Study Guide Chapter 1
advertisement
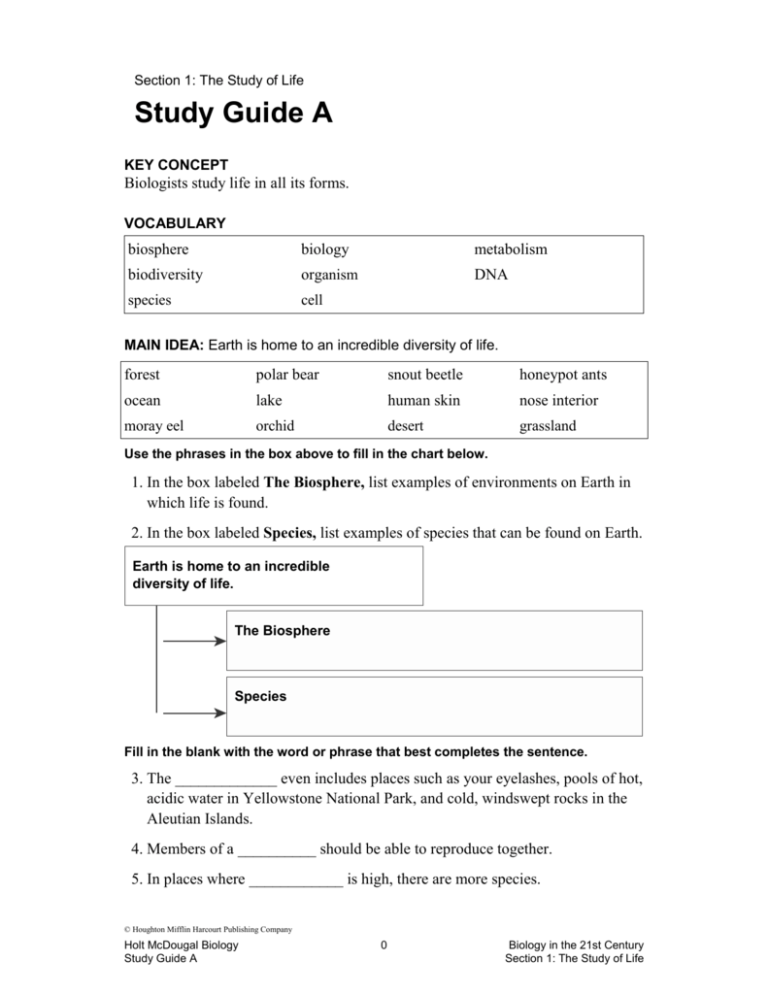
Section 1: The Study of Life Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. VOCABULARY biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA species cell MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible diversity of life. forest polar bear snout beetle honeypot ants ocean lake human skin nose interior moray eel orchid desert grassland Use the phrases in the box above to fill in the chart below. 1. In the box labeled The Biosphere, list examples of environments on Earth in which life is found. 2. In the box labeled Species, list examples of species that can be found on Earth. Earth is home to an incredible diversity of life. The Biosphere Species Fill in the blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 3. The _____________ even includes places such as your eyelashes, pools of hot, acidic water in Yellowstone National Park, and cold, windswept rocks in the Aleutian Islands. 4. Members of a __________ should be able to reproduce together. 5. In places where ____________ is high, there are more species. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 0 Biology in the 21st Century Section 1: The Study of Life Study Guide A continued MAIN IDEA: All organisms share certain characteristics. 6. In the box below, circle the four items that are characteristic of all living organisms. Cross out the items that are not characteristics of all living organisms. need energy need sunlight can reproduce made up of one or more cells produce seeds can move ability to feel pain need to sleep react to environment Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 7. The most common organisms on Earth have one cell / more than one cell. 8. Animals need energy / DNA in order to build up or break down materials. 9. Cells reproduce by dividing / combining. 10. When organisms reproduce, they pass on their metabolism / genetic material. Vocabulary Check Choose the answer that best completes each sentence. 11. All organisms store their genetic material in a. DNA. b. cells. c. species. d. metabolism. 12. An organism is a. a type of species. b. an environment in the biosphere. c. any individual living thing. d. the basic unit of life. 13. The scientific study of all forms of life is called a. geology. b. chemistry. c. physics. d. biology. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 1 Biology in the 21st Century Section 1: The Study of Life Section 2: Unifying Themes of Biology Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT Unifying themes connect concepts from many fields of biology. VOCABULARY system homeostasis ecosystem evolution adaptation MAIN IDEA: All levels of life have systems of related parts. Using the words in the box, fill in the outline with the basic systems of life. more complex 1. _____________ 2. _____________ 3. _____________ organism biosphere cell ecosystem 4. _____________ less complex MAIN IDEA: Structure and function are related in biology. Match each body part with its specialized function. 5. brain cells carry an organism 6. enzymes process information 7. feet pumps blood throughout the body 8. heart enable chemical processes 9. teeth grind food © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 2 Biology in the 21st Century Section 2: Unifying Themes of Biology Study Guide A continued MAIN IDEA: Organisms must maintain homeostasis to survive in diverse environments. 10. Circle the conditions that are regulated by homeostasis. temperature outside environment acidity thoughts blood sugar Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 11. Humans shiver in response to cold because of the body’s attempts to maintain an even temperature / acidity. 12. Homeostasis is important because behaviors / cells need certain conditions in order to function. 13. The body usually uses positive / negative feedback to maintain homeostasis. 14. The conditions outside the body are always the same / changing, but the conditions inside the body are generally very changeable / stable. MAIN IDEA: Evolution explains the unity and diversity of life. Choose whether each statement is true or false. 15. true / false All living species evolve and change over time. 16. true / false Adaptation occurs when you get cold and put on a coat. Vocabulary Check Match the words with their meanings. 17. organized group of related parts that interact to form a whole evolution 18. physical environment with different species that interact with each other and with nonliving things adaptation 19. an inherited trait that gives an advantage to individual organisms and is passed on to future generations homeostasis 20. the change in living things over time ecosystem 21. the maintenance of constant internal conditions in an organism system © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 3 Biology in the 21st Century Section 2: Unifying Themes of Biology Section 3: Scientific Thinking and Processes Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT Science is a way of thinking, questioning, and gathering evidence. VOCABULARY observation hypothesis independent variable constant data experiment dependent variable theory MAIN IDEA: Like all science, biology is a process of inquiry. Use the following words or phrases to fill in the blanks in the flow chart. forming hypotheses observing testing hypotheses evaluating results analyzing data 1. _______________ Scientists make observations and examine prior research. 5. _______________ Scientists evaluate data and conclusions presented by other scientists. 2. _______________ Scientists ask questions and try to explain observations. 4. _______________ Scientists analyze their data to draw conclusions about their research. 3. _______________ Scientists collect data that they use to support or reject a hypothesis. Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 6. A scientist begins his or her research by making observations / forming theories. 7. Scientists make observations and do experiments as a way to gather variables / evidence. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 4 Biology in the 21st Century Section 3: Scientific Thinking and Processes Study Guide A continued Fill in the chart using the words from the box. sights volume temperature mass sounds smells Qualitative data Quantitative data 8. ___________________________ 9. ___________________________ 10. ___________________________ 11. ____________________________ 12. ____________________________ 13. ____________________________ MAIN IDEA: Biologists use experiments to test hypotheses. Circle the dependent variable in each sentence. Draw a box around the independent variable. 14. A scientist is testing the effects of medication on the blood pressure of patients. 15. A scientist wants to find out how cellular respiration is affected by temperature. 16. A scientist is measuring the effect of precipitation on seed germination. Draw lines to match each type of investigation with an example. 17. Observational study Adding a solid to a liquid to find out if the solid will dissolve 18. Experiment Watching the migration patterns of white storks MAIN IDEA: A theory explains a wide range of observations. Choose whether each statement is true or false. 19. true / false A theory is a scientific idea that has been proven to be true. 20. true / false Theories can change over time as new evidence is discovered. Vocabulary Check Draw lines to connect the phrases that mean the same thing. 21. independent variable conclusion 22. dependent variable condition that is changed by a scientist 23. theory data 24. constant condition that does not change © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 5 Biology in the 21st Century Section 3: Scientific Thinking and Processes Section 4: Biologists’ Tools and Technology Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT Technology continually changes the way biologists work. VOCABULARY microscope molecular genetics gene genomics MAIN IDEA: Imaging technologies provide new views of life. Use the correct term from the box below to fill in the description with the correct type of technology. light microscope (LM) transmission electron microscope (TEM) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning electron microscope (SEM) 1. ___________________________ uses light and lenses to magnify images, can be used with living specimens, and can clearly magnify specimens up to about 1500 times. 2. ____________________________ uses electrons and computers to magnify specimens and produce three-dimensional images, cannot be used to observe living specimens, creates images that are computer colorized, and can clearly magnify specimens more than 100,000 times. 3. ____________________________ uses electrons and computers to magnify specimens and produce two-dimensional images, cannot be used to observe living specimens, creates images that are computer colorized, and can clearly magnify specimens more than 100,000 times. 4. _____________________________ uses strong magnetic fields to show a cross section of a body part and can show both soft tissues and dense tissues. Cross sections can be combined by computer to give a complete image of the whole area. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 6 Biology in the 21st Century Section 4: Biologists’ Tools and Technology Study Guide A continued MAIN IDEA: Complex systems are modeled on computers. Choose the best answer to the question. 5. Which of the following studies do you think would be most suitable for a computer model? a. A study of how fast an epidemic disease could spread in a city. b. A study of what life forms can be found in a local pond. c. A study of how animals react to confinement in a zoo or wildlife park. d. A study of how a new type of plastic could be used and what properties it has. 6. What kinds of systems are scientists most likely to model using computers? a. biological systems b. physical systems c. simple systems d. complex systems MAIN IDEA: The tools of molecular genetics give rise to new biological studies. Choose whether the statement is true or false. 7. true / false Scientists now have the ability to manipulate DNA. 8. true / false It is not possible to map the entire human genome. 9. true / false A gene is a type of computer model used to study diseases. Vocabulary Check Draw lines to match each word or phrase with its correct meaning. 10. gene the study of genomes 11. molecular genetics a tool for enlarging images 12. genomics the study and manipulation of DNA 13. microscope a segment of DNA that stores genetic information © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 7 Biology in the 21st Century Section 4: Biologists’ Tools and Technology Section 5: Biology and Your Future Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT Understanding biology can help you make informed decisions. VOCABULARY biotechnology transgenic MAIN IDEA: Your health and the health of the environment depend on your knowledge of biology. Fill in the mind map with three ways that biology affects your health and the world around you. 1. 2. Your health 3. Importance of biology The world around you 4. 5. 6. MAIN IDEA: Biotechnology offers great promise but also raises many issues. Use the chart below to list the benefits of biotechnology, as well as the risks and ethical concerns about biotechnology. Benefits Risks and Ethical Concerns 7. 8. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 8 Biology in the 21st Century Section 5: Biology and Your Future Study Guide A continued MAIN IDEA: Biology presents many unanswered questions. What questions do you have about biology or scientific research? List three topics in biology that you want to learn more about. 9. _______________________________________________________________ 10. _______________________________________________________________ 11. _______________________________________________________________ Vocabulary Check Choose the answer that best completes each sentence. 12. Biotechnology is technology based on a. geological processes. b. astronomical events. c. living things and biological processes. d. computer modeling. 13. A transgenic organism is one that a. already exists in nature. b. has been developed through genetic manipulation. c. developed when two species reproduced together in nature. d. exists only as a computer model, but not in real life. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 9 Biology in the 21st Century Section 5: Biology and Your Future