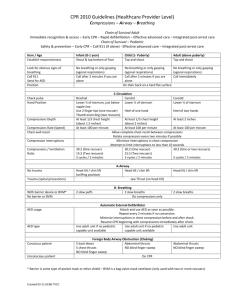
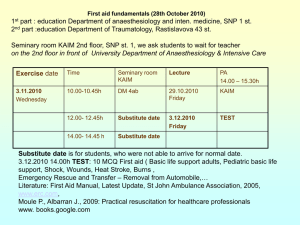
CPR Study Guide #1
advertisement

CPR Study Guide #1 Name_____________________________________________ 1. You may realize that an emergency has occurred only if you become aware of unusual _______________________, ________________________, and_______________________________ or_____________________________. 2. The vast majority of states have_________________ _________________________ laws that protect citizens when they give emergency care in good faith. 3. In general you should give care to an ill or injured person until: You see obvious signs of life, such as _________________________. Another __________________ ___________________________ or EMS take over. You are too__________________ to continue or the scene becomes _____________________. 4. You should always get permission to give care unless a person is _________________________ or unable to respond, _______________________, mentally impaired, seriously _____________________ or seriously _____________. In these cases, the law assumes that is the person could respond, he or she would agree to care. This is called __________________ ____________________. 5. While giving care avoid contact with _________________and other body fluids or objects that may be soiled with __________________ and other body fluids. Use protective CPR breathing barriers. Use barriers, such as _____________________ _______________. Cover any of your own cuts, scrapes or sores with a _______________________. Do not eat, drink or touch your ____________________, __________________, or _____________________ when giving care or before you wash your hands after care has been given. 6. The three emergency actions steps are: ___________________, ____________________, _________________. 7. ______________ first for an adult or child about 12 who is unconscious, a child or infant who you witnessed suddenly ___________________ or an unconscious child or infant known to have __________________ problems. 8. _______________ first for an unconscious child (younger than 12) who you did not see collapse or any drowning victim. 9. One of the most dangerous threats to a seriously injured or ill person is unnecessary _________________________. 10. Checking a conscious person with no immediate life-threatening conditions involves two basic steps: _______________________the person and bystanders. Check the person from ___________________ to _________________. 11. __________________ is a condition in which the circulatory system fails to deliver enough oxygen rich blood to the body’s tissues and vital organs. 12. When checking an unconscious person….always check to see if an unconscious person: has an _____________ ______________________ and is breathing normally or is ______________________ severely. 13. When someone is unconscious and lying on his or her back, the ___________________ may fall to the back of the throat and block the airway. 14. When checking an unconscious person for breathing, position yourself so you can ___________________, _______________________, and ________________ for breathing. Do this for no more than ________________ seconds. 15. After responding to an emergency involving a serious injury, illness or death, it is not unusual to experience acute________________________. CPR Study Guide #2 Name_______________________________________________ 1. A heart attack can be indicated by common signals such as; chest pain, discomfort or ____________________, discomfort in other areas of the ________________ _________________ in addition to the chest, trouble ____________________, skin may be __________________ or ashen. Men and women might have different signals. 2. If you suspect someone is having a heart attack you should: _______________ ___________ or local emergency number. Have a person stop what he or she is doing and ______________, _______________ any tight or uncomfortable clothing. Be prepared to perform _____________ and use an _______________. Ask the person if he or she has a history of heart disease and give them prescribed medication for chest pain if they have it. Offer ________________ if medically appropriate. Be ____________ and reassuring. Talk to bystanders to get information. Do NOT try to drive the person to the hospital yourself. 3. The Cardiac Chain of Survival is: Early __________________________ and early _____________ to EMS. Early _________________. Early ______________________. Early _________________________ __________________ care. 4. CPR is a combination of _________________________ ____________________ and _____________________ breaths. 5. For chest compressions to be the most effective, the person should be on his or her _______________ on a _______________, flat surface. 6. When giving compressions push the sternum down at least __________ inches. 7. Once you have given ___________ compressions, open the airway using the headtilt/chin-lift technique and give _______________ rescue breaths. 8. Every year in the Unites States more than _____________________ people die of sudden cardiac arrest. 9. When using an AED (Automated External Defibrillator), if CPR is in progress, do NOT interrupt until the AED is ________________ ____________ and the defibrillation pads are __________________. 10. The first step in operating an AED is to _________________ _____________ the AED. 11. Apply the AED pads to the person’s ______________, _____________ chest. 12. After delivering the AED shock, or if no shock is advised: perform about ________ minutes or (____________ cycles) of CPR and continue to follow the prompts of the AED. 13. When using an AED around water, remove him or her from the water before defibrillation. A shock delivered in the water could harm _____________________ and _______________________. 14. It is (circle one….) SAFE UNSAFE to deliver a shock to a person in cardiac arrest when he or she is lying on a metal surface, as long as appropriate safety precautions are taken. 15. You (circle one…) DO using an AED. DO NOT have to remove jewelry and body piercings when CPR Study Guide #3 Name___________________________________________________________ 1. Hyperventilation is the body’s way of compensating when there is a lack of enough ______________________. The result is an excess of carbon dioxide, which alters the ______________________ of the blood. 2. A severe allergic reaction can cause a condition called ______________________________. 3. Signs of breathing emergencies include: Trouble ______________________ or no breathing. __________________ or rapid breathing. Unusually deep or ______________________ breathing. _________________ for breath. Wheezing, gurgling or making high-pitched noises. Unusually _____________ or ____________ skin. Flushed, pale, ashen or _______________ skin. ________________________ of breath. ______________________ or lightheadedness. Pain in the _________________ or tingling in the hands, feet, or ___________. Apprehensive or fearful feelings. 4. If a person is not breathing or if breathing is too ________________, too ______________, ________________ or ___________________ call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number immediately. 5. If an adult is unconscious and not breathing, the cause is most likely a _________________ emergency. 6. Signals of choking include: ______________________ either forcefully or weakly. Clutching the _______________ with one or both hands. Inability to ________________, speak, _____________, or breathe. Making _____________________________ noises while inhaling or noisy breathing, panic, or __________________ skin. Losing consciousness if blockage is not removed. 7. To give abdominal thrusts to a conscious choking adult or child; Stand or kneel behind the person and wrap your arms around his or her waist. Locate the _______________ with one or two fingers of one hand. Make a _______________ with the other hand and place the _________________ side against the middle of the person’s abdomen, just above the navel and well below the lower tip of the _______________________. Grab you fist with your other hand and give quick, _______________ thrusts into the abdomen. 8. If a conscious choking person is too large for you to reach around , is obviously pregnant or is known to be pregnant, give _________________ ___________________ instead. 9. If you are alone and choking, bend over and press your _____________________ against any firm object. 10. For a choking person in a wheelchair, give _____________________ ___________________. CPR Study Guide #4 Name_______________________________________________________________ 1. If someone faints: ________________ the person to the ground or other flat surface and position him or her on their ___________________ lying __________________. Loosen any __________________ ________________________. Check that the person is _____________________. If the victim vomits, roll them onto one _______________________. 2. The general principles of managing a seizure are to prevent ____________________, protect the person’s _______________________ and make sure that the ___________________ is open after the seizure has ended. Do not hold or __________________ the person or put anything in the person’s __________________. 3. Signals of seizures include: A blank _______________, a period of distorted sensation during which the person is unable to _________________________. Uncontrolled muscular contractions called _____________________________, which lasts several minutes. 4. Although it may be frightening to see someone unexpectedly having a seizure, you should remember that most seizures last only for a ___________ __________________and the person usually recovers without problems. 5. Diabetes is a major risk factor for a _______________________. 6. You can help prevent stroke if you: Control _________________ _____________________. Quit ____________________________. Eat a _______________________ diet. ________________________ regularly. Maintain a _____________________ _____________________. Control ____________________. 7. For a stroke, think FAST, which stands for: Weakness, numbness or drooping on one side of the _____________________. Weakness or numbness in one _______________. Slurred ___________________or difficulty _____________________. Try to determine when the signals began as ____________________ is critical. 8. Warning signals of Type I diabetes included: Frequent ___________________________. Increase ______________________ or ____________________. Unexpected ______________________ loss. Irritability. Weakness and ____________________. 9. People with Type II diabetes often do not experience any warning signals. Possible warning signals of Type II include: Any of the warning signals of Type I. Frequent _____________________. ________________________ vision. _________________________ in the legs, feet and fingers. Cuts or bruises that are slow to ______________________. Itching. 10. If someone is poisoned you can call 9-1-1 or the National Poison Control Center hotline at _______________________________________________.