Reading Guide - Mr. Lundgren`s Science Site
advertisement

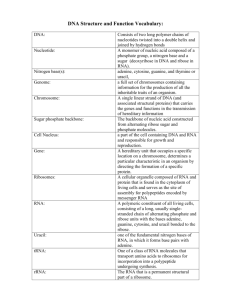
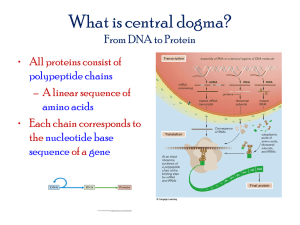
Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren Ch 13: RNA & Protein Synthesis I. Metacognition: By the end of this unit you are expected to be able to do/complete all learning targets below. Your teacher will help you understand this material, but it is ultimately your responsibility. Constantly ask yourself whether or not you are meeting these targets, and what are you doing to master them? Pre Check Post Check Objectives (*EOB) 1. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA. 2. Explain the process of RNA synthesis.* 3. Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read.* 4. Summarize the process of translation.* 5. Describe the effects mutations can have on genes.* II. Vocabulary Building: Due Date: __________________ How am I going to learn the terms? (select one or create your own idea that is teacher approved) ⃝ Make flashcards of all vocabulary terms and definitions. ⃝ Make a flip chart including all vocabulary terms and definitions. ⃝ Other Ideas (teacher approved)? ________________________________________________ III. Chapter Vocabulary and Root Words: Term Definition RNA Messenger RNA Ribosomal RNA Memory Cue Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Transfer RNA Transcription RNA Polymerase Introns Exons Polypeptide Genetic Code Codon Translation Date: Teacher: Lundgren Name: Biology 1-2 Anticodon Gene Expression Mutation Point Mutation Frameshift Mutation Mutagen Polyploidy Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren IV. Guided Reading Section Questions (*EOB): Section 13.1 p. 362-365: RNA Pre Objectives (*EOB) Check 1. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA. 2. Explain the process of RNA synthesis.* Post Check 1. Use the terms to compare the similarities and differences between DNA and RNA. Double strand Single strand Nucleic Acid Uracil Thymine Nucleotides Deoxyribose Genetic Instructions Build Proteins Ribose Both DNA RNA 2. What is similar to both DNA and RNA? ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. Based on Figure 13-1, which part represents DNA? Why? RNA? Why? _________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren 4. Complete the table below contrasting the three types of RNA. Name Picture Function Messenger RNA Ribosomal RNA Transfer RNA 5. Explain the process of transcription. * ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. Why is it important for a single gene to be able to produce hundreds or thousands of the same RNA molecules? ________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. Suppose you start with the DNA strand A C C G T C A C. Use the rules of base pairing to list the bases on a messenger RNA strand transcribed from this DNA strand (hint: remember what bases are present in DNA vs. RNA).* _________________________________________ 8. Compare introns to exons. _________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Section 13.2 p. 366-371: Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis Pre Objectives (*EOB) Check 1. Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read.* 2. Summarize the process of translation.* Date: Teacher: Lundgren Post Check 1. Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. ________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are codons and anticodons? _______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. Using Figure 13-6, identify the amino acids specified by codons: AUG, UGG, AAG, UAG. ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. Summarize the process of translation. * __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. How is protein synthesis different from DNA replication? ____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren 6. Describe the “central dogma” of molecular biology. * _______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. Why is the genetic code considered universal? _____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. In what way does controlling the proteins in an organism control the organism’s characteristics? ______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 9. Complete the flowchart below about protein synthesis. * 10. A certain gene has the following DNA base sequence: * TACGACAAGTCCACAATC a. From left to right, write the sequence of the mRNA molecule transcribed from this gene. ________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren b. Using Figure 13-6, read the mRNA codons from left to right. Then write the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide. _____________________________________________________________________ Section 13.3 p. 372-376: Mutations Pre Objectives (*EOB) Check 1. Describe the effects mutations can have on genes.* Post Check 1. Define mutations and describe the two main categories of mutations. * ________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. Complete the table below regarding mutation types. * Example Gene or Chromosomal Mutation Point, Frameshift, or both Specific Name of Mutation Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Example Gene or Chromosomal Mutation Date: Teacher: Lundgren Point, Frameshift, or both Specific Name of Mutation 3. What is a mutagen? Give examples of types of mutagens. ___________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren 4. List three effects mutations can have on genes. * __________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Can mutations have a positive effect? Explain. * ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. The effects of mutations are not always visible. Explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutations it is. * ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is the significance of mutations to living things? * ______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. A mutation in the DNA of an organism changes one base sequence in a protein-coding region from CAC to CAT. What is the effect of the mutation on the final protein? Explain.* ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren 9. How does the possible impact of a chromosomal mutation that occurs during meiosis differ from that of a similar event that occurs during mitosis of body cells that is not involved in reproduction? _______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 10. Use the following table to answer the questions below. * a. The table shows DNA codons for three amino acids. How would a substitution mutation in the third nucleotide position of the codons for alanine and valine affect the resulting protein? _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. The three amino acids shown in the table have very similar – though not identical – properties. What substitution mutations could result in switching one of these amino acids for another? What might be the result? ___________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren V. I can statements: Read the following I can statements and complete the table with evidence you know that I can statement. This could include a sentence, a picture, etc. You MUST complete this section for credit. TB I can statement (*EOB) Section 13.1 1a. I can describe three similarities between RNA and DNA. Evidence - 13.1 1b. I can describe three differences between RNA and DNA. - 13.1 1c. I can describe the three main types of RNA. - 13.1 1d. I can draw a picture of the three main types of RNA. - - 13.1 2a. I can describe the process of transcription.* 13.1 2b. I can describe the role of enzymes in the process of transcription.* Name: Biology 1-2 13.1 2c. I can transcribe a strand of mRNA from a DNA template.* 13.1 2d. I can explain the role of promoters in RNA synthesis. 13.1 2e. I can describe RNA editing during RNA synthesis. 13.2 3a. I can identify codons from a strand of mRNA.* 13.2 3b. I can read and provide an example of how to use a codon chart.* 13.2 4a. I can describe the role of a ribosome in translation. 13.2 4b. I can describe the role of tRNA in translation. 13.2 4c. I can describe the role of anticodons in translation. Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren Name: Biology 1-2 13.2 4d. I can describe the three major steps in how a polypeptide is assembled.* 13.2 4e. I can describe the central dogma of molecular biology. 13.2 4f. I can determine an amino acid sequence from an original DNA sequence.* 13.3 5a. I can describe a point mutation and give an example.* 13.3 5b. I can describe a frameshift mutation and give an example.* 13.3 5c. I can describe chromosomal mutations and give an example.* 13.3 5d. I can define mutagens and provide examples. Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren Name: Biology 1-2 13.3 5e. I can give examples of helpful mutations.* 13.3 5f. I can give examples of harmful mutations.* 13.3 5g. I can give examples of mutations that have no effect.* Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren Name: Biology 1-2 Period: Date: Teacher: Lundgren VI. Study Guide The final chapter assessment is on ____________________________ To study for the test I have completed the following: ___ Completing the entire reading guide ___ Rereading the entire chapter ___ Making flashcards ___ Making my own study guide ___ Reviewing all of my notes ___ Reviewing all of my labs ___ Reviewing all of my worksheets ___ Reviewing all of my quizzes ___ Quizzing myself ___ Quizzing a classmate ___ Creating a practice test ___ Outlining the chapter ___ Copying my notes ___Making a graph organizer ___ Getting additional help from my teacher ___ Taking online quizzes/tests on Biology.com website ___ Other (explain: _______________________________) ___ Other (explain: _______________________________) ___ Other (explain: _______________________________) ___ Other (explain: _______________________________) I predict that I will earn the following grade on my assessment ___________ because ___________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________