+NH4]+, 100%) S5 Spectroscopic data for new compounds (3a-h) Figure S 1: 1H NMR of 3a Figure S 2: 1H NMR of 3c S6 Figure S 3: 1H NMR of 3d Figure S 4: MS of 3d S7 Figure S 5: 1H NMR of 3e Figure S 6: 13C NMR of 3e S8 Figure S 7: 1H NMR of 3g Figure S 8: 13C NMR of 3g S9 Figure S 9: MS of 3g Figure S 10: 1H NMR of 3h S 10 Figure S 11: MS of 3h Figure S 12: 13 C NMR of 3h