PBMAS Improvement Plan 2014-2015 Career and Technology
advertisement
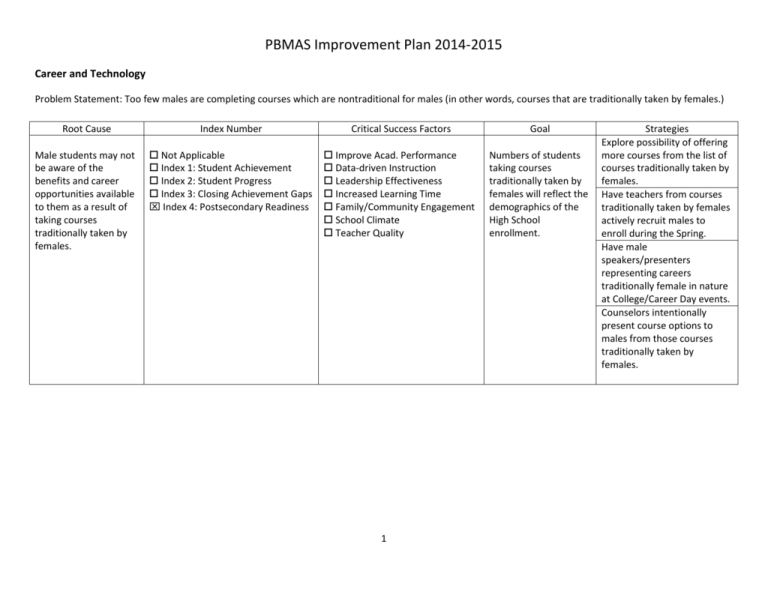
PBMAS Improvement Plan 2014-2015 Career and Technology Problem Statement: Too few males are completing courses which are nontraditional for males (in other words, courses that are traditionally taken by females.) Root Cause Index Number Critical Success Factors Goal Male students may not be aware of the benefits and career opportunities available to them as a result of taking courses traditionally taken by females. Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality Numbers of students taking courses traditionally taken by females will reflect the demographics of the High School enrollment. 1 Strategies Explore possibility of offering more courses from the list of courses traditionally taken by females. Have teachers from courses traditionally taken by females actively recruit males to enroll during the Spring. Have male speakers/presenters representing careers traditionally female in nature at College/Career Day events. Counselors intentionally present course options to males from those courses traditionally taken by females. Special Education Problem Statement: Too many students receiving SPED services failed to perform satisfactorily on the Science STAAR in grades 5 and 8 and on the Writing STAAR in grades 4 and 7. Root Cause Students receiving SPED services are not adequately learning and applying required concepts in science or writing. Index Number Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Critical Success Factors Goal Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality Students receiving SPED services will learn and apply required concepts so as to perform satisfactorily on the Science STAAR in grades 5 and 8 and on the Writing STAAR in grades 4 and 7. 2 Strategies Students will. be taught to utilize strategies for learning independently. Teachers will scaffold the sped supports afforded to students and will begin to pull those supports back as students achieve learning independence. Teachers will make maximum use of available Assistive Technology and other Supplemental Aids to support student learning. SES will continue campuswide implementation of both the Writing Academy strategies and the STEMScope curriculum. Teachers will utilize language development strategies including increased use of oral language and vocabulary development. SJH will explore implementation of “Writing Wednesdays” with more focused and intentional attention toward writing at all grade levels. Root Cause Index Number Critical Success Factors 3 Goal Strategies SJH will explore adding use of STEM-Scope science curriculum in grades 6-8. Problem Statement: Too many students receiving SPED services participated in assessment with the STAAR-Modified version of the test. Root Cause Students requiring instructional support are not properly identified early enough within their school careers and effective intervention is not provided so as to remediate learning deficits before statemandated testing occurs. Index Number Critical Success Factors Goal Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality Parents, teachers and administrators will have high expectations for academic achievement for students receiving SPED services. 4 Strategies Diagnostic testing will be performed by campus interventionists and teachers to clearly identify areas of specific interventions that will address learning deficits. SES will consider implementing campus-wide or grade-level ability testing. SES will continue implementation of classbased intervention time to provide instructional support to struggling learners. Problem Statement: Too few students receiving SPED services (ages 6-11) are placed within the general education classroom for greater than 80% of their day. Root Cause Index Number Critical Success Factors Teachers and administrators sometimes assume that students require more individualized special education services than are necessary for FAPE. Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality 5 Goal Students receiving SPED services will be served in the Least Restrictive Environment possible while providing FAPE. Strategies Conduct staff development for teachers to improve use of differentiation strategies within the regular classroom. Consider staffing allocations to make good use of existing staff in co-teach, in-class support, and content mastery settings. Evaluate scheduling practices to create most effective inclass support for students and teachers. Provide opportunity for increased staff development for SPED teachers (especially secondary) within the specific content areas with which they provide in-class support. Explore scheduling possibilities for common planning and conference periods for content gen-ed teachers and the SPED teachers that provide their inclass support. Problem Statement: Too many students receiving SPED services (ages 6-11) are placed within the general education class for less than 40% of their day. Root Cause Index Number Critical Success Factors Teachers and administrators sometimes assume that students require more individualized special education services than are necessary for FAPE. Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality 6 Goal Students receiving SPED services will be served in the Least Restrictive Environment possible while providing FAPE. Strategies Conduct staff development for teachers to improve use of differentiation strategies within the regular classroom. Consider staffing allocations to make good use of existing staff in co-teach, in-class support, and content mastery settings. Evaluate scheduling practices to create most effective inclass support for students and teachers. Provide opportunity for increased staff development for SPED teachers (especially secondary) within the specific content areas with which they provide in-class support. Explore scheduling possibilities for common planning and conference periods for content gen-ed teachers and the SPED teachers that provide their inclass support. Problem Statement: The rate of identification of Hispanic students requiring SPED services is out of proportion as compared to the number of Hispanic students in the District enrollment. Root Cause Index Number Critical Success Factors Goal Outside influences, including cultural differences, sometimes hinder teachers from understanding and meeting students’ learning needs, especially those students of various ethnicities, resulting in over-identification in SPED. Not Applicable Index 1: Student Achievement Index 2: Student Progress Index 3: Closing Achievement Gaps Index 4: Postsecondary Readiness Improve Acad. Performance Data-driven Instruction Leadership Effectiveness Increased Learning Time Family/Community Engagement School Climate Teacher Quality The rate of identification of Hispanic students requiring SPED services will reflect proportions of Hispanic students enrolled in the District. 7 Strategies Provide staff development so teachers can better understand (second language learner) SLL-related learning difficulties. Provide additional staff development for teachers related to creating a language-rich classroom. Provide additional staff development for teachers related to building academic language skills. Provide additional staff development for ESLendorsed teachers. Provide professional development in multicultural sensitivity on topics including cultural social interactions and practices, cultural attitudes toward education/educators, etc.