Calculating Comparative Advantage
advertisement
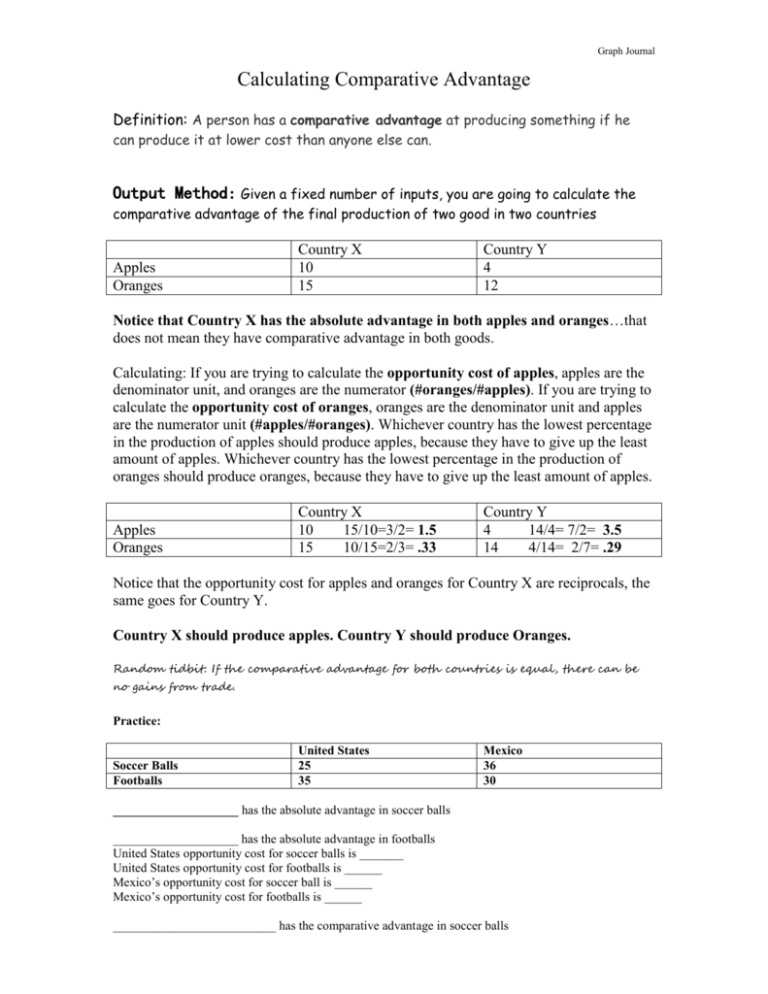
Graph Journal Calculating Comparative Advantage Definition: A person has a comparative advantage at producing something if he can produce it at lower cost than anyone else can. Output Method: Given a fixed number of inputs, you are going to calculate the comparative advantage of the final production of two good in two countries Apples Oranges Country X 10 15 Country Y 4 12 Notice that Country X has the absolute advantage in both apples and oranges…that does not mean they have comparative advantage in both goods. Calculating: If you are trying to calculate the opportunity cost of apples, apples are the denominator unit, and oranges are the numerator (#oranges/#apples). If you are trying to calculate the opportunity cost of oranges, oranges are the denominator unit and apples are the numerator unit (#apples/#oranges). Whichever country has the lowest percentage in the production of apples should produce apples, because they have to give up the least amount of apples. Whichever country has the lowest percentage in the production of oranges should produce oranges, because they have to give up the least amount of apples. Apples Oranges Country X 10 15/10=3/2= 1.5 15 10/15=2/3= .33 Country Y 4 14/4= 7/2= 3.5 14 4/14= 2/7= .29 Notice that the opportunity cost for apples and oranges for Country X are reciprocals, the same goes for Country Y. Country X should produce apples. Country Y should produce Oranges. Random tidbit: If the comparative advantage for both countries is equal, there can be no gains from trade. Practice: Soccer Balls Footballs United States 25 35 Mexico 36 30 ____________________ has the absolute advantage in soccer balls ____________________ has the absolute advantage in footballs United States opportunity cost for soccer balls is _______ United States opportunity cost for footballs is ______ Mexico’s opportunity cost for soccer ball is ______ Mexico’s opportunity cost for footballs is ______ __________________________ has the comparative advantage in soccer balls Graph Journal __________________________ has the comparative advantage in footballs Input method: Given a fixed output, you are going to calculate the comparative advantage based on the input costs of production (this could be currency, capital, labor, land) for two goods in two countries. This is the labor time it takes to gather one bushel of each fruit, in each country. Country X Country Y Apples 2 hours 1 hour Oranges 3 hours 2 hours Calculations: When you are using the input method, the thought process is flipped. When you are trying to calculate the opportunity cost of apples, apples will be the numerator and oranges will be the denominator (apple hours/ orange hours). When you are trying to calculate the opportunity cost of oranges, oranges will be the numerator and apples will be the denominator (orange hours/apple hours). Apples Oranges Country X 2h 2/3=.66 3h 3/2= 1.5 Country Y 1h ½= .5 2h 2/1= 2 Country Y has the comparative advantage in apples. Country X has the comparative advantage in oranges. Practice Production cost of 1 pizza Production cost of 1 steak Great Britain 2€ 5€ Spain 4€ 3€ Great Britain’s opportunity cost for producing pizza is ________________ Great Britain’s opportunity cost for producing steak is ________________ Spain’s opportunity cost for producing pizza is _______________ Spain’s opportunity cost for producing steak is _______________ ______________________ has the comparative advantage in pizza ______________________ has the comparative advantage in steak









