Using Dictionaries to Find Etymologies
advertisement

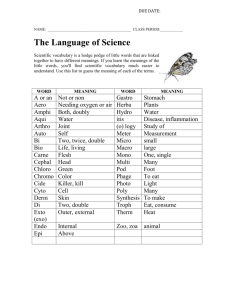
9th Honors Literature Using Dictionaries To Find Etymologies ELACC9-10L4: c. Consult general and specialized reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation of a word or determine or clarify its precise meaning, its part of speech, or its etymology. Where do words come from? How and when were they invented? Why are there so many different languages? Why do many languages share the same or similar words for the same things? The answers to all these questions lie in the study of etymology. This concerns the roots of words and how the sounds and spellings, as well as the meanings, have evolved over time. et·y·mol·o·gy [et-uh-mol-uh-jee] noun, plural et·y·mol·o·gies. 1. the derivation of a word. Synonyms: word origin, word source, derivation, origin. 2. a chronological account of the birth and development of a particular word or element of a word, often delineating its spread from one language to another and its evolving changes in form and meaning. Synonyms: word history, word lore, historical development. 3. the study of historical linguistic change, especially as manifested in individual words. Origin: 1350–1400; Middle English < Latin etymologia< Greek etymología,equivalent to etymológ(os) studying the true meanings and values of words (étymo(s) true (see etymon) + logos word, reason) + -ia-y3 Word etymologies can be found in an ordinary dictionary. 1. Look in your dictionary at the word aquiline. 2. In brackets, you will see the word origin followed by a definition for the term as it occurred in the language: [Latin aquila eagle]. 3. The word aquiline developed from the Latin word for eagle. 4. Not all words will have an etymological entry. 5. Look in the preface to the dictionary for abbreviation meanings if the language is not written out. For example, OE means Old English.