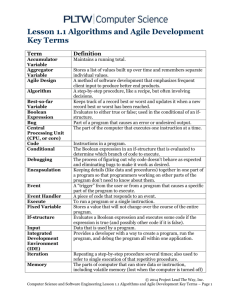
Agile Overview
advertisement
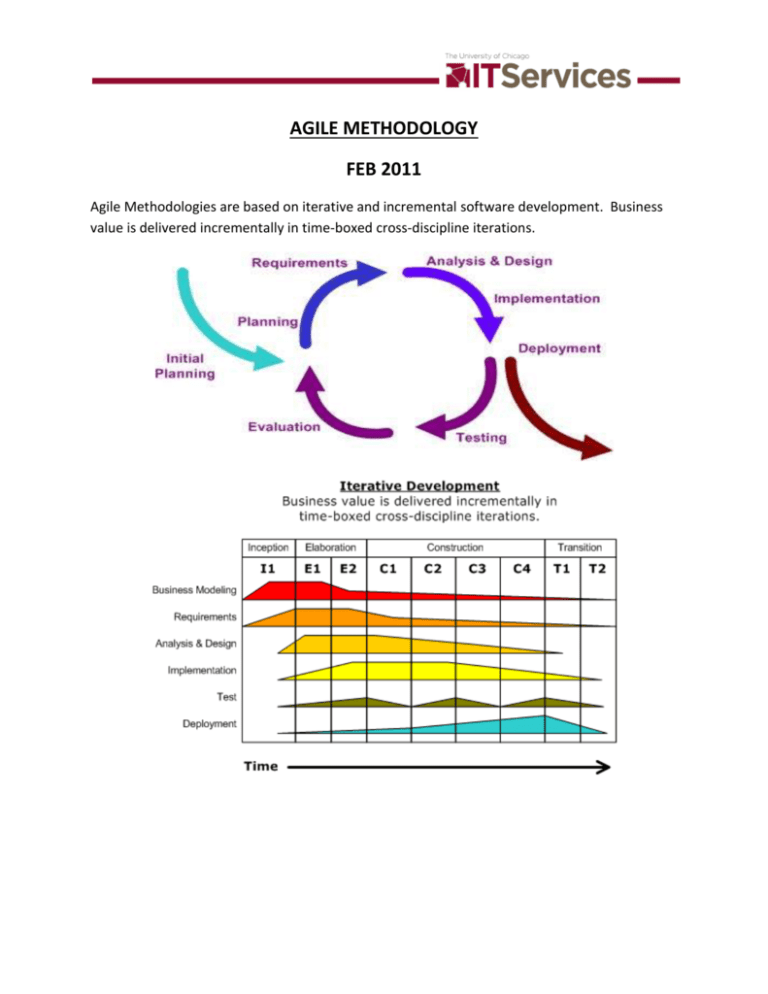
AGILE METHODOLOGY FEB 2011 Agile Methodologies are based on iterative and incremental software development. Business value is delivered incrementally in time-boxed cross-discipline iterations. Twelve principles: Customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of useful software Welcome changing requirements – even late in deployment Working software is delivered frequently (weeks versus months) Working software is the principal measure of progress Sustainable development – able to maintain constant pace Close daily co-operation between business and developers Face-to-face conversations is best form of communication Projects are built around motivated individuals Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design Simplicity Self-organizing teams Regular adaption to changing circumstances Basically Agile breaks tasks into small increments with minimal planning. It does not involve long term planning. Each iteration involves a full development cycle. Team size is typically small (5-9 people). Each team contains a customer representative appointed by stakeholders to act on their behalf and makes a personal commitment to being available to developers to answer mid-iteration problem-domain questions. With working software as the measure of progress less written documentation is produced. Stakeholders need to prioritize their wants with other iteration outcomes based on business value. Comparison: Methodologies exist on a continuum from adaptive to predictive. ADAPTIVE--------------------------------------------------------------------PREDICTIVE ADAPTIVE: Agile lies on the adaptive side. Adaptive focuses on adapting to quickly changing realities. When the needs change on a project, the team changes as well. The adaptive team will have difficulty describing exactly what will happen in the future. The further away the date the more vague it is. They cannot report exactly what tasks are being done next week but only which features are planned for next month. When asked about a release 6 months from now, an adaptive team may only be able to report the mission statement for the release or expected value vs. cost. PREDICTIVE: Predictive methods focus on planning the future in detail. A predictive team can report exactly what features and tasks are planned for the entire project. Predictive teams have difficulty changing direction. The plan is optimized for original destination and changing direction can require completed work to be started over. These types of teams institute change control boards to ensure only the most valuable changes are considered. Costs are closely monitored. DRAWBACKS: Some things that negatively impact the success of an agile project: Mission critical systems where failure is not an option Large-scale development efforts Distributed development efforts (non-colocated teams) Forcing an agile process on a development team AGILE METHODS: Well known agile software development methods include: Agile Modeling Agile Unified Process (AUP) Dynamic Systems Devl Method (DSDM) Essential Unified Process (EssUP) Extreme Programming (XP) Feature Driven Development (FDD) Open Unified Process (OpenUP) Scrum Velocity tracking IT Project Delivery: E. Lorenzo Feb 2011