Exam 4 Review
advertisement

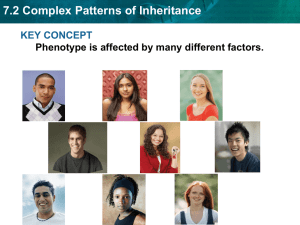
Exam Review Chapters 17,23,24, 25 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Adam Course: Bio 211 (2) Instructor: Wilsey Date: 1. Calico coat pattern in cats is the result of a. X inactivation b. Epistasis c. Extranuclear inheritance d. Genomic imprinting e. Maternal inheritance 2. A type of gene interaction in which the alleles of one gene mask the effects of a dominant allele or another gene. a. X inactivation b. Epistasis c. Extranuclear inheritance d. Genomic imprinting e. Maternal inheritance 3. Inheritance pattern of genes found in the genomes of mitochondria or chloroplasts. Usually these genes are inherited from the mother. a. X inactivation b. Epistasis c. Extranuclear inheritance also known as cytoplasmic inheritance example is maternal inheritance d. Genomic imprinting e. Maternal inheritance 4. Phenomenon of female mammals in which one x chromosome is inactivated in every somatic cell, producing a mosaic phenotype. a. X inactivation b. Epistasis c. Organelle heredity d. Genomic imprinting e. Maternal inheritance 5. Inheritance pattern in which the genotype of the mother determines the phenotype of the offspring. a. X inactivation b. Epistasis c. Maternal effect d. Genomic imprinting e. Maternal inheritance 6. The inheritance of characters with clearly defined phenotypic variants, such as tall and short height in pea plants are known as __________ traits, because the phenotypes do not overlap. a. Unique b. Discrete Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. c. Quantitative d. Polygenic For most traits, they show a continuous variation over a range of phenotypes. These traits are called _________ traits. a. Unique b. Discrete c. Quantitative d. Polygenic Quantitative traits that have several or many genes which contribute to the outcome of the trait are called ________. a. Unique b. Discrete c. Quantitative d. Polygenic True or False: for Maternal effect, the phenotype of the mother determines the phenotype of the offspring. The genotype of the farther and of the offspring themselves does not affect the offspring phenotype. a. True b. False the genotype of the mother determines Through x inactivation a barr body in created. A barr body would be found in the nucleus of a. every human cell every human somatic cell b. female somatic cells c. male somatic cells A change in one or more characteristic of a population that is heritable and occurs from one generation to the next is called? a. Natural selection b. Sexual selection c. Population genetics d. Evolution The phenotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross is a. a. 9:3:3:1 b. b. 9:3:4 c. 1:2:1 d. 3:1 Which of the following terms best describes when the phenotype of the heterozygote differs from the phenotype of both homozygotes? a. Epistasis b. pleiotrophy c. multiple alleles d. incomplete dominance. All of the alleles for every gene in a given population is called a ______? a. Species b. Gene Pool c. Locus d. Hybrid Zone Two alleles that both affect the phenotype in separate distinguishable ways is known as? 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. a. Complete dominance b. Codominance c. Incomplete dominance d. Partial dominance True or False: A species is a group of related organisms that share a distinctive form and are capable of interbreeding while a population is all the organisms that belong to different species and live in the same area. a. True b. False Can there be multiple population of one species? a. Yes b. No Can a population consist of more one than one species? a. Yes b. No Fitness of an animal relies on which component a. Survival b. Strength c. Reproductive rate d. Intelligene e. A and D f. A and C The long snouts and tongues of the giant anteater and the echidna allow them to feed on ants. These two organisms that show similar adaptation is an example of a. Analogous structure b. Convergent traits c. Convergent evolution d. All the above. 21. There are three types of Homology that are used as evidence for evolution. Homology is the fundamental similarity of animals due to descent from a common ancestor. Which is not a homology that is used as evidence a. Anatomical b. Developmental c. Speciation d. Molecular 22. The people involved with evolution and their Proposals _____Founded taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ______ Developed a theory similar to Darwin’s accept 20 years after. ____1st to state evolutionary change but had the wrong mechanism. Hypothesized that species evolve through use and disuse and through the inheritance of acquired traits. ____This person’s view on life was descent with modification B. Carolus Linnaeus E. Jean-Baptiste de Lamark G. Alfred Wallace 23. Which is the correct Hardy-Weinberg equation? a. P2 +pq + q2=1 F. Charles Darwin b. P2 – 2pq – q2=100 c. P2 + 2pq + q2 =100 d. P2 +2pq + q2 = 1 24. True or False, the Hardy Weinberg equation describes a population that is evolving? a. True b. False 25. P2 and q2 represents a. The frequency of the heterozygote genotype b. The frequency of the alleles c. The frequency of the homozygous genotype 26. Using the Hardy-Weinberg equation with two alleles A and a, the frequency of the a allele is .6. What is the percentage of the population that is heterozygous for this allele? (show calculations) a. .12 b. .4 c. .48 d. .8 27. Genetic drift has a large impact on _________ populations a. Small b. Large 28. Migration tend to _________ difference in allele frequency between populations while _____ genetic diversity within population a. Increase, decrease b. Decrease, increase 29. __________ speciation occurs when some members of a species occupy a habitat that is geographically isolated from other members while ___________ speciation occurs in population that live in the same geographic area. a. Allopatric, sympatric b. Sympatric, allopatric 30. Any Questions?