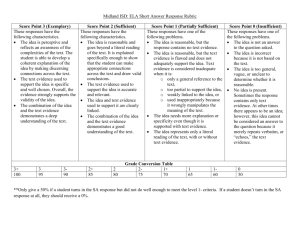
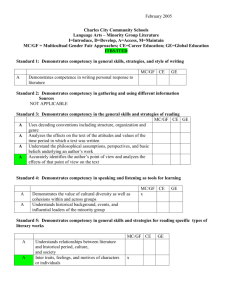
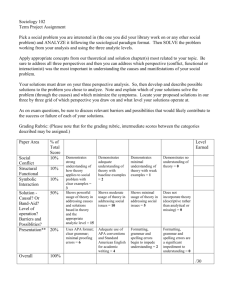
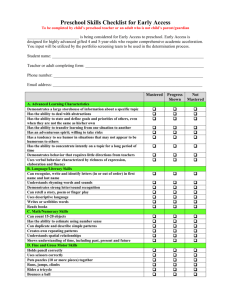
Competency Library - Florida Gulf Coast University
advertisement

FGCU Performance Management Competency Library Florida Gulf Coast University Human Resources, April 2013 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Table of Contents Change Management ........................................ 1 Perspective & Understanding Others ................ 10 Delegation .......................................................... 21 Adaptability.......................................................... 1 Leadership........................................................... 11 Developing Direct Reports and Others.............. 22 Dealing with Ambiguity ....................................... 1 Command Skills .................................................. 11 Directing and Measuring Others ....................... 22 Facilitating Change ............................................... 2 Ethics and Values ............................................... 12 Effective Hiring and Staffing .............................. 23 Gaining Commitment ........................................... 2 Integrity and Trust ............................................. 12 Fairness to Direct Reports ................................. 23 Innovation Management ..................................... 3 Managing Vision and Purpose ........................... 13 Knows the Team ................................................ 24 Stress Tolerance ................................................... 3 Stakeholder Focus .............................................. 13 Managing Through Systems .............................. 24 Communication ................................................... 4 Strategic Agility – Visioning ............................... 14 Motivating Others .............................................. 25 Communication .................................................... 4 Timely Decision Making ..................................... 14 Organizational Know-How ................................. 26 Informing .............................................................. 4 Other ..................................................................... 15 Valuing Diversity ................................................ 27 Listening ............................................................... 5 Action Oriented.................................................. 15 Work Process ..................................................... 28 Persuasiveness ..................................................... 5 Active Learning................................................... 15 Continuous Improvement.................................. 28 Presentation Skills ............................................... 6 Contributes to Team Success ............................. 16 Information Monitoring..................................... 28 Written Communications .................................... 6 Decision Making ................................................. 16 Managing Work/Time Management ................. 29 Interpersonal Relationships ............................ 7 Drive ................................................................... 17 Meeting Leadership ........................................... 29 Approachability .................................................... 7 Follow-Up ........................................................... 17 Meeting Participation ........................................ 29 Boss Relationships ............................................... 7 Ownership/Accountability ................................ 17 Planning and Organizing .................................... 30 Collaboration ....................................................... 7 Technical/Functional Skills and Learning .......... 18 Problem Solving ................................................. 30 Composure ........................................................... 8 Supervision ......................................................... 19 Process Management ........................................ 31 Conflict Management .......................................... 8 Builds Effective Teams ....................................... 19 Interpersonal Know-How .................................... 9 Building Partnerships ......................................... 20 Interpersonal Negotiation ................................... 9 Coaching ............................................................. 20 Peer Relationships ............................................. 10 Confronting Direct Reports................................ 21 Resource Utilization ........................................... 31 Safety Awareness ............................................... 32 Safety Intervention ............................................ 32 Technical/Professional Knowledge and Skills .. 32 1 *Ctrl+ Click on any section in the Table of Contents to jump directly to the page Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Change Management Adaptability Adaptability- Maintains effectiveness when experiencing major changes in work responsibilities or environment; adjusts effectively to work within new work structures, processes, requirements, or cultures; actively seeks information about new work situations; strives to understand rationale and implications for changes in work responsibilities or environment; treats change and new situations as opportunities for learning or growth; identifies the benefits of change, speaks positively about change to others ; does not persist with ineffective behaviors. Over Demonstrates Adaptability- So adaptable that they don’t take a stand on anything; others have lack of trust due to lack of stance; advocates so much change and is so adaptable others are in constant state of upheaval; leaves others feeling unsettled. Under Demonstrates Adaptability- Can’t get anything done until fully settled with new process; doesn’t seek information to understand the whole; may focus only on a few parts of change; doesn’t see the benefit of change; negative to coworkers and infects others; may dig in heels and actively speak out against change; builds alliances against change. Over Demonstrates Dealing with Ambiguity- May move to conclusions without enough data; may fill in gaps by adding things that aren’t there; may frustrate others by not getting specific enough; may undervalue orderly problem solving; may reject precedent and history; may err toward the new and risky at the expense of proven solutions; may over-complicate things. Under Demonstrates Dealing with Ambiguity- May block change; not comfortable with change or uncertainty; may not do well on fuzzy problems with no clear solution or outcome; may prefer more data than others and structure over uncertainty; prefers things tacked down and sure; less efficient and productive under ambiguity; may have a strong need to finish everything; may like to do things the same way time after time. Dealing with Ambiguity Dealing with Ambiguity- Can effectively cope with the process of change; can manage the transitions phase; can shift gears comfortably; can decide and act without having the total picture; isn’t upset when things are up in the air; doesn’t have to finish things before moving on; can comfortably handle risk and uncertainty; can simultaneously manage old and new; has a feel for what’s right. 1 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Facilitating Change- May look to change first, rather than correct errors and resolve problems; may oversimplify change; may not explore repercussions of change adequately, may not plan for resistance to change, may not communicate change to all stake holding parties; thinks everyone accepts change as they do. Under Demonstrates Facilitating Change- May resist change, may try to patch broken systems to prevent change, does not provide opportunities for feedback on current systems or encourage others to think of a better way to do things. Over Demonstrates Gaining Commitment- Whips team into state of frenzy without ensuring understanding; focus on ideas but not action; constantly looking to influence others but fails to follow through and initiate. Under Demonstrates Gaining Commitment- Describes expectations, goals, requests or future states as a mandate; doesn’t understand or value importance of sparking interest; takes a hammer approach; leaves others to flounder if they don’t understand the expectations; takes a sink or swim approach. Facilitating Change Facilitating Change- Encourages boundary breaking; challenges associates to ask “why” until underlying cause is discovered; consistently remains open to ideas offered by others; helps individuals overcome resistance to change; shows empathy with people who feel loss as a result of change; tries to minimize complexities, contradictions and paradoxes; clarifies direction and smooths the process of change. Gaining Commitment Gaining Commitment- Describes expectations, goals, requests, or future states in a way that provides clarity and excites interest; seeks, gives, and summarizes information; ensures situation is understood; presents own ideas; seeks and develops suggestions of others; uses appropriate influence strategies to gain genuine agreement; summarizes outcomes of discussions and establishes next steps if needed. 2 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Innovation ManagementMay err toward the new and reject the old; may prefer creative people and undervalue those less creative; may get too far out in front of others in thinking and planning. Under Demonstrates Innovation Management- Overly focused on own ideas; can’t select from among ideas which would work the best; doesn’t innovate; may not be open to the creative suggestions of others; may be stuck in comfort zone of tasks and methods of doing them; may not understand creativity or the process of innovation; may be a perfectionist avoiding risk and fearing failures and mistakes; may not use experiments to learn and improve, and may block the innovations of others. Over Demonstrates Stress Tolerance- May not take “crunch time” situations seriously; may not put extra effort into achieving goals by established deadlines; may not stay focused on the task at hand; may not consider downstream effects of incomplete work. Under Demonstrates Stress Tolerance- May act frantic or chaotic in times of stress; may create drama in the office; may take stress out on others; may have unreasonable expectations of others in order to get work done; may work to a point of excess and become physically unwell. Innovation Management Innovation Management- Is good at bringing the ideas of others to fruition; has good judgment about which creative ideas and improved processes and suggestions will work; can facilitate effective brainstorming; can project how potential ideas may play out; easily makes connections among previously unrelated ideas. Stress Tolerance Stress Tolerance- Stays focused on work tasks and productively uses time and energy under stress; presents positive disposition and maintains constructive interpersonal relationships under stress; develops appropriate strategies as needed to alter conditions that create stress and to sustain physical and mental health. 3 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Communication Communication Communication- Clearly conveys information and ideas through a variety of media to individuals or groups in a manner that engages the audience and helps them understand and retain the message; clarifies purpose and importance; stresses major points; follows a logical sequence; seeks input; checks understanding. Over Demonstrates CommunicationCommunicates so much that people get annoyed, takes too much time; fails to leave out the small or trivial; unable to discern communication needs of others; thinks everything holds the same importance; unable to emphasize main points; engages audience but leaves message unclear; may share inflammatory information without care. Under Demonstrates Communication- Fails to communicate even fundamental information; keeps people in the dark; hoards information; may convey essential message but fails to fill in the details to broaden understanding; may not share information with all stakeholders; fails to engage audience; may not adapt communication to different learning styles; may not share message through multiple channels. Over Demonstrates Informing- May provide too much information; may upset people by giving them information they can’t handle or preliminary information that turns out not to be true; guesses at outcomes and may waste the time of others without understanding proper direction; shares confidential information with inappropriate parties. Under Demonstrates Informing- Not a consistent communicator; tells too little or too much or too late; may be unclear, may inform some better than others; may not think through who needs to know by when; doesn’t understand the data needs of others; may inform but lack follow-through; may either hoard information or not see informing as important; may only have one method—written or oral or email. Informing Informing- Provides the information people need to know to do their jobs and to feel good about being a member of the team, unit, and/or the organization; provides individuals information so that they can make accurate decisions; is timely with information; conveys information regarding the strategy and direction of the organization. 4 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Listening- May spend too much time listening; may avoid necessary action; others may confuse listening with agreement. Under Demonstrates Listening- Doesn’t listen well; cuts people off and finishes their sentences if they hesitate; interrupts to make a pronouncement or render a solution or decision; doesn’t learn much from interactions with others; appears not to listen or is too busy constructing a response; misses the point others are trying to make; may appear arrogant, impatient or uninterested; may listen to some groups or people and not to others; inaccurate in restating the case of others; doesn’t make eye contact; doesn’t value listening. Over Demonstrates Persuasiveness- May build confidence in ideas without information or understanding; may leverage support factors for own personal benefit; may use derisive or inappropriate techniques to gain agreement; may rely on relationships rather than actual benefits to get others onboard with ideas. Under Demonstrates Persuasiveness- May hesitate to overcome objections with facts and supporting evidence; may not seem confident or positive about ideas; may refuse to build rapport in order to establish effective relationships; may refuse to compromise or collaborate to win support. Listening Listening- Practices attentive and active listening; has the patience to hear people out; can accurately restate the opinions of others even when he/she disagrees; understands other’s points of view; people feel heard. Persuasiveness Persuasiveness- Seeks information to understand situations, needs, and desired potential benefits; develops approaches that best position services or ideas; leverages supportive factors, overcomes or minimizes barriers, and addresses unique needs and preferences of key decision makers; makes favorable impressions by interacting with prospects in a manner that builds effective relationships; presents services of ideas in a manner that clearly shows how they would meet needs and provide benefits; builds confidence in services or ideas; uses appropriate techniques to move others to action or to gain agreement. 5 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Presentation Skills- May try to win with style and presentation skills over fact and substance; may be able to wing it and dance without really being prepared; may be able to sell things that shouldn’t be sold; may lack follow through beyond initial presentation; lack of substance may lead to lack of trust. Under Demonstrates Presentation Skills- Not a skilled presenter in varying situations; may be shy; may be disorganized, presentations lack focus; may have a flat or grating style; doesn’t listen to audience; may have personal idiosyncrasies and habits that get in the way; may be unprepared for or unable to handle tough questions; may not be able to incorporate in-the-moment feedback; may always present the same way, not adjusting to audiences; may lose his/her cool during hot debate; may be nervous, even scared when speaking. Over Demonstrates Written CommunicationsMay invest too much time crafting communications; may too often try for perfection when something less would do the job; may be overly critical of the written work of others. Under Demonstrates Written Communications- Not a clear communicator in writing; may be hard to tell what the point is; may be too wordy or too terse or have grammar/usage problems; may not construct a logical argument well; may not adjust to different audiences; may have a single style of writing. Presentation Skills Presentation Skills- Is effective in a variety of formal presentation settings: one-on-one, small and large groups, with peers, direct reports, and bosses; is effective both inside and outside the organization on both cool data and hot and controversial topics; commands attention and can manage group process during the presentation; can change tactics midstream when something isn’t working; can inspire others to action. Written Communications Written Communications- Is able to write clearly and succinctly in a variety of communication setting and styles; can get messages across that have the desired effect; can convince people through writing. 6 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Interpersonal Relationships Approachability Approachability- Is easy to approach and talk to; spends the extra effort to put others at ease; can be warm, pleasant, and gracious; is sensitive to and patient with the interpersonal anxieties of others; builds rapport well; is a good listener; is an early knower, getting informal and incomplete information in time to do something about it. Over Demonstrates Approachability- May waste too much time building rapport in meetings; may be misinterpreted as easy-going or easy to influence; may have too strong a desire to be liked; may avoid necessary negative or unpleasant transactions; may try to smooth over real issues and problems; may waste time as the unofficial office factotum or “helper”. Under Demonstrates Approachability- Distant, not easy to be around; not comfortable with first contacts; may be shy, cool or a person of few words; doesn’t reveal much, hard to know what he/she is really like; doesn’t build rapport, may be a “let’s get on with it” type; may be a poor listener or appear uninterested; may not pick up on social cues that others would recognize; may be tense; transactions doesn’t go smoothly. Over Demonstrates Boss Relationships- May be over dependent on bosses and high status figures for advice and counsel; may shut out other sources of feedback and learning; may take direction only from immediate supervisor, disregarding other team members; may pick the wrong boss to model. Under Demonstrates Boss Relationships- Not comfortable with bosses; may be tense in boss’s presence; may not be open to coaching or direction from bosses; problems dealing comfortably with authority; may not be comfortable approaching boss with issues effecting productivity or to request resources; poor boss relationships get in the way of working productively. Over Demonstrates Collaboration- Develops so many collaborative relationships that nothing gets done; helps others to the point of neglecting own work; sacrifices own goals in order to help others. Under Demonstrates Collaboration-Fails to see the value of working with others; overly focused on own goals; sacrifices organization goals to achieve own; self-focused. Boss Relationships Boss Relationships- Responds and relates well to bosses; would work harder for a good boss; is open to learning from bosses who are good coaches and who provide latitude; likes to learn from those who have been there before; easy to challenge and develop; is comfortably coachable; views feedback as an opportunity for growth. Collaboration Collaboration- Works effectively and cooperatively with others; establishes and maintains good working relationships; places higher priority on team or organizational goals than on own goals; offers to help others achieve goals. 7 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Composure- May not show appropriate emotion; may be seen as cold and uncaring; may seem flat in situations where others show feelings; may be easily misinterpreted; may not be able to relate well to those whose actions and decisions are based more on feelings than on thinking. Under Demonstrates Composure- Gets rattled and loses cool under pressure and stress; may blow up, say things he/she shouldn’t; gets easily overwhelmed and becomes emotional, defensive or withdrawn; may be defensive and sensitive to criticism; may be cynical or moody; may be knocked off balance by surprises and get easily rattled; may contribute to others losing composure or being unsettled; may let anger, frustration and anxiety show. Over Demonstrates Conflict Management- May be seen as overly aggressive and assertive; may get in the middle of the problems of others; may drive for a solution before others are ready; may have a chilling effect on open debate; may spend too much time with obstinate people and unsolvable problems. Under Demonstrates Conflict Management- Avoids conflict in situations and with people; may accommodate, want everyone to get along; may get upset as a reaction to conflict, takes it personally; can’t operate under conflict long enough to get a good result; gives in and says yes too soon; gets into conflict by accident; doesn’t see it coming; will let things fester rather than dealing with them directly; will try to wait long enough for it to go away; may be excessively competitive and have to win every dispute; sets up a win-lose and takes sides rather than working through; feeds conflict by refusing to participate in solutions. Composure Composure- Is cool under pressure; does not become defensive or irritated when times are tough; is considered professionally mature; can be counted on to hold things together during tough times; can handle stress; is not knocked off balance by the unexpected; doesn’t show frustration when resisted or blocked; is a settling influence in a crisis. Conflict Management Conflict Management- Steps up to conflicts, seeing them as opportunities; reads situations quickly; good at focused listening; can negotiate agreements and settle disputes equitably; can find common ground and get cooperation with minimum noise; looks for win-win solutions. 8 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Interpersonal Know-HowMay be able to get by with smooth interpersonal skills; may spend too much time building networks and glad-handing; may not be taken as substantive by some; may not be a credible take-charge leader when that’s necessary; may have some trouble and freeze when facing serious conflict; may manage up too much; may be seen as too political and ambitious; may spend too much time with more senior managers, parrot their positions, overestimate the meaning and usefulness of the relationships; career may be too dependent on champions; may be too free with confidential information. Under Demonstrates Interpersonal Know-How- Lacks self-awareness; doesn’t relate smoothly to a variety of people; may not build relationships easily—may lack approachability or good listening skills; doesn’t take the time to build rapport; may be too raw and direct at times; may try to build rapport inappropriately; may be excessively work oriented or intense; may be impatient to get on with the agenda; judgmental or arrogant toward others; may not read others well; may freeze or panic in the face of conflict, attack or criticism; may be shy or lack confidence around others. Lacks self-confidence in front of more senior people; may appear nervous and tense, not at his/her best; may lose composure or get rattled when questioned by executives; doesn’t know how to influence or impress more senior managers ;may not understand what executive are looking for; may say or do things that don’t fit the situation. Over Demonstrates Interpersonal NegotiationMay leave people-damage in his/her wake; may walk over people’s feelings; may always need to win; may hang on to a position too long; may become overly accommodating and be reluctant to walk away; may need to smooth over everything; may take too long to get things decided. Under Demonstrates Interpersonal Negotiation- May have to win every battle or gives away too much to get to agreement; doesn’t come away with much; may use ineffective tactics—too hard or too soft; poor conflict manager; trouble dealing with attack, contention or nonnegotiable points; may hold back and be afraid to take tough stands; poor listener; may not seek or know how to find common ground; may be too noisy and do too much damage to relationships; may not know how to be diplomatic, direct and polite. 9 Interpersonal Know-How Interpersonal Know-How- Relates well to all kinds of people—up, down, and sideways, inside and outside the organization; builds appropriate rapport; builds constructive and effective relationships; uses diplomacy and tact; can defuse even high tension situations comfortably; can deal comfortably with more senior managers; can present to more senior managers without undue tension and nervousness; understands how senior managers think and work; can determine the best way to get things done with them by talking their language and responding to their needs; can craft approaches likely to be seen as appropriate and positive. Interpersonal Negotiation Interpersonal Negotiation- Can negotiate skillfully in tough situations with both internal and external groups; can settle differences for win-win outcomes; can win concessions without damaging relationships; can be both direct and forceful as well as diplomatic; gains trust quickly of other parties to the negotiations; has a good sense of timing; uses listening to enhance outcome. Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Peer Relationships- May touch base with too many peers; may be too accommodating; may invest too much in peer relationships at the expense of others; may be uncomfortable with relationships where everyone’s not equal; may share sensitive information inappropriately just to solidify a relationship; may get in trouble by being too candid with peers; may be seen by others as someone who continually tries to seek the favor of and do anything to please higher ups. Under Demonstrates Peer Relationships- Has difficulty with peer boundaries; doesn’t strike fair bargains or understand what peers expect or need; not open to negotiation; a loner, not seen as a team player, doesn’t have the greater good in mind; may withhold resources from the other team members; may not respect their functions or disciplines and somehow communicates that; may be very competitive, play and maneuver for advantage and withhold information; may have a chilling effect on the entire unit because he/she won’t play; may deal with peer conflict noisily or uncooperatively. Over Demonstrates Perspective & Understanding Others- Might have trouble concentrating on the present; may leave others behind when he/she speculates on the broad view of an issue; may not set practical priorities; may always be reaching for too much and/or the ideal; may see connections that aren’t there. Under Demonstrates Perspective & Understanding Others- Is narrow and parochial; has narrow views of issues and challenges; doesn’t have far-ranging interests, not well-read; background may be narrow; isn’t good at running “what if” scenarios; lacks interest in the future and how social and political events affect the organization; won’t be a good strategist or visionary; a here-and-now person who is often surprised by unexpected change; may be a single function/profession/technical area/skill person. Peer Relationships Peer Relationships- Can quickly find common ground and solve problems for the good of all; can represent his/her own interests and yet be fair to other groups; can solve problems with peers with a minimum of drama; is seen as a team player and is cooperative; easily gains and maintains trust and support of peers; encourages collaboration; can be candid with peers. Perspective & Understanding Others Perspective & Understanding Others- Looks toward the broadest possible view of an issue/challenge whether a work process or interpersonal concern; can easily pose future scenarios; can think globally; can discuss multiple aspects and impacts of issues and project them into the future. Understands economic and social impact decisions. 10 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Leadership Command Skills Command Skills- Relishes leading; takes unpopular stands if necessary; encourages direct and tough debate but isn’t afraid to end it and move on; is looked to for direction in a crisis; faces adversity head on; energized by tough challenges; able to keep team focused in tough times; knows when to address issues; provides current, direct, complete and “actionable” positive and corrective feedback to others; lets people know where they stand; faces up to people problems on any person or situation (not including direct reports) quickly and directly; is not afraid to take negative action when necessary; is seen as having executive presence. Over Demonstrates Command Skills-May not be a team player; may not be tolerant of other people’s ways of doing things; may choose to strongly lead when other more team-based tactics would do as well or better; may not develop other leaders; may become controversial and be rejected by others; may look to take credit for work of others; may be overly critical may be too direct and heavy-handed when providing feedback or addressing issues; may provide too much negative and too little positive feedback; may put too much emphasis on the dark side; may fight too many battles. Under Demonstrates Command Skills-More comfortable following; may avoid conflict and crises, be unwilling to take the heat, have problems with taking a tough stand; too concerned about what others may say or think; may worry too much about being liked, correct or above criticism; may be conflict shy or lack perseverance; may not be cool under pressure; may not display a sense of urgency; doesn’t take tough stands with others; holds back in tough feedback situations; doesn’t know how to present a tough position; knows but doesn’t disclose; doesn’t step up to issues; intimidated by others in power; hangs back and lets other take the lead; is a conflict avoider unwilling to take the heat of controversy; afraid to be wrong, get in a win/lose situation, or make a tough personnel call. 11 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Ethics and Values-May go to battle based on beliefs and values when not appropriate; may be overly sensitive to situations he/she sees as litmus test of principles, values, and beliefs; may be seen as stubborn and insensitive to the need for change and compromise; may be overly critical of those who do not hold the same values; may use ethics statements to close off discussion. Under Demonstrates Ethics and Values-Values may be out of sync with those of the organization; blind to the values of others; makes others uncomfortable; may not think about own values much and have no idea how he/she comes across; behavior may vary too much across situations; values may be seen as too self-serving; he/she doesn’t walk the talk; says one thing, does another. Over Demonstrates Integrity and Trust- May be too direct at times, which may catch people off guard and make them uncomfortable; may push openness and honesty to the point of being disruptive; may be so “only the facts” driven as to omit drawing reasonable conclusions, rendering opinions, or fixing blame, even when it’s reasonable. Under Demonstrates Integrity and Trust- Is not widely trusted; may hedge or not take a stand; may treat others differently or indifferently at times; may not walk the talk and be seen as inconsistent; may have trouble keeping confidences and talks out of school; makes promises that can’t be kept; may lack follow-through and causes problems for others; blames others for own mistakes; seen as just out for him/herself; causes team dysfunction by discussing performance issues or problems with others on the team rather than responsible parties. Ethics and Values Ethics and Values- Adheres to an appropriate and effective set of core values and beliefs during both good and bad times; acts in line with those values; practices what he/she preaches; understands and acknowledges personal core values and how they affect our work; understand relationship of values to larger context of public employee setting; seen by others as a role model. Integrity and Trust Integrity and Trust- Is widely trusted; is seen as a direct, truthful individual; can present the unvarnished truth in an appropriate and helpful manner; keeps confidences; admits mistakes; doesn’t operate with a hidden agenda; doesn’t play games. 12 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Managing Vision and Purpose- May leave people behind; may lack patience with those who don’t understand or share his/her vision and sense of purpose; may lack appropriate detail-orientation and concern for administrative routine; may lack follow-through on the day-to-day tasks. Under Demonstrates Managing Vision and PurposeCan’t communicate or sell a vision; not a good presenter; can’t persuade; uncomfortable speculating on the unknown future; isn’t charismatic or passionate enough to excite and energize others; tries to force vision on others; can’t simplify enough to help people understand complex strategy; may not understand how change happens; doesn’t act like he/she really believes in the vision; more comfortable in the present moment. Over Demonstrates Stakeholder Focus- May be overly responsive to stakeholder demands; may be too willing to change established processes and timetables to respond to unreasonable stakeholder requests; may make too many exceptions and not form consistent policies, practices and processes for others to learn and follow; sticks so close to current stakeholder needs that breakthroughs are missed. Under Demonstrates Stakeholder Focus- Doesn’t think of stakeholders first; may think he/she already knows what they need; may focus on internal operations and get blindsided by stakeholder problems; may not make the first move—won’t meet and get to know stakeholders; uncomfortable with new people contacts; may be unwilling to handle criticisms, complaints and special requests; may not listen well to stakeholders, may be defensive; may not make the time for stakeholder contact. Managing Vision and Purpose Managing Vision and Purpose- Communicates a compelling and inspired vision or sense of core purpose; talks beyond today; talks about possibilities; is optimistic; creates mileposts and symbols to rally support behind the vision; makes the vision sharable by everyone; can inspire and motivate entire units or organizations. Stakeholder Focus Stakeholder Focus- Dedicated to meeting the reasonable expectations and requirements of internal and external stakeholders; gets first-hand stakeholder information and uses it for improvement; acts with stakeholders in mind; establishes and maintains effective relationships with stakeholders and gains their trust and respect. 13 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Strategic Agility – VisioningMay be seen as too theoretical; may not be tolerant of or have patience with day-to-day details; may over-complicate plans; may not be able to communicate with tactical or less complex people; wants to be seen as the expert. Under Demonstrates Strategic Agility – VisioningDoesn’t think or talk strategy; can’t put together a compelling strategic plan; more comfortable in the dayto-day activity; lacks the perspective to pull together varying elements into a coherent strategic view; can’t weave a vision of the future; may reject the usefulness of strategy, considering it pie in the sky; may have narrow experience and not be knowledgeable of business and world events; may try to simplify too much or be very tactical; may lack the disciplined thought processes necessary to construct a strategic view. Over Demonstrates Timely Decision Making - May jump to conclusions and take action before reasonable consideration of the information; may get caught up in deciding for its own sake; may have a chilling effect on getting everyone’s input before deciding; might be considered impulsive and impatient; might have some trouble and freeze on issues and problems that are close calls; may make decisions quickly to avoid debate and personal discomfort. Under Demonstrates Timely Decision Making - Slow to decide or to declare; conservative and cautious; may procrastinate, seek more information to build confidence and avoid risk; may be a perfectionist, needing to be right, protect strongly against criticism; may be disorganized and always scrambling to meet decision deadlines; may be slow to make decisions on more complex issues. Strategic Agility – Visioning Strategic Agility – Visioning- Sees ahead clearly; can anticipate future consequences and trends accurately; has broad knowledge and perspective; is future oriented; can articulate a clear picture of the future; can create competitive and breakthrough strategies and plans. Can adapt strategies and initiatives within challenging political environments. Timely Decision Making Timely Decision Making - Makes decisions in a timely manner, sometimes with incomplete information and under tight deadlines and pressure; able to make a quick decision with needs of organization as whole in mind; understands how decision impacts organization both positive and negatives; makes decisions that support strategies, mission and vision of the organization. 14 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Other Action Oriented Action Oriented- Enjoys working hard; is action oriented and full of energy for the things he/she sees as challenging; not fearful of acting with a minimum of planning seizes more opportunities than others; a prudent risk-taker. Over Demonstrates Action Oriented- May be a workaholic; may push solutions before adequate analysis; may be non-strategic; may over manage to get things done too quickly; may have personal and family problems due to disinterest and neglect; may not attend to important but nonchallenging duties and tasks; may ignore personal life, burn out; may exhaust team members by expecting them to work at accelerated pace. Under Demonstrates Action Oriented- Slow to act on an opportunity; may be overly methodical, a perfectionist, or risk averse; may procrastinate; may not set very challenging goals; may lack confidence to act; may know what to do but hesitates to do it; may not be motivated; may be bored with the work or burned out. Over Demonstrates Active Learning- May leave others behind; may frustrate others with his/her need for change; may tend to change things too often; people may interpret openness as indecisiveness or being wishy washy; may seek out change for the sake of change regardless of the situation; may not be good at routine administration or unchallenging tasks or jobs. Under Demonstrates Active Learning- Not versatile in learning to deal with first-time or unusual problems; may not analyze problems carefully or search for multiple clues and parallels; may be afraid to take a chance on the unknown; learns new things slowly; may be stuck in historical, tried-and-true methods; uncomfortable with ambiguity and quick to jump to a solution; doesn’t look under rocks, just sticks to the obvious, looks for the simplest explanation too soon; gives up too soon and accepts a marginal solution; functions on the surface; doesn’t, go deep; may block or cut-off good ideas by ending discussions too soon; impatient with anything new. Active Learning Active Learning- Learns quickly when facing new problems; a relentless and versatile learner; open to change; analyzes both successes and failures for clues to improvement; experiments and will try anything to find solutions; enjoys the challenge of unfamiliar tasks; quickly grasps the essence and the underlying structure. 15 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Contributes to Team SuccessAs proponent for team appears to be controlling; puts pressure on others to achieve team goals without consideration for individual goal accomplishment; sets team expectations and guidelines too high; makes others uncomfortable with high level of personal commitment to team; assumes everyone on team has same level of contribution and same value. Under Demonstrates Contributes to Team SuccessMakes few, if any, suggestions for achieving team goals; appears disinterested in team accomplishments; doesn’t listen or involve others in decisions or actions; fails to see effect of individual differences and talents. Over Demonstrates Decision Making- Collects so much information it becomes invaluable in decision making; stays too long in information gathering mode; information gathering becomes safety zone; uses only one source of information.; makes decisions too quickly. Under Demonstrates Decision Making- Refers all decisions to higher-ups; won’t make any decisions; lacks clear decision criteria; doesn’t obtain buy-in. Contributes to Team Success Contributes to Team Success- Makes procedural or process suggestions for achieving team goals or performing team functions; provides necessary resources or helps to remove obstacles to help the team accomplish its goals; listens to and fully involves others in team decisions and actions; values and uses individual differences and talents; shares important or relevant information with the team; adheres to the team’s expectations and guidelines; fulfills team responsibilities; demonstrates personal commitment to the team. Decision Making Decision Making- Recognizes issues, problems, or opportunities and determines whether action is needed; identifies the need for and collects information to better understand issues, problems, and opportunities, integrates information from a variety of sources; detects trends, associations, and cause-effect relationships; creates relevant options for addressing problems and achieving desired outcomes; formulates clear decision criteria; evaluates options by considering implications and consequences; includes others in the decision-making process as warranted to obtain good information, makes the most appropriate decisions, and ensures buy-in and understanding of the resulting decisions. 16 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Drive- May stick to efforts beyond reason in the face of overwhelming odds and evidence to the contrary; may be seen as stubborn and unyielding; may not set appropriate priorities; may find it difficult to change course; may confuse personal have-to-do’s with what most needs to be done. Under Demonstrates Drive- Gives up too soon or moves on to something that’s going better; doesn’t push hard enough to get things done; doesn’t go back with different strategies for the third and fourth try; may take rejection too personally; may hesitate to push when met with conflict, disagreement or attacks; may agree too early just to get it over with; may compromise for less than the original goal or objective; may simply not want to take charge and be out front; may not show a sense of urgency to finish longstanding projects. Over Demonstrates Follow-Up- Follows-up to the point of micromanagement; doesn’t give people a chance before inquiring about progress; asks so many questions it gets in the way; constantly asking for feedback; everything is urgent. Under Demonstrates Follow-Up- No sense of urgency or timeliness; develops no milestones; doesn’t anticipate results or ask questions; conveys a laissez-faire attitude. Over Demonstrates Ownership/AccountabilityMay be a loner and not a good team player or team builder; may not give appropriate credit to others; may be seen as too self-centered; may not wear well over time; may cling too tightly to their projects and resist productive change; may become personally offended when given unsolicited feedback; may not be effective if reassigned to another project. Under Demonstrates Ownership/Accountability-Isn’t comfortable going it alone; prefers to be in the background; may prefer to be one of many or be part of a team; doesn’t take the lead on unpopular standards; doesn’t take on controversial issues by him/herself; may avoid and shrink from dispute and conflict; may not have passion, may be burned out; prefers not to know the details or have deep knowledge of projects and deflects responsibility for outcomes on other team members. Drive Drive- Pursues everything with energy, drive and a need to finish; seldom gives up before finishing, especially in the face of resistance or setbacks; knows when to quit. Follow-Up Follow-Up- Builds due dates into assignments and task delegation; effectively communicates milestones and expected results; asks questions to obtain relevant information; convenes meetings review progress and share information; gets feedback on results from those directly involved. Ownership/Accountability Ownership/Accountability- Doesn’t shirk personal responsibility; can be counted on when times are tough; willing to be the only champion for an idea or position; is comfortable working alone on a tough assignment. 17 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Technical/Functional Skills and Learning- May be seen as too narrow; may overdevelop or depend upon technical and functional knowledge and skills at the expense of personal, interpersonal and managerial skills; may use deep technical knowledge and skills to avoid ambiguity and interpersonal contact; may learn but not act; may overdo learning at the expense of using it; may be seen as too academic; may not relate well to those who can’t catch on as quickly. Under Demonstrates Technical/Functional Skills and Learning- Not up to functional or technical proficiency; makes technical/functional errors; judgment and decision making marginal because of lack of knowledge; may be stuck in past skills and technologies; may be inexperienced, new to the area, or lack interest in it; lack of detail orientation to go deep; may not make the time to learn; doesn’t learn new technical skills readily; is among the last to learn or adopt new technology; may be stuck on past technologies and resist switching to new ones; may be intimidated by technology; may lack experience or exposure with new technologies; may not be interested in things technical or areas involving lots of detail; may not know how to or may reject using others to learn new technologies. Technical/Functional Skills and Learning Technical/Functional Skills and Learning- Has the functional and technical knowledge and skills to do the job at a high level of accomplishment; picks up on technical/functional things quickly; can learn new skills and knowledge; is good learning new technical or functional information; stays on top of trends, like internet technology. 18 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Supervision Builds Effective Teams Builds Effective Teams- Creates strong morale and spirit in his/her team; defines effective outcomes, expectations, and results; fosters open dialogue; lets people finish and be responsible for their work; defines success in terms of the whole team; creates a feeling of belonging in the team; holds each member accountable for team contributions and success; selects appropriate people for teams as needed; understands different roles needed for team development. Over Demonstrates Builds Effective Teams- May not treat others as unique individuals; may slow down reasonable process by having everything open for debate; may go too far in not hurting people’s feelings and not making tough decisions; may not develop individual leaders; might not provide take-charge leadership during tough times. Under Demonstrates Builds Effective Teams- Doesn’t assemble, build or manage in a team fashion; manages people on a one-to-one basis; doesn’t create a common mindset or common challenge; rewards and compliments individuals not the team; may not hold many team meetings; doesn’t create any synergies in the team; everyone works on his/her own projects; doesn’t manage in a way that builds team morale or energy; doesn’t have the skills or interest to build a team; may be very action and control oriented and won’t trust a team to perform. 19 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Building Partnerships- Wants partners to do all the work; builds so many partnerships that true area of responsibility gets lost; overly concerned with effect of work on partners without seeing effect on own team; may spend more time managing team dynamics than achieving goals. Under Demonstrates Building Partnerships- Territorial; doesn’t build partnerships or see value of working together; can’t define true area of responsibility; puts it all on others; places higher priority on own work than organization’s goals; may be unwilling to assist others achieve their goals; may not consider downstream effects of decisions. Over Demonstrates Coaching- Creates overreliance on coaching for others; wastes time by including everyone even when there is no reason for inclusion; builds dependency; provides too much feedback to the point of causing doubt; may give advice in a condescending way instead of instructional or supportive coaching. Under Demonstrates Coaching- Fails to clarify behaviors; is a poor role model; thinks criticism is coaching; uses coaching as an excuse for micromanagement; fails to enable others; uses a “do as I say” approach; may not include the opportunity for employee feedback in coaching; may wait to provide feedback until information is no longer useful . Building Partnerships Building Partnerships- Builds effective working relationships with other departments. Exchanges information with potential partner areas to clarify benefits and potential problems; collaboratively determines expectations so needs of both can be met; places higher priority on organization’s goals than on own area’s goals; anticipates effects of own area’s actions and decisions on partners; influences others to support partnership objectives. Coaching Coaching- Clarifies expected behaviors, knowledge, and level of proficiency by seeking and giving information and checking for understanding; provides instruction, positive models, and opportunities for observation in order to help others develop skills; encourages questions to ensure understanding; gives timely, appropriate feedback on performance; reinforces efforts and progress; establishes good interpersonal relationships by helping people feel valued, appreciated, and included in discussions (enhances self-esteem, empathizes, involves, discloses, supports). 20 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Confronting Direct ReportsMay be too quick to act on problem direct reports; may not put enough developmental effort toward the problem; may expect turnarounds in too short a time; may expect miracles; does not negotiate steps for change or managed improvement. Under Demonstrates Confronting Direct Reports- Not comfortable delivering negative messages to direct reports; procrastinates and avoids problems until forced to act; may not communicate clear standards or provide much feedback; lets problems fester hoping they will go away; may give in too soon to excuses; may give people too many chances; can’t pull the trigger even when all else has failed; has low standards or plays favorites. Over Demonstrates Delegation- May over delegate without providing enough direction or help; may have unrealistic expectations for direct reports and others, or may over structure tasks and decisions before delegating them to the point of limiting individual initiative; may not do enough of the work him/herself. Under Demonstrates Delegation- Doesn’t believe in or trust delegation; lacks trust and respect in the talent of direct reports and others; does most things by him/herself or hoards, keeps the good stuff for him/herself; doesn’t want or know how to empower others; may delegate but micromanages and looks over shoulders; might delegate but not pass on the authority; may lack a plan of how to work through others; may just throw tasks at people; doesn’t communicate the bigger picture. Confronting Direct Reports Confronting Direct Reports- Deals with problem direct reports firmly and in a timely manner; doesn’t allow problems to fester; regularly reviews performance and holds timely discussions; can make unpopular decisions when all other efforts fail; deals effectively with troublemakers. Delegation Delegation- Clearly and comfortably delegates both routine and important tasks and decisions including developmental and stretch assignments; broadly shares both responsibility and accountability; tends to trust people to perform; lets direct reports and others finish their own work; understands skill levels of subordinates. 21 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Developing Direct Reports and Others- May concentrate on the development of a few at the expense of many; may create work inequities as challenging assignments are parceled out; may be overly optimistic about how much people can grow; adapts self to individuals needs and stages of direct reports; may expect overnight results; overuses good people and may wear them out. Under Demonstrates Developing Direct Reports and Others- Not a people builder; very results driven and tactical; no time for long-term development; doesn’t see long-term development as his/her job; plays it safe— can’t or doesn’t assign stretching work; thinks development is going to a course—doesn’t know how development really happens; may not know the aspirations of people, may not hold career discussions or provide coaching, may not push people to take their development seriously; may prefer to select for talent rather than develop it; doesn’t understand development takes time; manages day-to-day. Over Demonstrates Directing and Measuring Others-Is seen as overly controlling; may have a chilling effect on others, discouraging input and ideas, intolerant of disagreements; may only delegate pieces and not share the larger picture; may be overly directive and stifle creativity and initiative; may look over people’s shoulders; may prescribe too much and not empower people; edits the work of others without providing developmental feedback; just wants their own stamp on the work. Under Demonstrates Directing and Measuring OthersUnclear or cryptic communicator to direct reports; doesn’t set goals, targets, mileposts and objectives; not purposeful in giving out work—just gives out tasks; mostly tells; doesn’t listen much; plays favorites and is tough on others; may be too impatient to structure work for others; doesn’t delegate well; doesn’t take the time to manage; may lack interest in managing and be more eager to work on own assignments; doesn’t use goals and objectives to manage self or others; not orderly in assigning and measuring work; isn’t clear about who is responsible for what; may be disorganized, just throw tasks at people, or lack goals or priorities; may manage time poorly and not get around to managing in an orderly way; doesn’t provide work-in-progress feedback; doesn’t set up benchmarks and ways for people to measure themselves. Developing Direct Reports and Others Developing Direct Reports and OthersUnderstands and responds to needs of direct reports; understands developmental stages of direct reports and adapts to those needs; is a people builder; provides challenging and stretching tasks and assignments; holds frequent development discussions; is aware of each person’s career goals; constructs realistic development plans and executes them; pushes people to accept developmental moves; will take on those who need help and further development. Directing and Measuring Others Directing and Measuring Others- Is good at establishing clear directions; sets stretch objectives; distributes the workload appropriately; lays out work in a well-planned and organized manner; maintains two-way dialogue with others on work and results; brings out the best in people; is a clear communicator. Clearly assigns responsibility for task and decisions; sets clear objectives and measures; monitors process, progress, and results; designs feedback loops into work; uses the talents of all staff members; involves everyone; is able to assist people in feeling part of larger whole and see how their work fits in. 22 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Effective Hiring and StaffingMay select on surface characteristics; may assemble a team of individual performers who aren’t good team players; may prefer currently talented people who aren’t broad enough for further growth; may be too quick to replace rather than work with a person; may be hypercritical of others; takes small pieces of interview information out of context and magnifies it; may be unwilling to alter an initial judgment about others; may not look for or be open to further evidence; may miss on slow starters and quiet and less expressive people. Under Demonstrates Effective Hiring and StaffingDoesn’t have a good track record in hiring and/or staffing; may clone him/herself or focus on one or two preferred characteristics; may look narrowly for people who are similar to him/her; may play it safe with selections; doesn’t value diversity; may not know what competence looks like, lack criteria, or assume he/she just knows; may lack the patience to wait for a better candidate; isn’t accurate in his/her impressions of people; does not evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of others well; biases and stereotyping may play too much in his/her appraisals; may have simplistic models of people; may make instant judgments on almost no data; doesn’t change after the initial appraisal; his/her estimates and projections of what people will do in certain circumstances turns out to be wrong; may be such a poor listener to and observer of others that he/she really doesn’t know what they’re like; doesn’t learn or listen to others to understand the job requirements, just matches up words on a resume. Over Demonstrates Fairness to Direct ReportsMay spend too much time pleasing everyone; may worry about distributing the work evenly and not using, challenging, or developing the best; his/her need to be fair may mask real problems and differences. Under Demonstrates Fairness to Direct Reports- Is not equitable toward direct reports; doesn’t listen to direct reports; concerns and needs; may not read people’s needs well and not be able to tell how they are responding to his/her treatment; hides or keeps things from his/her people they have a right to know; may be inconsistent and play favorites; may not think about it or be too busy to pay attention to equity; may bucket people into good and bad buckets and treat them accordingly. 23 Effective Hiring and Staffing Effective Hiring and Staffing- Has a nose for talent; hires the best people available from inside or outside; is not afraid of selecting strong people; assembles talent staffs. Is a good judge of talent; after reasonable exposure, can articulate the strengths and limitations of people inside or outside the organization; can accurately project what people are likely to do across a variety of situations; identifies and selects talented people by gaining appropriate knowledge to serve on committees and panels; learns about the position and function to make appropriate calls; develops interview questions appropriate for specific job role and reflective of candidate’s past performance; respects the balance of technical and soft skills. Fairness to Direct Reports Fairness to Direct Reports- Treats direct reports equitably; acts fairly; has candid discussions; doesn’t have hidden agenda; doesn’t give preferential treatment; is available and ready to help. Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Knows the Team- May have trouble being firm with direct reports; may give them too much room for excuses; may not challenge them to perform beyond their comfort zone; may get too deep into their lives; work related feedback may be taken personally by employees because of close personal relationship; may not be able to make objective calls on performance and potential; may not know when to stop showing care when efforts are rejected. Under Demonstrates Knows the Team- May not care much about the personal needs of direct reports; may be too busy to know much about direct reports; may believe work and personal life should be separate; may be more work and task oriented than most; may be very tense and impersonal with direct reports; may lack the listening skills or interest to know people’s hopes and problems; may give the impression that organizational goals are more important than employee emotional and physical well-being. Over Demonstrates Managing Through SystemsIs uninvolved and/or unavailable; is out of touch with the details; may get too comfortable having things run on autopilot; may get surprised by negative events; may be slow to change existing systems; spends excessive amount of time developing systems for minor or one-time projects. Under Demonstrates Managing Through SystemsPrefers hands-on management; doesn’t set up rules, procedures and tie breakers so people know what to do in his/her absence; may be very controlling and a micromanager; relies on personal intervention; has to physically be there for things to go well; doesn’t think or manage in terms of policies, practices and systems; doesn’t delegate much; doesn’t really believe people can perform on their own; may not communicate clearly enough for people to know what to do without repeated inquiries of him/her; does not train team members well. Knows the Team Knows the Team- Is interested in the lives of direct reports; asks about their plans, problems and desires; know about their concerns and questions; is available for listening to problems; monitors workloads and appreciates extra effort. Managing Through Systems Managing Through Systems- Can design practices, processes, and procedures which allow managing at arm’s length; is comfortable letting things manage themselves without intervening; can make things work through others without constant supervision; can impact people and results remotely; trusts employees to do their job and is not adverse to taking the risk of letting employees do their job; mistakes are understood as learning opportunities; trains employees using standard and/or repeatable processes. 24 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Motivating Others- May not be good at building team spirit because of an emphasis on individuals; may be seen as providing inequitable treatment by treating each person individually; may not take tough stands when the situation calls for it; may take too long getting input; may be reluctant to assign work with tough deadlines. Under Demonstrates Motivating Others- Doesn’t know what motivates others or how to do it; people under him/her don’t do their best; not empowering and not a person many people want to work for, around or with; may be a one-style-fits-all person, have simplistic models of motivation, or many not care as much as most others do; may be a driver just interested in getting the work out; may have trouble with people not liking him/her; may be a poor reader of others, may not pick up on their needs and cues; may be judgmental and put people in stereotypic categories; intentionally or unintentionally demotivates others. Motivating Others Motivating Others- Creates a climate in which people want to do their best; can motivate many kinds of direct reports and team or project members; can assess each person’s core needs and use it to get the best out of him/her; pushes tasks and decisions down; empowers others; invites input from each person and shares ownership and visibility; makes each individual feel his/her work is important; is someone people like working for and with. 25 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Organizational Know-HowMay spend too much time maneuvering for advantage; may spend too much time and energy working on issues that lack substance; may be seen as excessively political; may not be trusted; may tell other what they are expecting to hear rather than what he/she knows to be true; may overstate what he or she knows; may be seen as manipulative and scheming; may sacrifice worthy goals in order to retain connections or political advantage; may be viewed as nosey or waste valuable work time cross training on functions or processes they do not use. Under Demonstrates Organizational Know-HowDoesn’t get things done in organizations beyond his/her area; may lack the interpersonal skills to get things done across boundaries; may not negotiate well within organizations; may be too timid and laid back to maneuver through organizations; may reject the complexity of organizations; may lack the experience or simply not know who and where to go; may be too impatient to learn; may neither know nor care to know the origins of how things work around the organization. Doesn’t know how to navigate smoothly and quietly through political waters; says and does things that cause political problems; doesn’t understand how to deal with not-invented-here and territory protection; rejects politics and may view self as apolitical; others might see this as naïve; may not deal with upper management persuasively; may be impatient with political process and make procedural errors; may be too direct and not consider impact on others; may not project out consequences of his/her actions well. Organizational Know-How Organizational Know-How- Knowledgeable about how organizations work; knows how to get things done both through formal channels and the informal network; understand the origin and reasoning behind key policies, practices, and procedures; understands the cultures of organizations; sensitive to how people and organizations function. Can maneuver through complex political situations effectively and quietly; is sensitive to how people and organizations function; anticipates where the land mines are and plans his/her approach accordingly; views corporate politics as a necessary part of organizational life and works to adjust to that reality; is seen as an asset by others. 26 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Valuing Diversity- May make too many allowances for members of a particular class; may not apply equal standards and criteria to all classes; may show an inappropriate preference for a single class of people; may compromise standards to achieve diversity. Under Demonstrates Valuing Diversity- Not effective with groups much different from him/her; may be uncomfortable with those not like him/her; may act inappropriately with those different from him/her; defends turf from outsiders; avoids conflict and the noise of differing views and agendas; doesn’t see the value of diversity; treats everybody the same without regard to their differences; very narrow and ethnocentric; believes his/her group to be superior; may carry around negative and demeaning stereotypes he/she has trouble getting rid of. Valuing Diversity Valuing Diversity- Manages all kinds and classes of people equitably; deals effectively with all races, nationalities, cultures, disabilities, ages and both sexes; hires variety and diversity without regard to class; supports equal and fair treatment and opportunity for all; is seen as supporting Guiding Principle of Diversity. 27 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Work Process Continuous Improvement Continuous Improvement- Reviews processes to determine any gaps between current outputs and expected requirements; identifies conditions that contribute to gaps or key variances; explores relationships between conditions and outcomes; distinguishes causes from symptoms and identifies primary causes; generates ideas for solutions; analyzes the potential effect or impact of each solution; selects appropriate solutions; gathers feedback on effectiveness. Over Demonstrates Continuous ImprovementStarts another change before giving most recent change enough time to validate whether new process is working or improved; changes for the sake of change; sees relationships between conditions and outcomes where none exist; tries to solve everything; flies into change mode before understanding root cause; sees symptoms as cause; generates solution to address symptom; fails to consider potential effect or impact of proposed solutions. Under Demonstrates Continuous Improvement-Does not view change process as adding value; resists change; may view temporary fixes as long-term solutions; may refuse to devote appropriate time and resources to improvement efforts. Over Demonstrates Information MonitoringCollects data with no stated purpose in mind; looks for correlations or draws conclusions not in evidence; doesn’t understand that anecdotal information is also data; creates monitoring systems that are disruptive; constantly changes monitoring systems. Under Demonstrates Information Monitoring- Does not value monitoring information; rejects the idea of collecting information due to fear of negative findings or results; cannot accurately analyze data for correlations; can’t see the story in the data; does not seek to prove or disprove premises based on data. Information Monitoring Information Monitoring- Determines which processes or areas need to be monitored; identifies what information needs to be obtained; establishes systems to monitor activities or outputs that are easy to use and that provide timely and pertinent information; effectively puts in place monitoring systems with minimal interruption; collects and reviews data on a regular basis to determine progress, anticipates needs and makes necessary adjustments. 28 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Managing Work/Time Management- May over plan or schedule every moment of work time; may be unable to adjust to shifting priorities; may be unable to manage emergencies that do not fall into “the plan”; may utilize others to do work that should be completed by self; may be overly concerned with details of managing work and miss the “big picture”; may stress others with rigidity. Under Demonstrates Managing Work/Time Management- May be known as a procrastinator; may not prioritize work effectively; may spend excessive amounts of time dealing with urgent but not important matters; may scramble at the last minute to complete projects; may not be able to utilize the assistance of others because there is no time to stop and instruct them. Over Demonstrates Meeting Leadership- May attempt to control all aspects of a meeting without allowing participants to contribute; may be seen as overly aggressive or “ruling with an iron fist”; may dwell on process or parliamentary procedure; may contribute own opinion too often without allowing feedback; may exclude quiet or more reserved participants. Under Demonstrates Meeting Leadership- May not create agendas or meeting plan; may not manage meeting time well; may allow meetings to run over because of excessive and repetitive discussion; may not attempt to summarize discussion or push the group to decisions; may create chaos by trying to allow participants to lead without direction. Over Demonstrates Meeting Participation- May try to contribute to every portion of the discussion even if the points are already covered; may not listen to the views of others, but only waits for their turn to speak; may take the group off topic with unrelated discussion; may be seen as confrontational or argumentative. Under Demonstrates Meeting Participation- May not prepare for meetings ahead of time; may not pay attention during meetings; may become distracted by technology (emails/text messages); may often arrive late or leave early; may behave flippantly or act as if the meeting is unimportant. Managing Work/Time Management Managing Work/Time Management- Identifies more critical and less critical activities and tasks; adjusts priorities as appropriate; ensures required equipment and/or materials are in appropriate locations so work can be done effectively; allocates own time to complete work; takes advantage of available resources (individuals, processes, tools) to complete work efficiently; uses time effectively and prevents irrelevant issues or distractions from interfering with work completion. Meeting Leadership Meeting Leadership- Helps to establish purpose and importance of meeting; seeks, gives, and summarizes information; checks for understanding; makes procedural suggestions; tries to build agreement on outcomes and establishes follow-up; establishes good interpersonal relationships by helping people feel valued, appreciated and included in discussions. Meeting Participation Meeting Participation- Seeks, gives and summarizes information; checks for understanding; seeks, makes and develops suggestions; makes procedural suggestions; tries to build agreement on outcomes and actions; establishes good interpersonal relationships by helping people feel valued, appreciated, and included in discussions. 29 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Planning and Organizing- May be overly obsessed with details that are less important than the value of overall content; may not be able to “see the forest because of the trees”; may have difficulty making changes or adjusting the initial plan; may make unreasonable resource demands that prevent progress. Under Demonstrates Planning and Organizing- May not know where to begin when planning large projects; may forget to address essential planning details and needs; may not effectively manage staff and volunteers by giving appropriate tasks at the appropriate time; may cause “rework” by omitting steps in the process; may have to request additional resources because of unanticipated problems. Over Demonstrates Problem Solving- May tend toward analysis paralysis; may wait too long to come to a conclusion; may not set analysis priorities; may get hung up in the process and miss the big picture; may make things overly complex; may do too much of the analysis personally. Under Demonstrates Problem Solving-Protects current process; may be stuck in the past and what worked before; afraid to solve problems; many times has to come back and rework the problem a second time; may be a fire-ready-aim type; may get impatient and jump to conclusions too soon; may not stop to define and analyze problems; doesn’t look under rocks; may have a set bag of tricks and pull unfit solutions from it; may miss the complexity of the issue and force-fit it to what he/she is most comfortable with; unlikely to come up with the second and better solution, ask penetrating questions or see hidden patterns. Planning and Organizing Planning and Organizing- Identifies more critical and less critical activities and assignments; adjust priorities when appropriate; determines project requirements by breaking them down into tasks and identifying types of equipment, materials, and people needed; allocates appropriate amounts of time for completing own and others’ work; avoids scheduling conflicts; develops timelines and milestones; takes advantage of available resources to complete work efficiently; coordinates with internal and external partners; uses time effectively and prevents irrelevant issues or distractions from interfering with work completion. Problem Solving Problem Solving- Uses rigorous logic and methods to solve difficult problems with effective solutions; knows the resources to use to solve the problem; can see hidden problems; is excellent at honest analysis; looks beyond the obvious and doesn’t stop at the first answers. 30 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Process Management- May always be tinkering and refining—nothing is ever the same for long, or finished; may have trouble explaining the vision of a process; may never finish anything; may always be dissatisfied because of unreasonably high standards and expectations of self and others; may attempt to put too much together at once; may misjudge the capacity of others to absorb change; may be seen as a perfectionist or nitpicker. Under Demonstrates Process Management-Not good at figuring out effective and efficient ways to get things done; uses more resources than others to get the same thing done; works in a disorganized fashion; doesn’t take advantage of opportunities for synergy and efficiency with others; can’t visualize effective processes in his/her head; lays out tasks for self and others in a helter-skelter way; does not work to simplify things; lacks attention to detail; doesn’t anticipate the problems that will arise; not a systems thinker; doesn’t understand or use process improvement principles. Over Demonstrates Resource Utilization- May be hesitant to problem solve when additional resources are needed; may not be tolerant of normal chaos, may too often want to do things their own way; may not be open to suggestions and input; may lose effectiveness when things don’t go as planned. May be overly dependent on rules, regulations, procedures, and structure; may leave out the human element of work; may be inflexible and have trouble with rapid change. Under Demonstrates Resource Utilization- Doesn’t pull resources together effectively; may be a poor delegator and planner and not very motivating to work with; performance decreases as the number of simultaneous activities increase; may rely too much on self; may scramble at the last minute and may have to work long hours to get things done; may not anticipate or be able to see how multiple activities come together. Doesn’t plan for much; may be a seat-of-the-pants performer scratching it out at the last minute; doesn’t follow an orderly method of setting goals and laying out work; may be uncomfortable with structure and process flow; may be disdainful of planning and comes across to others as loose or too simple; may not have the patience to establish goals and objectives, scope out difficulties, plan for task completion, develop schedules, and do roadblock management; may be confusing to work for and with; may be demotivating to others who work with him/her. Process Management Process Management- Good at figuring out the processes necessary to get things done; knows how to organize people and activities; understands how to separate and combine tasks into efficient work flow; knows what to measure and how to measure it; can see opportunities for synergy and integration where others can’t; can simplify complex processes; gets more out of fewer resources; obtains buy-in for new and improved processes; can operationalize new processes. Resource Utilization Resource Utilization- Can manage resources (people, funding, material, support) to get things done; can orchestrate multiple activities at once to accomplish a goal; uses resources effectively and efficiently; arranges information and files in a useful manner. Accurately scopes out length and difficulty of tasks and projects; sets viable objectives and goals; breaks down work into the process steps; develops schedules and task/people assignments; anticipates and adjusts for problems and roadblocks; measures performance against goals; evaluates results; eliminates roadblocks; creates and maintains focus; looks for ways to continuously improve. 31 Florida Gulf Coast University Performance Management Core Competency Library Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Under Demonstrates Over Demonstrates Safety Awareness- May be seen as overly cautious; may waste time looking for hazards that do not exist; may upset or scare others with unfounded concerns. Under Demonstrates Safety Awareness- May not be aware of surroundings; may not think before acting; may not check actions afterwards to assure safety; may make “careless mistakes”; may lack vigilance in questionable safety situations. Over Demonstrates Safety Intervention- May be overly vigilant when identifying safety hazards; may inflate safety issues; may pester others unnecessarily with safety policy and regulations. Under Demonstrates Safety Intervention- Does not promote a culture of safety; may choose to ignore evident safety issues; may not consider safety intervention part of his/her job role; may exhibit a distasteful attitude about safety policy and protocols. Over Demonstrates Technical/Professional Knowledge and Skills- May rely solely on technical knowledge; may not utilize relationships to get work done; may not tolerate those lacking technical knowledge; may not be able to explain complex processes to others. Under Demonstrates Technical/Professional Knowledge and Skills-Does not have technical knowledge; may have surface technical knowledge, but unable to apply it; may not show interest in learning technical skills; may prefer to rely on others to complete technical tasks. Safety Awareness Safety Awareness- Detects hazardous working conditions and safety problems; checks equipment and/or work area regularly; reports or corrects unsafe working conditions; makes recommendations and/or improves safety and security procedures; enforces safety regulations and procedures; monitors safety or security issues after taking corrective action and ensures continued compliance. Safety Intervention Safety Intervention- Follows regulations and safety procedures, including organizational safety practices; asks others to follow regulations and safety procedures; provides assistance to others to ensure safety; continually monitors and checks equipment and work area to ensure operational and safety compliance; detects hazards and safety problems; reports or corrects unsafe working conditions until resolved. Technical/Professional Knowledge and Skills Technical/Professional Knowledge and SkillsUnderstands technical terminology and developments; knows how to apply a technical skill or procedure; knows when to apply a technical skill or procedures; performs complex tasks in area of expertise. 32