Chapter 4 Booklet
advertisement

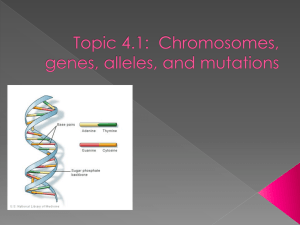
Grade 9 Science Unit 2 Reproduction Chapter 4: The nucleus controls the functions of life. Name: Homeroom #: _____ 1 The Function of the Nucleus The that is responsible for the functions of the cell. The The nucleus contains the master set of instructions that determines… and for controlling centre of the cell. Heredity A particular feature that can vary in size or form from individual to individual within a species is called a . Inherited from The process through which patterns of traits are passed on from an individual to its offspring is called . . DNA Carries the instructions in the A long, Forms a helix structure or a . The sides of the “ladder” are made from and . molecule. 2 The steps are made of 4 bases. These are: 1. 2. 3. 4. The bases in a DNA molecule always join in a specific way: joins with Joins with When a cell is ready to divide, each coil of loosely coiled DNA folds up further into a compact, structure called a . Chromosomes within the nucleus are found in Most humans have . pairs of chromosomes including one pair that determines . Genes Found on chromosomes. Small Store information needed to produce Can vary in length, from The arrangement of Each chromosome contains of DNA located at specific places on a chromosome. used by body cells. to bases. will determine the protein produced. of genes. 3 Proteins determine what body cells will become and how they will function. Examples: 1. Specialized cells will form ; tissues will form 2. Specialized proteins called chemical reactions that occur within each cell. Ex. speed up the 3. Some proteins act as chemical messengers called Mutations A change in the specific order of the that make up a particular A base may be or Effects of Mutations… , for another. 1. Ex. 2. Ex. 3. Ex. What type of mutation is this? Give your reasons. 4 Substances or factors that can cause mutations in DNA are called For Example Mutations can be caused by… 1. Ex. 2. Ex. 5 Chapter 2 Questions 1. What is a trait? Give an example. (Page 112) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2. What is heredity? (Page 112) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3. Where is heredity information stored? (Page 113) _________________________________________________________________ 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called “the control centre of the cell”? (Page 114) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5. Why is DNA required in every cell? (Page 115) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 6. How many chromosomes does a human body cell contain? (Page 117) _________________________________________________________________ 6 7. How does a gene differ from a chromosome? (Page 118) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 8. What are genes? Where are they located? (Page 118) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 9. What are the functions of proteins in cells? (Page 119) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 10. Explain the function of a gene in a cell. (Page 119) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 11. If you think of DNA as a chemical alphabet, how could you describe genes and chromosomes? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 7 12. What is a gene mutation? (Page 122) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 13. How can a gene mutation create a change in an organism? (Page 124) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 14. Give an example of a positive mutation. (Page 124) _________________________________________________________________ 15. Give an example of a negative mutation. (Page 125) _________________________________________________________________ 16. Give an example of a neutral mutation. (Page 126) _________________________________________________________________ 17. What is a mutagen? (Page 127) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 18. Describe two sources of mutagens. (Page 127) 1. .______________________________________________________ 2. .______________________________________________________ 8 19. How do viruses cause mutations? (page 127) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 20. List three examples of environmental mutagens. (Page 127) 1. ______________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________ 21. Describe an example of a mutation caused by human activity. (Page 127) ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Practice Test 1. Which of the following is a trait? A. age B. C. name D. eye colour number of siblings 2. Which of the following gives a cell the instructions it needs to develop into a muscle cell, a bone cell, or a skin cell? A. chromosome B. DNA C. gene D. nucleus 3. Which one of the following statements is true? A. A gene stores the information to make a particular protein. B. All the genes within the nucleus of a cell will be copied to make a protein at some time in the life cycle of a cell. C. Different proteins have the same sequences of bases. D. Different types of cells in your body contain different genetic information. 4. What does DNA do when a cell is ready to divide? A. It divides into 46 parts. B. It divides into two parts. C. It folds up into a chromosome. D. It unfolds into a gene. 9 5. A gene mutation is which of the following? A. a change in the specific order of the sugar and phosphates that make up a particular protein. B. a change in the specific order of the A, G, C, and T bases that make up a particular protein. C. a substance that causes genes to be copied incorrectly. D. a substance that changes the DNA structure. 6. Which of the following is an example of a natural mutagen? A. cigarette smoke B. cleaning products C. industrial waste D. virus Match the Term on the left with the best Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may be used only once. Term _____ 7. _____ 8. _____ 9. _____10. _____11. _____12. chromosome DNA gene gene mutation nucleus trait Descriptor A. feature that varies from individual to individual B. controls the functions of the cell C. long, two-stranded molecule that carries instructions for cell activities D. small segments of DNA located at specific places on a chromosome E. X-shaped structure of loosely folded DNA F. change in the order of A, G, C, and T bases in a gene Short Answer Questions 13. Explain how the nucleus controls the activities within a cell. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 14. Describe two effects of specific gene mutations. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 10