Chemical bonding worksheet 5 answer
advertisement
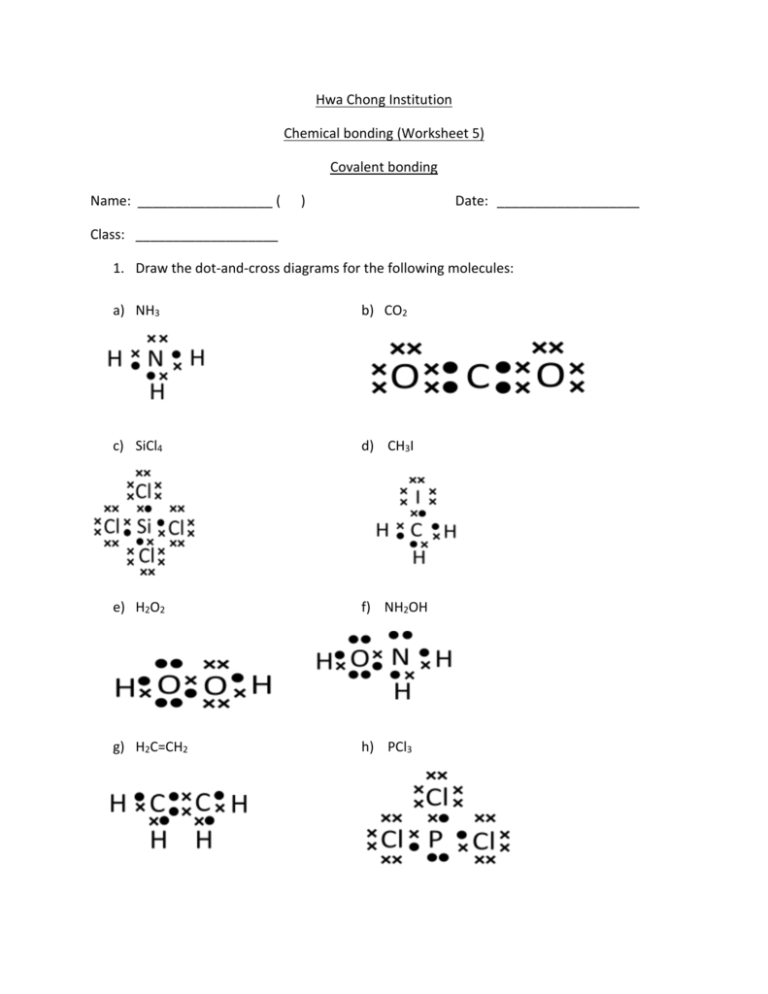
Hwa Chong Institution Chemical bonding (Worksheet 5) Covalent bonding Name: __________________ ( ) Date: ___________________ Class: ___________________ 1. Draw the dot-and-cross diagrams for the following molecules: a) NH3 b) CO2 c) SiCl4 d) CH3I e) H2O2 f) NH2OH g) H2C=CH2 h) PCl3 2. Fill in the blanks accordingly. Compound Fluorine Oxygen Nitrogen Ethene (H2C=CH2) Ethyne (HCCH) Number of sigma bonds 1 1 1 5 3 Number of pi bonds 0 1 2 1 2 3. Predict which of the following contains polar bonds and whether they are polar molecules (fill in yes or no to each of the blanks). Compound NH3 H2S CO CH4 CH3Cl Contains polar bonds Yes Yes Yes Yes/No Yes Is a polar molecule Yes Yes Yes No Yes 4. The data of fluoromethane, ethane and methanol are shown below. Compound Structure Fluoromethane H H Ethane H Methanol H C F H H H C C H H H C O Number of electrons per molecule 18 Boiling point/ OC Solubility in water -78.2 Moderate 18 -89 Very low 18 65 Miscible H H H *Miscible means that methanol can mix with water in any proportion. i) Explain the trends observed for the boiling points of the molecules. All three molecules have the same number of electrons and hence possess almost equal instantaneous dipole-induced dipole interactions. Methanol has the highest boiling point because its molecules can form hydrogen bonds with one another. More energy is required to break hydrogen bonds than van der Waals’ forces. Fluoromethane has slightly higher boiling point than ethane because the molecules are polar and exhibit permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions too, requiring higher energy to break. ii) Explain the trends observed for the solubility in water of the molecules. Methanol is very soluble because it possesses an O which can form hydrogen-bonds to the H atoms in H2O, as well as a H bonded to an O, which can form hydrogen-bonds to the O atom in H2O. Fluoromethane is moderately soluble as the F atom can hydrogenbond to H atoms in H2O. Ethane is hardly soluble because it is non-polar and no hydrogen bonding can take place. 5. Explain why water has a much higher boiling point than ammonia and hydrogen fluoride even though all three compounds are able to form hydrogen bonds. Each water molecule has 2 lone pairs on O, and 2 H atoms, all of which can take part in H-bonding, hence a water molecule can form 4 H-bonds. Ammonia has 3 H atoms but only one lone pair of electrons on N, hence it can only form at most 2 H-bonds. Similarly for hydrogen fluoride, it has 3 lone pairs on F, but only one H atom. Hence it can only form 2 H-bonds. The greater the number of H-bonds, the higher the energy required to break them, and the higher the boiling point. 6. Ethanoic acid (shown below) is found to exist as dimers in the vapour state at 120 oC. This means that two molecules of ethanoic acid are joined together by bonds in the vapour state. Propose a way by which the molecules can join together. Draw your proposed structure below. Why is this structure possible? H H C H O C O ethanoic acid H H H H O C C C O H H O C O H H H Ethanoic acid can form a dimer because the two molecules can form hydrogen bonds with each other, as shown above. 7. The nucleotides adenine (A) and thymine (T) are building blocks of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Their structures are shown below. H H N O C C C N H C H N H H H C C H N C N H C N C N C H H O Thymine Adenine DNA is made up of two strands of polymer. A and T from 2 opposite strands bind together via two H-bonds which stabilize the DNA structure. What do you think will happen to the DNA structure if A and T were modified as shown below? Why? H H H C P H N H N C C H C S C H H C C P C N P N H C H C H O There will no longer be any hydrogen bonds that can occur between A and T, hence the DNA structure will likely unravel instead of the 2 opposite strands binding together. (NOTE: DNA also contains Cytosine and Guanine which also bind together using H-bonds. This question assumes that only A and T are present.) 8. The beta-pleated sheet is one form of secondary structures in proteins. Hydrogen bonds hold the sheet together as shown in the figure below: What do you think will happen when a protein containing beta-pleated sheets was heated? Why? Upon heating, the energy supplied causes hydrogen bonds to break apart and the arrayed and orderly structure of the protein will be destroyed. This is normally irreversible. The protein is said to be denatured. 9. Silicon and carbon both belong to Group IV of the Periodic table. The compound silicon carbide contains only silicon and carbon. It is known that one form of silicon carbide has a structure that resembles the diamond structure. Every carbon atom is covalently bonded to 4 silicon atoms, and every silicon atom is covalently bonded to 4 carbon atoms. i) Predict the formula of this form of silicon carbide. SiC. ii) Predict two physical properties of this form of silicon carbide. It is hard. It does not conduct electricity. It is not soluble in water or organic solvents.









