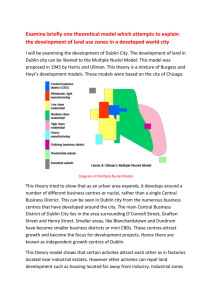
Functional zones in cities
advertisement

The Growth of Dublin Dublin is a primate city, this means that it has more than twice the population of the next largest city in the state. Throughout history Dublin had expanded significantly. This process is known as Urbanisation. Most urban areas grow for a variety of reasons- Economic activities, Administration and social activites. The Growth of Dublin Viking times Dublin began as a Viking settlement on the south side of the Liffey. This settlement was beside a dark pool in the river which gave the city its nameDubh Linn. The Vikings named their settlement Dyflinn. Norman times Around 200 years later the Normans arrived. They took control of the city and it began to expand. Dublin Castle was built and it was surrounded by many narrow streets. As the Normans had good trade links with England, Dublin grew as an important port. Georgian times During the 18th Century Dublin became very fashionable. Beautiful streets and squares were built (O Connell St., Merrion Sq.) Wealthy landlords built large townhouses (now called tenements) Trade grew in importance, canals were built, the port was developed and manufacturing thrived in the Liberties area with textiles and Guinness. 19th Century Many suburbs grew, like Dalkey, Killiney and Dun Laoghaire as the inner city became run down. The grand Georgian buildings gave way to slums. 1900 onwardsThis is the time of most rapid growth. Became the main focus point for roads, air, rail and sea transport. Main manufacturing and administration centre. A lot of rural to urban migration. Functional zones in cities Most cities contain several functional zones. CBD (Central Business District) Shopping/Retail areas Industrial areas Residential areas Recreational areas Case study- Paris CBD in Paris- In the heart of the city. Main st. is called the Champs Elysees. Also has many world famous shops and attractions such as the Eiffel Tower and The Louvre. Shopping areas- Paris has several large shopping areas outside its CBD. Residential- Most people live in the suburbs. Western suburbs are the wealthiest. Industrial- Specially planned industrial areas located around the city, whereas expensive Jewellery, cosmetics and fashion are still made in the city centre. Recreation- Paris has several beautiful parks. Eg. The Luxembourg Gardens. Case study- Dublin CBD- O’ Connell Street and down along the Liffey towards the port. Shopping- Outskirts of the city. Blandchardstown, Liffey Valley and Dundrum. Residential- Suburbs like Tallaght, now even stretching as far as Mullingar. Industrial- Several Industrial estates & around the docks and airport. Recreation- Phoenix Park and St. Stephens Green. Letterkenny- Case study CBD- Main Street Shopping- Retail park (Next, TK Maxx, Tempest) Residential- Mountain top, Ballymacool. Industrial- Ballyraine Ind. Est. Recreation- Two town parks. Land values in cities Generally, the closer to the CBD you get, the higher the land values will be. Also, the intensity of land use (Height of buildings) will also be at its greatest. On the other hand, the further away from the city centre you go, the lower the land values and the lower the density of use. A bungalow in Dublin city centre would look as much out of place as a high rise block of flats in Glenfin. Housing in Cities Houses tend to be older and smaller in the inner city than they are in the suburbs. The size and quality of these houses also vary greatly. Traffic patterns There are clear patterns in traffic movement. There are ‘rush hours’ in the morning @ 8-9 and in the evening @ 5-6. This is because it is at these times when most working people are travelling to or from work. Traffic congestion can be reduced by restricting the amount of private cars in the inner city. This can be achieved by Improved public transport (Buses, railways, trams etc) Building underground railway systems Ring roads and motorways around the city Other traffic solutions e.g. One way systems etc Urban problems Urban decline- old, poor quality houses and buildings fall into decay, people leave the area for the suburbs. ↓This leads to another problem Urban Sprawl- This is the rapid growth of housing from urban areas outwards into the countryside. Valuable farmland being used for building purposes Villages become swallowed into the city, and lose their identity. E.g. Dundrum Inadequate services Poor public transport means more people resort to private cars > Traffic congestion Poor water quality Waste disposal problems associated with Landfill and Incinerators Nothing for young people to do contributes to anti-social behaviour Overcrowded Schools/Hospitals Urban solutions Urban renewal- Older houses and buildings are refurbished or replaced. Urban redevelopmentThis is when people being re-housed in new suburbs so the inner city areas can be used instead for commercial uses. New towns Like Tallaght, Blanchardstown are built to cater for the growing populations of the city. They are well connected with road and rail and are planned so as they will not suffer urban sprawl.