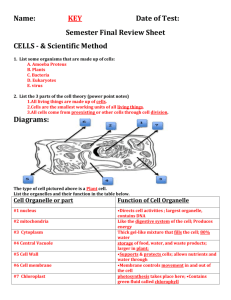
HERE - Shawnee Science
advertisement

1. What term is used to describe two alleles that both call for the non-dominant trait? A. Homozygous recessive B. Heterozygous C. Homozygous dominant D. Carrier E. Genotype 2. What term is used to describe two alleles that call for different traits (like tall and not tall)? A. Homozygous recessive B. Heterozygous C. Homozygous dominant D. Carrier E. Genotype 3. There is a string of nucleic acids that code for something very specific about you. What are these codes called? A. Genotypes B. Phenotypes C. Alleles D. Chromosomes E. Genes 4. There are very specific loci (locations) on a chromosome where codes for traits, like hair color, can be found. What are these locations called? A. Genotypes B. Phenotypes C. Alleles D. Chromosomes E. Genes 5. Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine, and Adenine are the chemicals that code for something important. What are these called? A. Sugar-phosphates B. Nucleic acids C. Genotypes D. Loci 6. How are the chemicals mentioned in question #5 above paired up? A. C = C, T = T, G = G, A = A B. C = T, A = G C. A pairs with all of them and with itself D. G = C, A = T 7. Which enzyme is responsible for separating the two strands of RNA? A. RNA Primase B. Helicase C. Ligase D. Telomeres 8. There is a protective “coating” at the ends of your chromosomes. After replication, the DNA gets shorter and shorter. What is this coating called? A. RNA Primase B. Helicase C. Ligase D. Telomeres 9. There is an enzyme that moves along the lagging strand of DNA that glues the pieces together. What is this enzyme called? A. RNA Primase B. Helicase C. Ligase D. Telomeres 10. This most important enzyme in replication is responsible for matching nucleic acid base pairs and proofreading them. A. RNA Primase B. Helicase C. Ligase D. Telomeres 11. This enzyme is responsible for finding the starting point to begin DNA replication. A. RNA Primase B. Helicase C. Ligase D. Telomeres 12. What does the box (the Punnett Square) look like for a simple cross? A B C 13. What are the odds that an offspring would be tall if you crossed two heterozygous parents (tall is dominant)? A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 75% E. 100% 14. Could two brown haired parents have a blond haired child? A. Yes B. No C. Depends on their ethnicity 15. What would you call a cross like this – Rr x rr. A. Homozygous dominant crossed with heterozygous B. Homozygous recessive crossed with homozygous dominant C. Heterozygous crossed with homozygous recessive D. Heterozygous crossed with homozygous dominant E. Heterozygous crossed with heterozygous 16. Who is the ‘father of modern genetics’? A. Mendel B. Einstein C. Darwin D. Lamarck E. Crick 17-27. Match the description with the type of cross. Your choices for type of cross are below. A. Simple monohybrid B. Co-Dominance D. Incomplete C. Dihybrid E. X-linked (sex-linked) 17. In this cross you can have two phenotypes show up coded from the same allele. 18. These kind of cross results in males who typically get an undesirable trait more often than the female. 19. Possible genotypes to cross might be XNXn. 20. In this cross, you might end up with a 3rd phenotype that is a blend of the other two. Yellow and blue make green, for example. 21. In this type of cross you end up with “this” or “that”, meaning there are only two possible pehnotypes (they are unrelated to gender) 22. In this cross type, you might end up with two linked traits or none because they come as a package deal. 23. Tt x TT? 24. You use two different letters to code for the allele in this type of cross. Write down BOTH answers! 25. This kind of cross is necessary because there are two chromosome that pair up, but they are the only ones that DO NOT code for similar traits. 26. Crossovers rarely happen between two different allele codes in this kind of cross. 27. A third mixture of phenotypes show up in this kind of cross. For example, my dog inherited black coat color from mom and brown coat color from dad and the pup turned out black AND brown! 28. Which genotype expresses the male gender? A. XX B. XY 29. GREEN SPACE! Answer A in the scantron sheet here, but answer this question in the green space. Please make sure to number it so I know what I’m looking at! Thanks! Using a Punnett Square, show the phenotypes of a male and a female who are expecting a kid. 30. Why are males more likely to be colorblind? A. Males are the weaker species and have a harder time defending themselves against the disorder. B. Females have just the one X chromosome, so it is more likely they will get affected because they do not have another chance to get the normal dominant trait. C. Males simply have more alleles so they are more likely to get things like color blindness. D. No one knows quite why males get it more often. 31. What are the odds of a cross between a female who is heterozygous for color vision and a male who is color blind produces a GIRL that is color blind? Seeing color is the dominant trait. A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 75% E. 100% 32. T/F: Female cats cannot be calico. GREEN SPACE! In the green space above, tell me briefly how you know the answer to this question. Thanks! A. True B. False 33. What do you call the alleles that you carry around? For example, what do you call this – Ggmm? A. Genotypes B. Phenotypes C. Alleles D. Chromosomes E. Genes 34. What do you call the expression of your genes? i.e. what you see from the outside. A. Genotypes B. Phenotypes C. Alleles D. Chromosomes E. Genes 35. What do you call someone who has an allele for a disorder but they do not show it? For example, I have the allele for blonde hair but I do not show it. What am I called? A. Genotype B. Phenotype C. Carrier D. Host E. Infiltrator 36. What is the “backbone” of the DNA molecule called (what is it made of?)? A. Nucleic Acids B. RNA C. Polymerase D. Sugar and Phosphate E. Silicon and Iron 37-41. Match the following term with its proper definition. A. Chromatin B. Homologous pairs D. Sister Chromatids C. Tetrad E. Chromosomes 37. These are four copied and partnered condensed DNA strands that bundle together during meiosis. 38. These are long, thin, wispy strands of genetic material that are all stretched out 39. These are two identical copies of DNA pieces 40. These are condensed pieces of DNA that can be dragged around the cell as needed 41. These are similar DNA strands – you get a version of it from mom and the other from dad 42. What would be the genotype of a calico cat? A. XOXO B. XBYO C. XBY D. XOYB E. None of these 43. In an incomplete inheritance, what would the possible genotypes be of a cross between a green plant and a blue plant? Yellow is the third phenotype. A. Green only B. Green and Blue C. Yellow, Blue, and Green D. Yellow and Blue only E. None of the above 44. GREEN SPACE!! Please bubble ‘A’ in for #44. Using a Punnett Square, show how a brindle dog inherit its coat. 45. In a co-dominant inheritance, what are the possible phenotypes of a cross between a flower with blue and white petals with a homozygous blue flower. A. Blue only B. Pale only C. Blue and White only D. Blue/White and Blue only E. Blue/White, White, and Blue 46. What blood type is considered the universal donor? A. BB. ABC. OD. O+ E. A+ 47. What blood type is the universal recipient? A. AB. ABC. O- E. B+ D. O+ 48. What is the + & - after the blood type? A. It refers to the presence of HIV B. It refers to the presence of Hepatitis C. It refers to the presence of the papiloma virus D. It refers to the presence of enhanced blood iron E. It refers to the presence of a protein GREEN SPACE: Why is in important to know this, especially when pregnant? Number this #48 please! 49. What type of blood can be given to someone who is B-? A. B+ B. ABC. O+ D. AE. None of the above GREEN SPACE: Show the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents and offspring in a cross between a parent with AO and BO type blood. 50. What is an antigen? A. It’s anything that fights off foreign substances in your body B. It’s a rare blood type C. It’s an anti-viral medicine you get D. It’s anything that tells your immune system to ‘turn on’ 51. What are the stages of mitosis (in order)? A. PMAT B. TMAP C. PAMT D. TMPA 52. Which two kinds of cells that go through mitosis (mark both that apply!) A. Skin B. Egg C. Sperm D. Muscle 53-57. Match the picture with the proper phase of mitosis. A B D C E 53. Telophase 54. Anaphase 55. Metaphase 56. Prophase 57. Interphase 58. How do the daughter cells genetically compare to the parent after a mitotic division? A. Similar B. Identical C. Nothing alike at all D. Depends on the individual 59. How many chromosomes does the typical human have? A. 2 B. 23 C. 46 D. 92 E. 138 60-65. Match the pictures below with the correct phases of meiosis. A D B C E AB 60. Metaphase II 61. Anaphase II 62. Telophase I 63. Metaphase I 64. Telophase II 65. Anaphase I 66. Which two cells in humans undergo meiosis? A. Skin B. Egg C. Sperm D. Muscle 67. Which phase is skipped in meiosis 2? A. Anaphase B. Metaphase C. Telophase D. Interphase 68. What is the splitting of a cell in to two cells called? A. Telekinesis B. Telophase C. Introphase D. Lysophase E. Cytokinesis 69. What are crossovers? A. When new species are formed B. When genetic material is swapped during meiosis C. When alleles combine and are interpreted D. When nucleic acid sequences are decoded 70. When do crossovers happen? A. During meiosis B. During mitosis C. During conception D. During interphase 71. Why are crossovers significant? A. They allow for greater variation in the population B. They make us smarter C. They create antibodies D. They allow for babies to grow in the womb and for differentiation to occur 72. What is an antibody? A. It’s something that turns your immune system on B. It’s the opposite of a dominant allele C. It’s anything that fights off unwanted things in your body D. It’s a rare disorder carried only by females