Ch 9 notetaking guide
advertisement

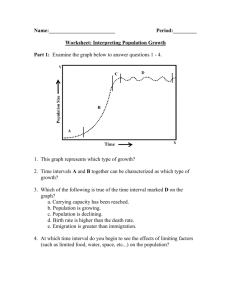
Ch 9 Note-taking Guide - Stuff to Absolutely Include 1) From the Core Case Study (“Is the World Overpopulated?”), why is human population a sensitive topic? 2) What are three reasons human population growth has been able to continue expanding exponentially for the past 200 years? (p. 172) 3) What is the current trend with global population growth rates? (p. 172) 4) Write the equation for calculating population change using births/deaths and immigration/emigration. (p. 173) 5) See bar chart in Figure 9-3, p. 174: o (HINT: The rate of population growth has _____ (slowed or sped up); the population is _________ (increasing/decreasing) o Which region of the world has the highest birth rate? o Which region of the world has the highest death rate? 6) Differentiate between the following terms: replacement-level fertility and total-fertility rate (TFR) (p. 174) 7) What are the top four most populous countries in the world? (See Figure 9-4, p. 174) 8) How did population growth rates change after World War II? (p. 175) 9) List the factors that can affect birth rates and fertility rates. (p. 176) 10) List factors affecting death rates. (p. 177) 11) Define the following terms: migration, immigration & emigration. (p. 177) 12) Sketch age structure diagrams and list example countries for the following types of population change: expanding rapidly, expanding slowly, stable, and declining. (See Figure 9-9, p. 179) 13) Sketch typical age structure diagrams for developed v. developing countries. (See Figure 9-10, p. 179) 14) What percent of the world’s people live in countries with stabilized or declining populations? (p. 180) 15) What problems can result from rapid population decline? (p. 181) 16) What tends to happen to birth and death rates as countries become economically developed? (p. 182) 17) List and describe three good ways to slow population growth. (pp. 184-185) 18) Human impacts: with the demands of a rapidly growing population, we have altered nature to meet our needs. What are some ways we have degraded natural capitol in this process? (See Figure 9-17, p. 188) Ch 9 Note-taking Guide - Stuff to Absolutely Include 1) From the Core Case Study (“Is the World Overpopulated?”), why is human population a sensitive topic? 2) What are three reasons human population growth has been able to continue expanding exponentially for the past 200 years? (p. 172) 3) What is the current trend with global population growth rates? (p. 172) o (HINT: The rate of population growth has _____ (slowed or sped up); the population is _________ (increasing/decreasing) 4) Write the equation for calculating population change using births/deaths and immigration/emigration. (p. 173) 5) See bar chart in Figure 9-3, p. 174: o Which region of the world has the highest birth rate? o Which region of the world has the highest death rate? 6) Differentiate between the following terms: replacement-level fertility and total-fertility rate (TFR) (p. 174) 7) What are the top four most populous countries in the world? (See Figure 9-4, p. 174) 8) How did population growth rates change after World War II? (p. 175) 9) List the factors that can affect birth rates and fertility rates. (p. 176) 10) List factors affecting death rates. (p. 177) 11) Define the following terms: migration, immigration & emigration. (p. 177) 12) Sketch age structure diagrams and list example countries for the following types of population change: expanding rapidly, expanding slowly, stable, and declining. (See Figure 9-9, p. 179) 13) Sketch typical age structure diagrams for developed v. developing countries. (See Figure 9-10, p. 179) 14) What percent of the world’s people live in countries with stabilized or declining populations? (p. 180) 15) What problems can result from rapid population decline? (p. 181) 16) What tends to happen to birth and death rates as countries become economically developed? (p. 182) 17) List and describe three good ways to slow population growth. (pp. 184-185) 18) Human impacts: with the demands of a rapidly growing population, we have altered nature to meet our needs. What are some ways we have degraded natural capitol in this process? (See Figure 9-17, p. 188)