1.4.e.4 TESOL Endorsement
advertisement
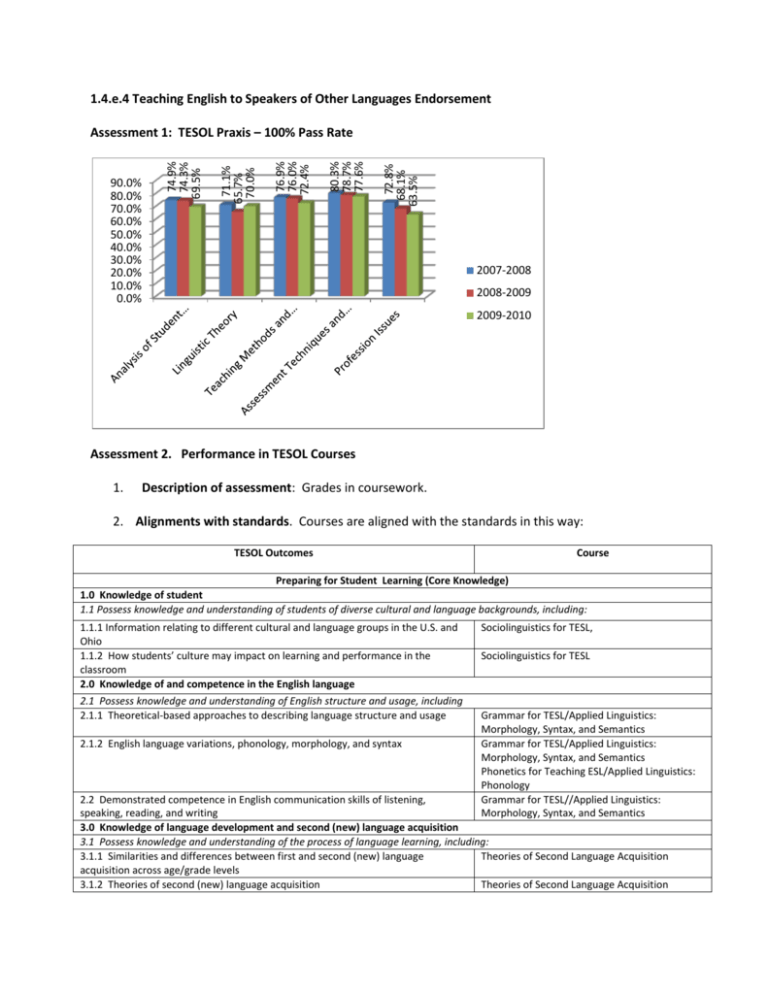
1.4.e.4 Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages Endorsement 72.8% 68.1% 63.5% 80.3% 78.7% 77.6% 76.9% 76.0% 72.4% 71.1% 65.7% 70.0% 90.0% 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% 74.9% 74.3% 69.5% Assessment 1: TESOL Praxis – 100% Pass Rate 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 Assessment 2. Performance in TESOL Courses 1. Description of assessment: Grades in coursework. 2. Alignments with standards. Courses are aligned with the standards in this way: TESOL Outcomes Course Preparing for Student Learning (Core Knowledge) 1.0 Knowledge of student 1.1 Possess knowledge and understanding of students of diverse cultural and language backgrounds, including: 1.1.1 Information relating to different cultural and language groups in the U.S. and Ohio 1.1.2 How students’ culture may impact on learning and performance in the classroom 2.0 Knowledge of and competence in the English language 2.1 Possess knowledge and understanding of English structure and usage, including 2.1.1 Theoretical-based approaches to describing language structure and usage 2.1.2 English language variations, phonology, morphology, and syntax Sociolinguistics for TESL, Sociolinguistics for TESL Grammar for TESL/Applied Linguistics: Morphology, Syntax, and Semantics Grammar for TESL/Applied Linguistics: Morphology, Syntax, and Semantics Phonetics for Teaching ESL/Applied Linguistics: Phonology Grammar for TESL//Applied Linguistics: Morphology, Syntax, and Semantics 2.2 Demonstrated competence in English communication skills of listening, speaking, reading, and writing 3.0 Knowledge of language development and second (new) language acquisition 3.1 Possess knowledge and understanding of the process of language learning, including: 3.1.1 Similarities and differences between first and second (new) language Theories of Second Language Acquisition acquisition across age/grade levels 3.1.2 Theories of second (new) language acquisition Theories of Second Language Acquisition 3.1.3 Effects of cognitive, affective, and socio-cultural variables on second (new) Theories of Second Language Acquisition language acquisition 4.0 Foundations of second (new) language instruction 4.1 Possess knowledge and understanding of the context of second (new) language instruction in the United States, including 4.1.1 Terminology and definitions related to second (new) language instruction Theories of Second Language Acquisition Sociolinguistics for TESL 4.1.2 Historical and legal precedents of programs for language minority students in Theories of Second Language Acquisition the U.S. Sociolinguistics for TESL 4.1.3 Demographics, immigration and migration issues Theories of Second Language Acquisition Sociolinguistics for TESL 4.1.4 Educational issues related to language minority students Theories of Second Language Acquisition Sociolinguistics for TESL Advancing Student Learning (Pedagogy) 5.0 Knowledge and skills instructional assessment 5.1 Possess knowledge of and skills in the assessment of second (new) language learners, including the ability to 5.1.2 Design and use varied age-appropriate assessment procedures and PreK-12 Practicum in TESL instruments to obtain information about students English language proficiency and academic achievement 5.1.3 Interpret assessment data to make instructional decisions PreK-12 Practicum in TESL Evaluation and Assessment for ESL 5.1.4 Provide assessment results to students, parents, and other Evaluation and Assessment for ESL 5.1.5 Assist students to use assessment results to make decisions about their TESL Methods II/ Evaluation and Assessment for learning ESL 6.0 Knowledge and skills in methodology and materials for teaching second (new) language learners 6.1 Possess knowledge of and skills in the instruction of linguistically diverse learners, including the ability to 6.1.1 Establish goals and objectives, and design curricula for second (new) language Phonetics for Teaching ESL/Applied Linguistics: learners that reflect Ohio’s grade-level learning outcomes in content areas Phonology 6.1.2 Apply current research to develop a repertoire of strategies to promote ageTESL Methods II /Evaluation and Assessment for grade-appropriate social and academic English learning ESL 6.1.3 Select, adapt, create, and use varied resources appropriate to age, diverse cultural groups, and different learning styles 6.1.4 Integrate technology in planning and delivering instruction 6.1.5 Create and maintain communication with students’ families to enhance the students’ educational experiences Field-based experience 7.0 Classroom observation and practice teaching 7.1 During their field experience, participants will 7.1.1 Observe and participate in second (new) language instruction in a classroom setting with experienced certified-licensure teachers having TESOL validation/endorsement 7.1.2 Practice teaching second (new) language learners in a formal classroom setting, mentored by experienced certified/licensure teachers having TESOL validation/endorsement 7.1.3 Analyze, evaluate, reflect on, and describe the quality of the field experience Methods in Teaching ESL/Teaching Methods and Techniques for ESL Methods in Teaching ESL I//Teaching Methods and Techniques for ESL Methods in Teaching ESL I //Teaching Methods and Techniques for ESL Practicum in TESL Practicum in TESL Practicum in TESL Practicum in TESL 3. Interpretation of the data: UC TESOL coursework is well aligned with institutional, state, and national Standards, as shown in the table above. The coursework covers a wide range of domains, such as core knowledge, English linguistics in general, teaching methods and strategies, pedagogy, and field-based experience, along with professional integrity. 4. Data are presented on the following page Please note that the course titles of LTCY 782P, LTCY 783P, LTCY 784P, and LTCY 787P have been changed in the academic year of 2009-2011. 2008-2009 A 18 LTCY 782P ESL Methods I 18 LTCY 782P Tchg Mthds/Tech ESL 18 LTCY 783P ESL Phonetics 18 LTCY 783P Appl Linguist: Phnol 18 LTCY 784P ESL Methods II 18 LTCY 784P Eval/Assess for ESL 18 LTCY 785P Sociolinguist TESL 18 LTCY 786P Practicum TESL P-12 18 LTCY 787P Grammar for TESL 30 A- B+ 2009-2010 B A A- 20 23 B B- C+ A A- B+ B B- 8 2 1 1 F 0 48 19 B+ 2010-2011 4 1 41 48 4 55 1 67 3 1 3 3 1 18 29 37 12 3 1 40 6 3 4 48 2 1 2 1 55 54 1 Assessment 3: Lesson Plans Indicator National and State ESL Standards applicable to your lesson plan Accommodations for your ESL students 3-5 objectives and their connection to the broader course objective(s); e.g. “At the end of this lesson, students will be able to …” Content to be covered Activities (lecture, group work, problem-solving, case studies, think-pair-share, collaborative projects, etc.) Resources and materials needed (including technology) Timing Out of class work and assessment Total: N 93-100 = A 87-89 = B+ 77-79 = C+ 67-69 = D+ >59 = F(Fail) 90-92 = A83-86 = B 80-82 = B73-76 = C 70-72 = C63-66 = D 60-62 = D- Assessment 5: Final Project Final Project: Profiles in English Language Learning Assignment as it appears in the syllabus: 10% 25% 5% 5% 2008 -9 A= 25 A- = 5 B+=1 I=1 2010 - 11 A=3 B-=1 2011 -12 A= 28 A=12 B+ =2 I =1 32 4 43 25% 10% 5% 15% 100 % In an effort to apply our new knowledge of theories related to language learning and teaching, you will be responsible for providing profiles of a population of learners you are likely to teach along with a detailed description of the theories and related practices that will apply to this context. The medium for presentation of this project can be chosen by the students, with permission from the facilitators, but creative use of technology is encouraged. Options for presentation include, but are not limited to, Powerpoints with video, audio, and pictures, iMovies, Photostories, Podcasts, Wikis, and Apps. A majority of the presentations will be devoted to a detailed description of the target teaching population with specific references to the factors described in each chapter of the text (you may use elements of your discussion papers as a basis for your description). Other components of the presentation should address specific ideas for teaching specific skills to this group of students. Include reference to the course text and 3-7 other references to justify your understanding of this demographic and your approach to teaching in the context you describe. In order to receive feedback in your planning of these presentations, you will need to provide weekly reports in the Discussion Board on the progress beginning in Week 2 of the course. Specific prompts and criteria for these weekly reports will be provided in the Discussion Board, where you will post your plans for others to see and use as they plan toward a final product. Rubric Learner Profile A B Student population is described in detail, with references to age, cultural and linguistic backgrounds, socioeconomic status, learning styles, reasons for learning English, and available resources. Challenges to teaching English to this student population are explained, with reference to the text and outside sources, in order to adequately identify theories and a methodological approach for overcoming them. Population is described in detail with references to key terms and concepts covered in each major part of the text, as well as from 3-7 additional sources. 23-25 points Student population is described, but more detail is required in reference to one of the following characteristics: age, cultural and linguistic backgrounds, socioeconomic status, learning styles, reasons for learning English, and available resources. Challenges to teaching English to this student population are identified, but only briefly Appropriate Theories The author synthesizes a variety of theories presented throughout the text, including a discussion of educational issues related to language minority students, in order to justify a methodological approach to teaching the target student population. Theories are described in detail, including definitions, a brief historical review, and a clear explanation of the reason for their application in the context described for this project. The author outlines a theoretical basis that is appropriate to this target teaching population. 22-25 points The author chooses a theory presented in the text, including a discussion of educational issues related to language minority students, in order to justify a methodological approach to teaching the target student population. Theories are described in some detail, but the author needs to clarify points using Methodological Approach (Practice) Reference is given to a variety of specific strategies (3-7)outlined in the text, as well as from additional resources. Strategies and methodological approaches are appropriate to the student population outlined in the Learner Profiles section of the presentation. Methodological approach reflects the author’s consideration of cognitive, affective, and socio-cultural variables influencing these learners. 22-25 points Reference is given to some strategies (1-2) outlined in the text, as well as from additional resources. More explanation is required to determine if the author understands how the outlined strategies and methodological approaches are Presentation Scoring Criteria Creative use of technology, with visual and auditory aids, as well as links to recommended resources and activities enhance conveyance of the author’s message Ideas are presented with clarity and detail. Topics are organized in a manner that depicts their relevance to each other and to major themes. There are few, if any, errors in conventions. 23-25 points There is a creative use of technology, but in order to enhance the conveyance of the author’s message, some improvement could be made with visual and auditory aids, as well as links to recommended resources and activities. Ideas are presented with adequate detail, but organization could be revised for clarification purposes, or there may be an issue that needs C D explained. More reference to the text and outside sources is required, in order to adequately identify theories and a methodological approach for overcoming these challenges. Population is described with only some reference to key terms and concepts covered in each major part of the text, and little or no reference to 3-7 additional sources.20-22 points definitions, a more thorough historical review, and/or a clearer explanation of the reason for their application in the context described for this project. The author outlines a theoretical basis that is probably appropriate to this target teaching population, but the reader may question this applicability due to theoretical contradictions or inadequate explanation from the author. 20-21 points Student population is described with minimal detail. More description is required in reference to at least two of the following characteristics: age, cultural and linguistic backgrounds, socioeconomic status, learning styles, reasons for learning English, and available resources. Challenges to teaching English to this student population are only briefly identified, but not thoroughly explained. There is little or no reference to the text and outside sources, in order to adequately identify theories and a methodological approach for overcoming these challenges. Population is described with few references to key terms and concepts covered in each major part of the text, and no reference to 3-7 additional sources. 18-19 points The author chooses a theory presented in the text, but clarification is needed in regards to the educational issues related to language minority students, and/or a justification for this methodological approach to teaching the target student population. Theories are described with little detail. The author needs to clarify points using definitions, a more thorough historical review, and/or a clearer explanation of the reason for their application in the context described for this project. The author outlines a theoretical basis that might not be appropriate to this target teaching population; the reader questions this applicability due to theoretical contradictions or inadequate explanation from the author. 17-19 points The author seems to outline a theoretical basis for approaches to teaching this population, but it is unclear if this approach is espoused in the text or in additional sources cited in a reference section. There is little or no evidence that the author understands the educational issues related to language minority students, and/or a Student population is not adequately described. More detail is required in reference to three or more of the following characteristics: age, cultural and linguistic backgrounds, socioeconomic status, learning styles, reasons for learning English, and available resources. Challenges to teaching English to this student population may appropriate to the student population. Methodological approach reflects the author’s consideration of two of the following factors influencing these learners: cognitive , affective, and sociocultural variables. 20-21 points Reference is given to some strategies outlined in the text or in additional resources, but not from both. It is questionable whether the outlined strategies and methodological approaches are appropriate to the student population. Methodological approach reflects the author’s consideration of only one of the following factors influencing these learners: cognitive , affective, and sociocultural variables. more explanation. There are some errors in conventions, but they do not seem to interfere with the message. 20-22 points Use of technology is not necessarily creative or, in order to enhance the conveyance of the author’s message, improvements need to be made with visual and auditory aids, or links to recommended resources and activities. Although the author may have adequate detail and relevant content material, the presentation needs to be revised so that the audience can better understand how topics relate to each other and to the overall theme. There are errors in conventions that need revised, because they could interfere with the message. 18-19 points 17-19 points Reference is given to strategies, but these are not strategies outlined in the text nor in any additional resources given in a reference list. There is evidence that the outlined strategies and methodological approaches are inappropriate to this student population. Use of technology is not creative. As a result, the audience is not engaged with author and his/her message. Increased use of visual and auditory aids, or links to recommended resources and activities are required. There are errors in conventions that interfere with the message. be identified, but explanations are confusing. There is little or no reference to the text and outside sources, in order to adequately identify theories and a methodological approach for overcoming these challenges. Population is described with few, if any, references to key terms and concepts covered in each major part of the text, and no reference to 3-7 additional sources. 15-17 points F Student population is not addressed. Challenges to teaching English to this student population are not identified. Population is not described with references to key terms and concepts covered in each major part of the text, and no reference to 3-7 additional sources. 0-14 points justification for this methodological approach to teaching the target student population. Theories are not described in detail. The author needs to clarify points using many more definitions, a more thorough historical review, and a clearer explanation of the reason for their application in the context described for this project. The author outlines a theoretical basis that is not appropriate to this target teaching population; there is clear evidence of theoretical contradictions. 15-16 The author does not outline a theoretical basis for approaches to teaching this population. There is no evidence that the author understands the educational issues related to language minority students. 0-14 points Methodological approach reflects the author’s consideration of only one of the following factors influencing these learners: cognitive , affective, and sociocultural variables. 15-17 points 15-16 points No strategies are identified and no description of a methodological approach is provided. 0-14 points Presentation is not provided. If the project is completed, it is only with brief descriptions of content material that are disjointed. 0-14 points Data from assessment Learner Profile 2011: 25/25 – 11 candidates 24/25 – 1 candidate 23/25 – 1 candidate 22/25 - 1 candidate Appropriate Theories 2011: 25/25 – 11 candidates 24/25 – 1 candidate 22/25 – 1 candidate 20/25 - 1 candidate Methodological Approach (Practice) 2011: 25/25 – 13 candidates 19/25 – 1 candidate Presentation Scoring Criteria 2011: 25/25 - 4 candidates 23/25 – 2 candidates 22/5 – 4 candidates 20/25 – 3 candidates 19/25 – 1 candidate Assessment 6: Observational Project 1.Alignment of the Observational Project Assignment to the TESOL and Ohio TESOL Standards TESOL Standards Standard 1.a. Language as a system. Candidates demonstrate understanding of language as a system, including phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics, and [sic] support ESOL students as they acquire English in order to communicate with native speakers of English. 1.a.1. Demonstrates knowledge of the components of language and language as an integrative system. 1.a.2. Apply knowledge of phonology (the sound system), morphology (the structure of words), syntax (phrase and sentence structure), semantics (word/sentence meaning), and pragmatics (the effect of context on language) to help ESOL students develop oral, reading, and writing (including spelling) skills in English. 1.a.4. Demonstrate proficiency in English and serve as a good language model for ESOL students. Standard 1.b. Language acquisition and development. Candidates understand and apply theories and research, and language acquisition and development to support their ESOL students’ learning. 1.b.2. Candidates understand theories and research that explain how L1 language development differs from L2 language development. 1.b.5. Understand and apply knowledge of the role of individual learner variables in the process of learning English. Ohio TESOL Standards Addressed Standard 2: Candidates demonstrate knowledge and understanding of English structure and usage. 2.1. Candidates know and use theoretical-based approaches to describing language structure and usage. 2.2. Candidates know and use English language variations, phonology, morphology, and syntax. 2.3. Candidates demonstrate competence in English communication skills of listening, speaking, reading, and writing 2.Assignment Description: This activity is designed to help you gain more sensitivity to listening and noticing sociocognitive linguistic variables affecting usage. Although I do not expect you to go through the IRB process for this small observational project, I would like to alert you to an important piece about the ethics of data collection. Please use your judgment and discretion of the ethical guidelines that dictate academia when you make observations. In addition, please be aware of the complications of trying to make assumptions based on looks and appearances because the nature of phenomena is always deeper than appearances. Choose an item of expressive American English features that exhibit variability in a speech, advertisement, newspaper article, short story, or other language sample. Again, both spoken and written materials are acceptable. Some examples are: “if I were” vs. “if I was” “real” and “really” or “good” and “well” used as adverbs the use of objective (e.g., me) vs. nominative (e.g., I) case in object or subject position (particularly conjoined NPs such as “between you and I” or “Me and my brother went”) pronouns used to replace singular nouns of unspecified gender (e.g., “Someone has left their books here.”) the use of “whom” tag questions The above is only a few examples. You have many options to choose from. Data Collection Each time you hear or see a variant of your item, write it down with the utterance you heard it in (e.g., don’t just write down “who”, but write down “I don’t know who you’re talking about”). Keep your ears open (or your eyes—printed materials are sources, too). Every time you record a token, also record demographic information about the speaker and addressee(s) (gender, age, race/ethnicity, place of origin, relationship between the two interlocutors) and information about the setting. This is very important. What you are trying to do is to uncover the patterns of usage of your variable. These patterns typically reveal themselves in the categories. For example, Southerners may be more likely to say “y’all” for plural “you” than Northerners, and Northerners might be more likely to say “you guys.” If you collected lots of tokens of ways to say plural “you,” then you could look at the characteristics of speakers or settings to see who was using which variant in which setting. You may use data collection sheets so that you can quickly gather the sociocognitive linguistic variables upon hearing the utterance. You can construct your own data collection sheet. Here is a very basic template you may want to use. Date Speaker Data Collection Sheet Utterance Setting Grammar Point Note Once you have collected at least 20 (the more, the better!) tokens/examples, look for variations. First, identify all the variants you have found. Next, look for patterns. This means that you will look at, for example, how often different social groups (for example, groups by age or gender) used each of the variants and then compare groups to each other (for example, men to women). You might find, for example, that only women use “whom” and that men rarely do. You should also look at other variables such as settings or regions of origin. You might find, for example, that “whom” only occurs in print and never (or rarely) in spoken language. Your data probably may not fall into discrete categories, but you will notice tendencies for there to be factors that condition the occurrence of specific variations. After doing the analysis, you are expected to write a written report, and to post it on Bb. The report should describe the following: the aspect of American English that you have collected your data on how you collected your data the variants you have discovered an analysis of your data with a table for each of the analytic categories that you found to demonstrate patterns (e.g., Table 1: the variant as it is distributed by gender, Table 2: the variant as it is distributed by age, Table 3: the variant as it is distributed by setting, etc.) A written report is to be 10-12 pages long, including a cover page, tables/graphs, and references. The APA format is to be used. Again post your paper to the designated forum on Bb by 11:59 p.m., 6/3/11. This is not a big project, although it may sound like it. If you open your ears and eyes in your daily activities with increased awareness, you will get this project done very easily. A raised awareness matters! Rubric Elements Grading Rubric Incomplete (0-1 pts) Organization/Objectives (max. 5 pts) Standards Addressed: TESOL 1.a.1. Ohio 2.3 Weak logical flows; Needs further development in the structure of the argument. Objectives are missing, unclear, or inappropriate Evidence/ Literature Review (max. 5 pts) Standards Addressed: TESOL 1.a.1. TESOL 1.a.2. Ohio 2.1 Ohio 2.2 Ohio 2.3 Content (max. 5 pts) Standards Addressed: TESOL 1.a.2. Ohio 2.1 Ohio 2.2 Ohio 2.3 Acceptable (2-3 pts) Sequence is clear and major components are presented, but the argument is not supported in a logical fashion. Objective(s) are clearly stated; provides purpose, but main goals/objectives in relation to previous research are not provided Exemplary (4-5pts) Well organized with the major components of a prose (intro, body, and conclusion); aligned with the scope and sequence of the argument; logical structure and step-bystep sequence Objectives are measurable with precise research questions; connections are made between previous research and the present argument/research questions Shows a weak relevance from previous research to a topic under consideration. Most prior knowledge and concepts are clearly articulated but some important skills are missing Explanation/argumentation is supported by evidence and examples that are clearly attributed to sources for which proper citations are provided. Shows flaws or deficits in understanding of the topic and inabilities to integrate prior knowledge and a research topic into a paper. Methods are appropriate and marginally matched to the objectives/goals of the paper. Well developed; clear and logically coherent explanation and argumentation that fully respond to the question(s) posed. Unity, Conventions, and Mechanics (max. 5 pts) Lack of unity; a sloppy argument without supporting materials. Some coherence is found but insufficient to achieve a whole unity. Standards Addressed: Ohio 2.3. Needs improvements in terms of writing mechanics. Partially meets the writing conventions and shows frequent grammatical errors; too many quotations Lack of critical reflection Insufficient critical reflection Reflection (max. 5 pts) Standards Addressed: TESOL 1.a.4. TESOL 1.b.2. TESOL 1.b.5. Ohio 2.1 Ohio 2.2 Ohio 2.3 Candidates show low levels of understanding theories and research that explain L2 language development Candidates can explain theories and research that address L2 language development DATA – Scores are overall; future data will be by element. Mean 2009 (N=32) 23.5 2010 (N=52) 13.2 2011 (N-46) 23.04 Demonstrates a clear continuity from the beginning to the end; lays out the argument in a logical and convincing form. A clear, grammatical English prose; credits to sources are given, using the APA style; quotations are kept to an absolute minimum Clearly articulate original and critical insights into the given topic; states implications of the argument made. Candidate use theories and research that explain L2 language development Median 24 10 23







