The Earth`s Surface - BiologicalSciencesEDCU12037
advertisement
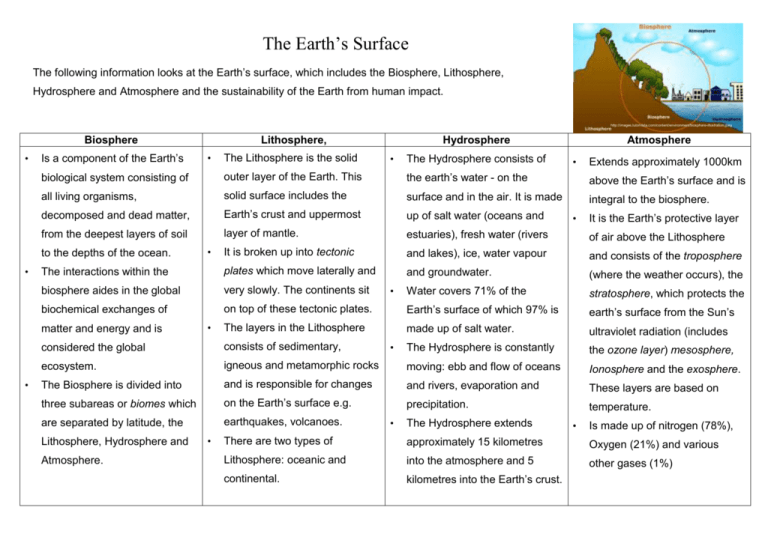
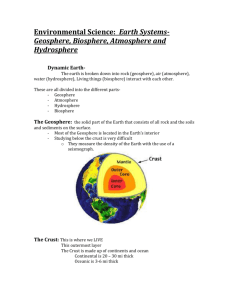
The Earth’s Surface The following information looks at the Earth’s surface, which includes the Biosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere and the sustainability of the Earth from human impact. http://images.tutorvista.com/content/environment/biosphere-illustration.jpeg Biosphere • Is a component of the Earth’s The Lithosphere is the solid • The Hydrosphere consists of Atmosphere • Extends approximately 1000km outer layer of the Earth. This the earth’s water - on the above the Earth’s surface and is all living organisms, solid surface includes the surface and in the air. It is made integral to the biosphere. decomposed and dead matter, Earth’s crust and uppermost up of salt water (oceans and from the deepest layers of soil layer of mantle. estuaries), fresh water (rivers of air above the Lithosphere It is broken up into tectonic and lakes), ice, water vapour and consists of the troposphere The interactions within the plates which move laterally and and groundwater. (where the weather occurs), the biosphere aides in the global very slowly. The continents sit Water covers 71% of the stratosphere, which protects the biochemical exchanges of on top of these tectonic plates. Earth’s surface of which 97% is earth’s surface from the Sun’s The layers in the Lithosphere made up of salt water. ultraviolet radiation (includes The Hydrosphere is constantly the ozone layer) mesosphere, matter and energy and is • • Hydrosphere biological system consisting of to the depths of the ocean. • Lithosphere, • • • • • It is the Earth’s protective layer considered the global consists of sedimentary, ecosystem. igneous and metamorphic rocks moving: ebb and flow of oceans Ionosphere and the exosphere. The Biosphere is divided into and is responsible for changes and rivers, evaporation and These layers are based on three subareas or biomes which on the Earth’s surface e.g. precipitation. temperature. are separated by latitude, the earthquakes, volcanoes. Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere. • • The Hydrosphere extends • Is made up of nitrogen (78%), There are two types of approximately 15 kilometres Oxygen (21%) and various Lithosphere: oceanic and into the atmosphere and 5 other gases (1%) continental. kilometres into the Earth’s crust. Human Impact Biosphere Lithosphere, Hydrosphere Atmosphere Impact from humans on the Earths Human impact on the Lithosphere The earth’s water surface is greatly Human impact on the atmosphere Biosphere include dangerous and includes: affected by humans in two main includes: irreversible changes such as: • areas: pollution and overuse. • • • • • Production of greenhouse Pollution is created from human gases, an excess of carbon vegetation deterioration. and animal waste products. dioxide and methane gases. Overgrazing, excessive This includes industrial, • Damage to the ozone layer. There has been damage to the cultivation of farming land, chemical and nutrient pollution. • Air pollution caused by fossil Earth’s ozone layer which is the “erosion, sediment deposition, stratospheric protecting against Global warming and the build- natural landscapes and up of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. • Land and soil degradation and • • Overuse of water, where water fuel combustion causing extractive industries, supply cannot keep up with the changes in the atmospheric the sun's harmful radiation. urbanization, disposal of water demand due to composition. Pollution of the Earth’s soil, industrial wastes, decline of population growth, industry water and air. plant communities, and the Erosion of the Earth’s surface effects of noxious plants and and results of deforestation. animals,” (Molebalebeng, 2012, p.1). The following YouTube provides easy to follow explanation of what is the Earth’s the Biosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere with great diagrams and images. Retrieved from: http://youtu.be/5FooHD0atuc A short video called “The Four Spheres of Earth” can be viewed via: http://bcove.me/hjq6dhdi • Deforestation Tectonic Plates • Make up the Earth’s outer layer called the Lithosphere: • Vary in size and thickness. • Are solid, and move/float on the inner layers of the Earth’s crust. • Movement of the tectonic plates depend on rock composition. • There are three tectonic boundaries, “convergent, where plates move into one another; divergent, where plates move apart; and transform, where plates move sideways in relation to each other”, (National Geographic, n. d. http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/the-dynamic-earth/plate-tectonics-article/) Australia shares the Indo-Australian tectonic plate with India. In recent years earthquakes have caused the plate to begin splitting into two pieces. The Indo-Australian tectonic plate is considered an atypical tectonic plate due to its unusual and thin shape compared to other tectonic plates. The eastern part of the Indo-Australian plate is slowly drifting north at a slightly faster rate than the western part of the plate, causing the plate to buckle, hence the cause of many earthquakes especially in the Indonesian region. Rock Cycle: The Rock Cycle is the changes in the formation and breakdown and reformation of rocks. Rocks are made up of minerals and vary due to chemical and crystal composition and structure. They are formed naturally, are nonliving, and are a coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that makes up part of the Earth. Igneous Rock: are crystal-like solids which change from a liquid state of molten rock called magma, into a solid form once cooled and vary in composition and texture. Metamorphic Rock is rock that is changed through a chemical, heat or pressure process, changing the mineralogy of the rock composition. Two types of metamorphic rocks: non-foliated metamorphic rocks and foliated metamorphic rocks Sedimentary Rock is the result of a build-up of broken small pieces of pre-existing rocks, caused by erosion and weathering. There are three types: Clastic, Chemical and Organic. Further reading and resources: Plate Tectonics for Kids (www.makemegenius.com), retrieved from: http://youtu.be/tcPghqnnTVk Exploring Earth, retrieved from: http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/investigations/es0602/es0602page01.cfm?chapter_no=investigation Mr Parr, (2012), Types of Rocks Song, retrieved from: http://youtu.be/lE3jR_RhxO4 Mr Parr (2011) Rock Cycle Song, retrieved from http://youtu.be/53lMdHzvGCQ References ABC Science, (2012). Quake start of Indo-Australia plate split, retrieved from: http://www.abc.net.au/science/articles/2012/09/27/3599041.htm Biosphere, retrieved from: http://climap.net/biosphere Clearfield, R. (2014). Lithosphere Facts, retrieved from: http://www.life123.com/parenting/education/geology/lithosphere-facts.shtml Ellis, E. (2013). The Encyclopedia of Earth, Biosphere, retrieved from: http://www.eoearth.org/view/article/150667/ Encyclopedia.com, Lithosphere, retrieved from: http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/lithosphere.aspx Everything Science, Threats to the Hydrosphere, (n. d.), retrieved from: http://everythingscience.co.za/grade-10/23-the-hydrosphere/23-thehydrosphere-05.cnxmlplus Geology.com, retrieved from: http://geology.com/rocks/ Hammonds, M. (2012), Breaking Plates, Australian Science, retrieved from: http://www.australianscience.com.au/news/breaking-plates/ Introduction to the Atmosphere, retrieved from: https://www.ucar.edu/learn/1_1_1.htm#top Kazmeyer, M. (n. d.) Human Impact on the Earth’s Atmosphere, Demand Media, retrieved from: http://science.opposingviews.com/humanimpact-earths-atmosphere-3677.html Lithosphere, retrieved from: http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Lithosphere.html Molebalebeng, (2012), Human Impact on LIthoshere, retrieved from: http://www.studymode.com/essays/Human-Impact-On-Lithosphere1005680.html National Geographic, (n .d.). Plate Tectonics, Moving and Shaking, retrieved from: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/thedynamic-earth/plate-tectonics-article/ Smithsonian Institution, (2002), The Effects Of Human-Caused Atmospheric Changes On Tropical Forests, retrieved from: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2002/08/020807065359.htm What is a Rock Cycle, (n. d. ) retrieved from: http://imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/geo/basics/diagrams.htm Young People’s Trust for the Environment (YPTE), (n. d.) Our Battered Biosphere, retrieved from: http://www.ypte.org.uk/environmental/ourbattered-biosphere/4