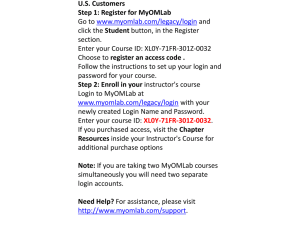
HASTAC Top Level Design

Top Level Design Document
Academic Supervisor
:
Dr. Ron Rymon
Presented By
:
Ronen Mendezitsky
Alon Weiss
Overview
HASTAC is an online security system that will be displayed at the login page of any password protected website as an extra security measure. The system will add another input field where the user will have to answer a question embedded in a picture that asks random questions about that image. A generated image will contain a large amount of details including randomly generated images and words. By using this extra security measure, we will decrease the amount of network traffic cause by brute force attacks.
The Problem
With increasing activity on the web, the quick and comfortable way of purchasing products, services and information online, more and more websites are being created to provide online paid services. This sort of development has caused the rapid increase of attempts to hack into these services providing websites. Websites owners are not only affected by the hacking of accounts, but more so by the hacking attempts, and more specifically brute force hacking attempts which increase the bandwidth load on web servers and can cause reduction in the speed and performance of the website, and could go as far as causing a DoS
(Denial of Service) on the website, which can cause site owners to create a significant loss of activity on their website.
The Target Audience
The target audience for HASTAC is any website or web service which are targeted by hackers or spammers who use brute force as a means to get a hold of user accounts and passwords or generate multiple accounts on a web service (such as email services). Such website owners suffer from these brute force attacks because of the large bandwidth those attacks generate on their server. HASTAC will help ease the pain of such bandwidth consuming operations.
The Proposed Solution
The proposed solution is a server-side component that is easily pluggable to an existing
ASP.NET website. It also provides an easy way to configure itself via a special back-office application.
Upon logging in to the website, a user is presented with a graphical image (called a
'Challenge'), that contains graphical and textual elements. Also embedded is a question that a human can easily answer, such as "What text is written in the blue box", or "Click on the old lady" (existing OCR tools easily crack the popular CAPTCHA images that always contain 3-
6 alphanumeric letters). This allows the server to validate the 'humanity' of the client.
In addition, the component contains a Denial Of Service sensor that allows itself to fortify the server against the DoS attack, and minimize traffic, HDD and CPU resource usage.
Top level client side flow diagram
Response rejected
Client is not allowed into the secured section of the website
Server sends a challange
Client sends a response
Server verifies the response
Response accepted
Client is allowed into the secured section of the website
Top level back-office flow diagram
Administrator is trying to log-in to the back-office
Server requests administrative credentials
Client sends his credentials credentials rejected
Client is not allowed into the administrative section of the website
Server verifies the credentials credentials accepted
Client is allowed into the administrative section of the website
Client logs out of the system
Client requests for statistics
Client asks for configuration
Client changes configuration
Server-side top level flow diagram
Server software receive a challenge request from the client
Server component processes the request
HASTAC Component sends a request for a new challenge
A Challenge does not exist on server
Request new challenge & response pair to be generated by the C&R generator
HASTAC
Component checks if a challenge exists on the server
A Challenge exists on server
Return the challenge
Background worker
C & R Generator
Server structure
HASTAC
Component
API
Verifer
Cache Manager
Policy
DB HDD
Sub-Module internal flow diagram
Server component receives a log-in request
Server component forwards the request to the HASTAC component
Policy request not validated
Check against the policy if the request is valid
Policy request validated
Reject the request Forward the request to the Cache manager
Start Background generator
(According to policy)
A Challenge does not exist on HDD & DB
Request new challenge & response pair to be generated by the C&R generator
Check if a C & R pair exist on the
HDD & DB
A Challenge exist on
HDD & DB
Return challenge
Request not founed
Reject the request
Server receives a response for the challenge
Server component forwards the request to the HASTAC component
Check against the DB if the request is valid
Request found on DB
Forward the request to the verifier
The request does not match the challenge
Check if the response matches the challenge
The request matches the challenge
User verified
DB
HDD
Level-0 Functional diagram
Server
Server
Software
( ASP.NET 2.0 )
HASTAC
Component
Client
Administrator
The HASTAC component consists of 7 modules:
1.
The API, which is the interface to the website.
2.
The Policy module that enforces the system policy and can be configured by the
Administrator.
3.
The Back-Office module, which is external to the system, but interfaces directly with it via a secured channel (typically SSL or TLS)
4.
Challenge and Response (C & R) Generator, which generates new challenge & response pairs at the server, and stores it on the SQL / HDD.
5.
Cache Manager that manages the pre-generated store, allowing the system to be responsive and fast during peak hours.
6.
Background worker, which is scheduled to run on timely basis and fill the cache during off-peak hours
7.
Verifier, which verifies the user response to the generated challenges, outputting true/false or the 'human' test.
8.
DB module, which interfaces with the SQL server
9.
HDD module, which saves and loads the requested images from the HDD
Interaction between component modules
1.
API-Policy communications:
API
Get configuration
Set configuration
Authenticate admin
2.
Policy-DB:
Policy
Get configuration
Set configuration
3.
API-Verifier
API
Verify response
Policy
Returns the requested configuration
Sets the requested configuration
Logs-in as administrator
DB
Loads the configuration from the DB
Sets the configuration at the DB
Verifier
Loads the challenge from the DB, compares the response to the correct response. Returns true or false
4.
Verifier-HDD
Verifier
Load response
HDD
Loads the response from the HDD and returns it
5.
Verifier-DB
Verifier
Load response
DB
Loads the response from the DB and returns it
6.
API-Cache manager
API
Request challenge
Get cache size
7.
Cache manager-DB
Cache manager
Get next challenge
Cache manager
Returns a pre-generated challenge
Returns the size of the cache
Get challenge count
DB
Returns the first unused challenge in the
DB
Returns the number of unused challenges in the DB
Cache manager
Generate
8.
Cache manager-C&R generator
C&R generator
Returns a newly generated challenge
9.
API-Background worker
API
Start generating
Background worker
Generate
10.
Background worker-C&R generator
Background worker
Generates N challenges and quits
C&R generator
Returns a newly generated challenge
11.
C&R generator-HDD
C&R generator
Store challenge & response
12.
C&R generator-DB
C&R generator
Store challenge & response
HDD
Stores challenge & response
DB
Stores challenge & response
The Architecture
The suggested architecture is designed to allow maximal modularization within the HASTAC component.
It was designed using the producer-consumer and strategy design patterns. It also provides a layer of abstraction between the component and its storage
Description of individual modules
The API
This class functions as the interface to the HASTAC component.
API
GetChallenge()
VerifyChallenge()
The Policy
Returns
A new challenge
Success/Fail
Description
Returns a new challenge
Verifies the challenge
API
GetConfiguration()
SetConfiguration()
Returns Description
The requested configuration Returns the requested configuration
Success/Fail
Success/Fail
Sets the requested configuration
Log-in as administrator AuthenticateAdmin()
Challenge and Response (C & R) Generator
Generate()
API Returns Description
A newly generated challenge Returns a newly generated challenge
Cache Manager
API
RequestChallenge()
GetChallengeCount()
Returns
A pre-generated challenge
The number of unused challenges in the DB
Description
Returns a pre-generated challenge
Returns the number of unused challenges in the DB
Background worker
API
StartGenerating()
StopGenerating()
Verifier
API
VerifyResponse()
Returns
Returns
Success/Fail
Description
Generates 'N' new challenges
Stop the current generation session
Description
Loads the challenge from the
DB, compares the response to the correct response.
Returns true or false
The DB
API
GetConfiguration()
SetConfiguration()
LoadResponse()
GetNextChallenge()
GetChallengeCount()
GetObjects()
InsertObject()
UpdateObject()
Returns
Sets the configuration at the
DB
Description
The requested configuration Loads the configuration from the DB
Success/Fail
The response from the DB
A pre-generated challenge
Loads the response from the
DB and returns it
Returns a pre-generated challenge
The number of unused challenges in the DB
A list of objects
Success/Fail
Success/Fail
Returns the number of unused challenges in the DB
Returns a list of objects that matches the query
Inserts a new object
Updates the object
The HDD
API
LoadResponse()
StoreChallenge()
RemoveChallenge()
Returns Description
The response from the HDD Loads the response from the
HDD and returns it
Success/Fail Stores the challenge on the
HDD
Success/Fail Removes the challenge from the HDD
The Algorithms used
The heart of the HASTAC component is the actual Challenge Generation system.
The modular system exposes two base classes that each Challenge type derives itself from. More challenges may be installed easily using external DLLs.
Challenge (Abstract)
The base class of all types of challenges in the system. Two deriving classes are defined:
ChallengeWithCallback
ChallangeWithoutCallback
They will be discussed below
Generate()
Save()
API Returns
Success/Fail
Success/Fail
Description
Generate a new challenge
Saves the challenge to the
HDD and/or DB (using the
HDD/DB module respectively)
ChallangeWithoutCallback (Abstract, derives from Challenge)
A challenge without a callback is a challenge that can be verified using simple string comparison. It is used for challenges where only one option is valid.
API (In addition to the challenge interface)
GetAnswer() A string
Returns Description
Returns the answer to the challenge
ChallengeWithCallback(Abstract, derives from Challenge)
A challenge with a callback is a challenge that has a custom verification process (the verify() method). ChallengeWithCallback has a derived implementation named ClickOnTheObjects.
API (In addition to the challenge interface)
Verify()
Returns Description
Success/Fail Verifies the user response against the challenge
ClickOnTheObjects (Derives from ChallengeWithCallback)
This is an implementation of a Challenge with a Callback. It generates a background with many objects (blurred), and on top of it, it draws several distinct objects (distinct in Color,
Size, Bevel, Shape etc.). The user is asked to click on a few of them, possibly in a specific order. When the user clicks on the image, the points are saved at the browsers, and when the submit button is clicked, the server receives the clicked coordinates. It then checks these coordinates against a black & white image that is also generated and stored on the HDD, to see if all coordinates where inside the white shapes.
WhatTextIsInTheShape (Derives from ChallengeWithoutCallback)
This is an implementation of a Challenge without a Callback. It generates a background with many objects (blurred), and on top of it, it draws several distinct objects (distinct in Color,
Size, Bevel, Shape etc.). On these objects, a randomized text is displayed. The user is asked to type what is written in one (or more) of the objects. When he submits his answer, the server compares the correct value answer with the user response, and acts accordingly.
WhatDoesObjectSay (Derives from ChallengeWithoutCallback)
This is an implementation of a Challenge without a Callback. It generates a background with many objects (blurred), and on top of it, it draws several distinct characters (distinct in Color,
Size, Weight, Height, etc.). Each of these characters has a balloon with a randomized text.
The user is asked to type what is written in one (or more) of the balloons near a specific character. When he submits his answer, the server compares the correct value answer with the user response, and acts accordingly.
The challenge hierarchy is described in the figure below.
Challenge
(Abstract)
Challenge without callback
(Abstract)
Challenge with callback
(Abstract)
What do objects say
What text is in the shapes
Figure 1 – The Challenge Hierarchy
Click on the objects challenge
DataBase Schemas
Images
Field Name
ImageID
ImageFileName
MetaData
Configuration
Field Name
ConfigurationKey
ConfigurationValue
Challenges
Field Name
ChallengeID
ChallengeFileName
Answer
ChallengeType
Field Description
Unique image ID (Key, Index)
Local image file name
Image Meta data
Field Description
Configuration Key name
Configuration Value
Field Description
Unique challenge ID (Key, Index)
Local challenge file name
Challenge answer/file name
1-challenge with callback
2-challenge without callback
Date challenge was used
Usage Counter
DateUsed
Count
Field Type
Integer
String(255)
String(255)
Field Type
String(255)
String(255)
Field Type
GUID
String(255)
String(255)
Integer
DateTime/Null
Integer
HASTAC Website Protection System - System
Configurations
HASTAC is controlled from a back-office system that will include 5 tabs:
Main a) Main b) Configuration c) Tools d) Statistics e) About
The 'Main' section shows general information about the system: a) System status b) System time c) Number of login transactions d) Number of pre-generated challenge and response pairs
In addition, it allows changing the system status, reset login transaction counters and a shortcut to generate more challenge and response pairs.
Configuration
The 'Configuration' section allows the administrator to define different aspects of the challenge and response generation process.
Number of login attempts
Number of allowed login attempts before a redirection to an "Access
Forbidden" page occurs.
Same difficulty for all attempts
When checked, this option allows to apply the same difficulty level to all login attempts. Otherwise, every login attempt will be configurable.
Number of shapes Average number of shapes shown in each generated picture.
Number of colors Average number of colors shown in each generated picture.
Background patterns
A variety of background patterns available for each generated picture.
Optical distortion Distort the generated image to harden the readability of words in order to prevent OCR mechanisms from cracking the words inside the generated image.
Word length
Salting
Varied length of words generated on the images.
Additional image processing that adds salt (noise to the picture in order to make OCR technology difficult to use).
Image file formats Select from a variation of image file formats.
Copyright notice A fixed string that will be shown on each generated picture on a random edge
Tools
The 'Tools' section allows the administrator to pre-generate challenge & response pairs in off-peak hours, to ease the CPU in peak hours. It also allows changing the 'pre-generated images' cache size.
Clicking on the "Pre-generate Challenge & Responses Now" button starts a background process at the server, which generates Challenge & Response pairs.
The timetable allows scheduling the generation process automatically for each day of the week and each hour of day. On websites with high traffic this will alleviate the CPU usage during the 'rush hours'.
A red box signifies that the generation process will take place
A clear box signifies that the generation process will take place only when the
Challenge and Response pair cache is empty. Websites with a limited storage, light traffic and/or low CPU usage may want to leave the boxes unchecked.
The "Generate up to # Challenge & Response pairs" field specifies the maximum number of
Challenge and Response pair to pre-generate.
Taking into account that an average file is 4Kb big, 1 Mb of storage space is equivalent to
256 Challenge and Response pairs.
Statistics
The 'Statistics' section displays meaningful information about the successful login attempts, login traffic, daily login statistics.
The "Successful login attempts" displays statistics about the percentage of successful login attempts to the site for each attempt. The shown statistics, for example, shows that 60% of the users manage to login on their first attempt. 25% of the users manage to login on their second attempt, 10% on their third attempt, and the rest 5% fail to login successfully.
The "Image Traffic So Far" field displays the amount of traffic utilized by the HASTAC
Protection system.
The Day login statistics shows the number of login attempt for every day in the current month.
The Most active accounts shows the top 10 most active accounts.
Development and production environment
Software requirements:
The development system requires Microsoft Visual Studio 2005, Microsoft SQL server 2005,
Microsoft Office 2007, and Microsoft Windows XP Operating System. (Estimated cost:
3000$)
A production environment would require Microsoft SQL server 2005, Microsoft Internet
Information Server (IIS) and ASP.NET runtime. (Estimated cost: 1500$)
Hardware requirements : (for both development and deployment environments)
a PC with a modern CPU (Pentium 4 and later)
1 GB of RAM
2 GB of free HDD space.
Expected Performance and Benchmarking
After carefully examining existing websites and the nature of the HASTAC component, we have devised a method to measure the performance of the module.
The properties of the component are:
A C&R Generation process that takes place on system start-up and whenever the cache level reaches a certain low level.
CPU, HDD & SQL resources are used while generating the challenges.
During peak-hours and whenever the system is not generating challenges, the resource usage is minimal
Our system is capable of collecting performance data during runtime (with the use of the
.NET framework). This data will be gathered and processed in Microsoft Excel, to produce a graph that will look like this:
120
Requests
100
Cache size 80
CPU Usage 60
SQL Usage
(Queries/s)
40
HDD Usage
(MB/s)
20
0
1 5 9 13 17 21 25 29 33 37 41 45 49 53
For a detailed view of how we measure performance and deal with DoS attacks, see the
Performance Testing Appendix.
SLA
Availability: 100% of the time, after the initial cache filling at startup.
Processing Speed: 100 Challenge generations / second.
< 10 CPU minutes per month, based on 50,000 login attempts.
Network throughput: 5-7 Kilobytes per generated image
Storage requirements: 10-14 Kilobytes per challenge
Response time:
(Multiply by cache size, which is configurable.)
Immediate (depends on system configuration and website profile)
Project plans for development and testing
Task
Build DB module
Build C&R Generator module
Build Specific Challenge types with sample data (Milestone #1)
Build Verifier
Build HDD Module
Build Cache Manager
Build Background Worker module
Build Policy module
Build Back-office
Build API module
Module integration (Milestone #2)
Performance testing
Write user manual
Fill database with more data
Build setup and deployment tool
Final Packaging (Project end)
Assigned to
Alon
Alon
Prerequisites
None
DB Module
Ronen C&R Generator module
Alon
Alon
None
None
Ronen DB, HDD Modules
Alon C&R Generator module
Ronen DB module
Ronen Policy Module
Alon
Alon,
Ronen
None
All modules, Milestone #1
Alon Milestone #2
Ronen None
Ronen Milestone #1
Alon
Alon,
Ronen
Milestone #2
Milestones #1 and #2