Application in Second Language Acquisition
advertisement

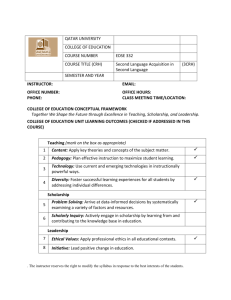
QATAR UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF EDUCATION EDUC 311: Applications in Second Language Acquisition (3 CRHs) SEMESTER AND YEAR: INSTRUCTOR: EMAIL: OFFICE NUMBER: OFFICE HOURS: PHONE: CLASS MEETING TIME/LOCATION: COLLEGE OF EDUCATION CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK Together We Shape the Future through Excellence in Teaching, Scholarship, and Leadership. COLLEGE OF EDUCATION UNIT LEARNING OUTCOMES (Checked if addressed in this course) Teaching 1. Content: Demonstrate understanding of the key theories and √ concepts of the subject matter. 2. Pedagogy: Plan effective instruction to maximize student √ learning. 3. Technology: Use current and emerging technologies in √ instructionally powerful ways. 4. Diversity: Foster successful learning experiences for all √ students by addressing individual differences. Scholarship 5. Scholarly Inquiry: Actively engage in scholarship by √ learning from and contributing to the knowledge base in education. 6. Problem Solving: Arrive at data-informed decision by √ systematically examining variety of factors and resources. Leadership 7. Ethical Values: Apply professional ethics in all educational √ contexts. 8. Initiative: lead positive change in education. √ COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides an introduction to the field of Second language acquisition and learning, an intricate process that involves the dynamic interaction of individual and social variables. It considers a wide range of theories, models, and research that have been proposed to account for this process and their implications for language learning and teaching. Participants are guided to evaluate and consider the implications of different perspectives for second language teaching in a variety of contexts. .. 1 Prerequisites: Acceptance into the B.Ed. in Education Primary Education Program COURSE OBJECTIVES Throughout this course, students will 1. examine different theories that account for the process of second language acquisition (SLA). 2. recognize personal and social factors influencing outcomes in second language acquisition 3. examine the role of learner’s individual characteristics, including learning strategies and styles in language learning 4. consider the implications of SLA research findings for teaching a second language 5. analyze second language learner data from multiple perspectives COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion of the course, students will be able to 1. demonstrate understanding of different theories of second language acquisition 2. explain the role of personal and social factors in second language acquisition 3. account for the role of learner’s individual characteristics, including learning strategies and styles in language learning 4. analyze second language learner language from different perspectives and identify possible sources of error 5. reflect on the application of research findings relating to SLA to teaching/learning a second language 6. formulate questions about aspects of SLA theories that they do not understand 7. summarize and present in class important studies and basic ideas of research studies 8. write coherent reflective papers on topics related to the field of SLA TEXTBOOKS & READINGS Gass, S.& Selinker, L. (2008). Second language acquisition: An introductory course (3rd ed.) London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Required Textbook Ellis, R. 1997: Second Language Acquisition . Oxford: Oxford University Press. Lightbown, P. and N. Spada 1999: How languages are learned. (2nd edition) Oxford: OUP SUPPORTIVE Texts Doughty, C. & Long, M. (Eds.). (2005). The handbook of second language acquisition. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell. . Long, M. (2006). Problems in SLA (Second language acquisition research. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Skehan, P. 1998: A cognitive approach to language learning . Oxford: OUP. .. 2 SUPPORTIVE WEBSITES Everything ELS. http://www.everythingesl.net/inservices/language_stages.php Center for Advanced Research in Language Acquisition. http://www.carla.umn.edu/strategies/ Dr. Cummin’s ESL and Second Language Learning Lab. http://www.iteachilearn.com/cummins/ http://www.tesol.org/s_tesol/index.asp TESOL Organization http://writing.berkeley.edu/tesl-ej/index.html TESL EJ http://iteslj.org/ Internet TESL Journal http://www.TEFLcommunity.com TEFL Community side www.gabrielatos.com On line papers on ELT and other related issues http://nnest.moussu.net/ Nonnative English speaking members of TESOL http://www.cal.org/ Center for Applied Linguistics http://www.ncela.gwu.edu National Clearinghouse for English Language Acquisition http://iteslj.org/Lessons/ Lesson plans and other information on Internet TESL Journal http://www.cal.org/ericell/digest/subject.html ERIC Clearinghouse on Languages and Linguistics (provides short articles on important topics by key writers). http://www.starfall.com/n/level-a/learn-to-read/load.html lesson plans www.lessonplanpage.com lesson plans http://www.rong-chang.com/methods.htm COURSE REQUIREMENTS 1. Each candidate is expected to attend class and contribute to the community of learners by being a positive participant in discussions, presentations, and hands-on projects. 2. All assignments should be submitted on the specified due date. Assignments turned in later are subject to point deductions. .. 3 3. All written assignments should have a cover sheet with assignment title, candidate name, course title, and date. 4. All written assignments should be word processed, double spaced, and in 12 point standard font. 5. All written assignments shall use appropriate citations and references in APA style. 6. In-class mid-term and final exams will be given in this class. Each candidate is expected to be present for these exams except in cases of certified emergency. USE OF BLACKBOARD Students are required to post their work on Blackboard and respond to each other in the Discussion Board. COURSE MATRIX Unit Learning Outcomes QNPS Course Objectives Course Learning Outcomes Assessment (Tasks/Artifacts) Content Pedagogy 1, 2,4, 8, 9 9.3 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Exams Reflective paper Diversity 1 2, 3 2, 3 Reflective paper Exams Technology 1, 2, 6 4 5, 8 Facilitate class discussion Problem solving 10, 11, 12 5 4 Data collection assignment 6, 7, 8 Reflective paper Data collection assignment Facilitate class discussion Scholarship inquiry Ethical values Initiative 10, 12 4, 5 COURSE OUTLINE .. Week 1 Introduction, SLA and Related Disciplines Week 2 Second and Foreign Language Data Week 3 The Role of the Native Language: An Historical Overview Week 4 Child language learning Week 5 Beyond the Domain of Language: Personal and social factors in SLA Week 6 Theories of SLA (1) Week 7 Theories of SLA (2) 4 Week 8 Mid-term Exam Week 9 Input, Interaction, and Output Week 10 Formal approaches to SL teaching Week 11 Task-based SL learning Week 12 SLA and teaching language as communication Week 13 Instructed Second Language Learning Week 14 An integrated view of SLA and learning Week 15 Revision Week 16 Final Exam METHODS OF INSTRUCTION This class is a student-centered class with several active learning strategies involved. Different groupings will be used for the purposes of discussions and social learning. The use of technology is part of this course either in the presentation, assignments or lecturing. Lecturing and discussions are part of the course methods. INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA The following equipment will be used: OHP, Whiteboard, computer and data projector, audiocassettes and CD players, video and DVD players. ASSESSMENTS Exams (40%) Student knowledge and interpretation of the readings and lectures will be assessed by two exams. The mid-term exam will be administered in Week 8 of the course during usual class times and in the same room. The midterm will focus on topics covered in lectures 1 - 7. The final exam will be given on the last week of the course at the same time and place as our usual classes. The final will focus on topics covered in lectures 9 - 14. The mid-term exam is worth 15% of the total final grade and the final exam is worth 25% of the final grade. Facilitate class discussion (20%). Students will collaborate in groups of two to facilitate a presentation and class discussion of one reading for ONE class session. They will lead class discussion of a reading for one class session. This means that you will need to prepare the reading carefully, present a summary of its content, make up study guide questions for your classmates to answer and lead the group through the discussion of the issues of the article. I will reduce your grade significantly if you are unprepared Presentations will be graded for effective communication and will be scored on a Presentation Evaluation Rubric to be provided by the instructor. .. 5 Reflective paper (20%). Each student will write a reflective paper on a topic suggested by the instructor. The paper should be no less than four pages. It has to be submitted in Week 10. Points will be deduced for late submissions. Data Collection Assignment (20%). This will require you to get two language samples from a second language learner; the language has to be elicited in two different ways. You will then analyze some aspects of the language and describe how the language differs between the two samples. GRADING SYSTEM A = 100 - 90 B+ = 89.99 - 85 B = 84.99 - 80 C+ = 79.99 - 75 C = 74.99 - 70 D+ = 69.99 - 65 D = 64.99 - 60 F = 59.99 – 0 SPECIAL NEEDS In accordance with Law No 2 of the year 2004, and Article 49 in the Constitution of Qatar: "Education is the right of all.", and "the State shall extend efforts to achieve fair and appropriate access in education for all". Qatar University seeks to ensure fair and appropriate access to programs, services, facilities, and activities for students with special needs. Any student who feels s/he may need an accommodation based on the impact of a disability should contact the instructor privately to discuss your specific needs. Please contact the Office for Disability Services to coordinate reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities. Special Needs Section Student Activities building Men’s Campus: 44033854, Fax: 44838925; Women’s Campus: 44033843, Fax: 44839802; Email: specialneeds@qu.edu.qa; Office hours: 7:30 AM – 2:30 PM STUDENT COMPLAINTS POLICY Students at Qatar University have the right to pursue complaints related to faculty, staff, and other students. The nature of the complaints may be either academic or non-academic. For more information about the policy and processes related to this policy, you may refer to the students’ handbook. ACADEMIC HONESTY Qatar University is an academic community actively engaged in scholarly pursuits. As members of this community, students are expected to recognize and honor standards of academic and intellectual integrity. The College of Education supports the ideals of scholarship and fairness by rejecting all .. 6 dishonest work when it is submitted for academic credit. Qatar University encourages students to be responsible and accountable for their decisions and actions. Any attempt by students to present the work of others as their own or to pass an examination by improper means is regarded as a most serious offense and renders those students who do so liable to disciplinary action. Assisting another student in any such dishonesty, or knowing of this dishonesty and not reporting it, is also considered a grave breach of honesty. Academic dishonesty and plagiarism are described on page 37 in the Qatar University Student Handbook. LEARNING SUPPORT Qatar University operates Learning Support Centers on each campus to provide services to students to supplement their in-class instruction and ability to meet course requirements. These services include tutoring, acquiring efficient learning skills and strategies, academic and learning assessment (in conjunction with the Counseling Center), and writing labs and workshops. Information about the Learning Center may be found at http://www.qu.edu.qa/students/services/slsc/ Appendix QATAR NATIONAL PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR TEACHERS 1. Structure innovative and flexible learning experiences for individuals and groups of students. 2. Use teaching strategies and resources to engage students in effective learning. 3. Foster language literacy and numeracy development. 4. Create safe, supportive, and challenging learning environments. 5. Construct learning experiences that connect with the world beyond school. 6. Apply information and communication technology in managing student learning. 7. Assess and report on student learning. 8. Apply knowledge of students and how they learn to support student learning and development. 9. Apply teaching/subject area knowledge to support student learning. 10. Work as a member of professional teams. 11. Build partnerships with families and the community. 12. Reflect on, evaluate, and improve professional practice. ________________________________________________________________________ . .. 7