DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
advertisement

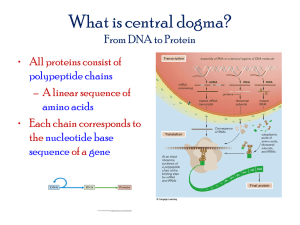
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary: DNA: Nucleotide: Nitrogen base(s): Genome: Chromosome: Sugar phosphate backbone: Cell Nucleus: Gene: Ribosomes: RNA: Uracil: tRNA: rRNA: Consists of two long polymer chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix and joined by hydrogen bonds A monomer of nucleic acid composed of a phosphate group, a nitrogen base and a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA). adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine or uracil, a full set of chromosomes containing information for the production of all the inheritable traits of an organism. A single linear strand of DNA (and associated structural proteins) that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information The backbone of nucleic acid constructed from alternating ribose sugar and phosphate molecules. a part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction. A hereditary unit that occupies a specific location on a chromosome, determines a particular characteristic in an organism by directing the formation of a specific protein. A cellular organelle composed of RNA and protein that is found in the cytoplasm of living cells and serves as the site of assembly for polypeptides encoded by messenger RNA A polymeric constituent of all living cells, consisting of a long, usually singlestranded chain of alternating phosphate and ribose units with the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil bonded to the ribose. one of the fundamental nitrogen bases of RNA, in which it forms base pairs with adenine. One of a class of RNA molecules that transport amino acids to ribosomes for incorporation into a polypeptide undergoing synthesis. The RNA that is a permanent structural part of a ribosome. mRNA: Codon: Anticodon: Transcription: Translation: Mutation: Point Mutation: Frame-shift mutation: Deletion Mutation: Insertion Mutation: Chromosomal Mutations: Mutagen: The form of RNA that mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from a DNA template during the process of transcription. a triplet of adjacent nucleotides in the messenger RNA chain that codes for a specific amino acid in the synthesis of a protein molecule. a sequence of three nucleotides in a region of transfer RNA that recognizes a complementary coding triplet of nucleotides in messenger RNA during translation by the ribosomes in protein biosynthesis the process by which genetic information on a strand of DNA is used to synthesize a strand of complementary RNA. the process by which a messenger RNA molecule specifies the linear sequence of amino acids on a ribosome for protein synthesis. A change of the DNA sequence within a gene or chromosome of an organism either through an alteration in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA coding for a gene or through a change in the physical arrangement of a chromosome. a change in a single base in a nucleotide sequence. A mutation in a DNA chain that occurs when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three, so that every codon beyond the point of insertion or deletion is read incorrectly during translation. A mutation that arises by deletion of one or more nucleotides from a DNA sequence. A mutation that arises by insertion of one or more nucleotides into a DNA sequence. any event that changes the genetic structure of a chromosome a substance capable of inducing mutation in nucleic acids.