A. Light Reactions
advertisement
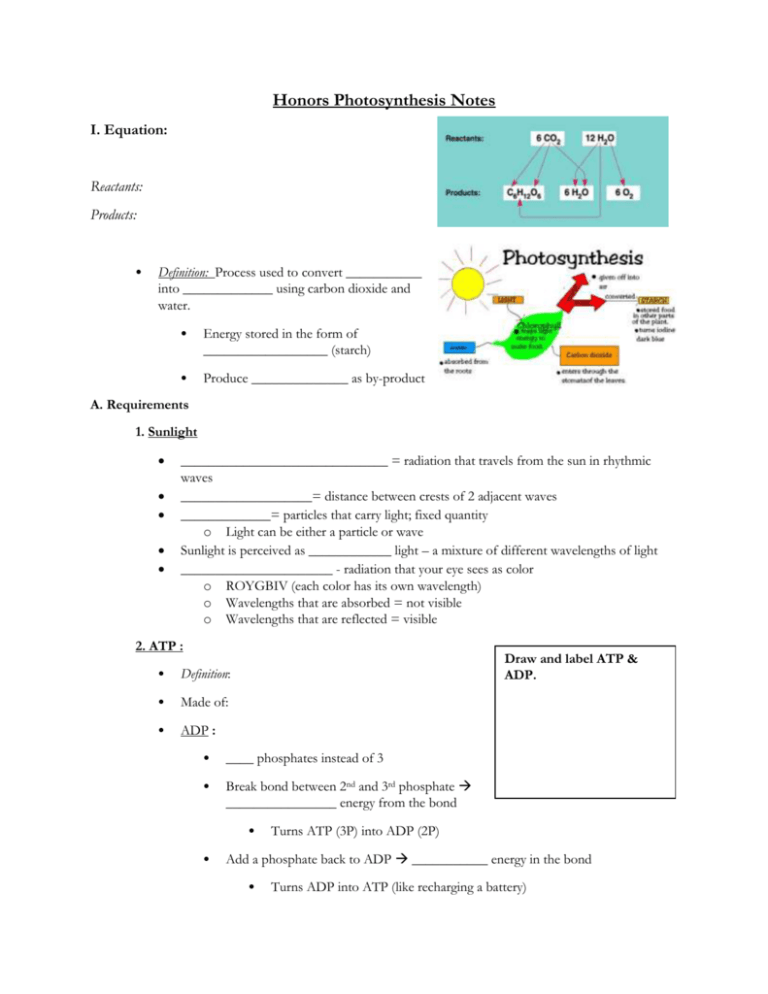
Honors Photosynthesis Notes I. Equation: Reactants: Products: • Definition: Process used to convert ___________ into _____________ using carbon dioxide and water. • Energy stored in the form of __________________ (starch) • Produce ______________ as by-product A. Requirements 1. Sunlight ______________________________ = radiation that travels from the sun in rhythmic waves ___________________= distance between crests of 2 adjacent waves _____________= particles that carry light; fixed quantity o Light can be either a particle or wave Sunlight is perceived as ____________ light – a mixture of different wavelengths of light ______________________ - radiation that your eye sees as color o ROYGBIV (each color has its own wavelength) o Wavelengths that are absorbed = not visible o Wavelengths that are reflected = visible 2. ATP : • Definition: • Made of: • ADP : Draw and label ATP & ADP. • ____ phosphates instead of 3 • Break bond between 2nd and 3rd phosphate ________________ energy from the bond • • Turns ATP (3P) into ADP (2P) Add a phosphate back to ADP ___________ energy in the bond • Turns ADP into ATP (like recharging a battery) 3. Pigments • Definition:__________ absorbing molecules that gather the sun’s energy A.Types of Pigment • Chlorophyll a (absorbs different wavelengths) • Chlorophyll b • • Found in __________________ • Reflects _____________ light • Absorbs blue/violet & red Carotenoids (yellow-orange) B. Structure of Chloroplasts • Trap ___________ (in chlorophyll) and transfer _________________________________ • Excited electrons drive photosynthesis • Mesophyll: green tissue on interior of leaf where _________________ are found • Stomata: tiny pores where _______ enters and ______ exits • Parts of Chloroplast: • _____ membranes (inner & outer) • _______________: fluid filled space where dark reaction occurs • ________________: membranous sac where light reactions occurs • _______________: stack of thylakoids Why is it logical that cells containing chloroplasts would be on the top of a leaf and not the bottom? Electron Transport • Sunlight ____________ the electrons in chlorophyll. Electrons gain a great deal of ___________. • ____________________ electrons need a special carrier (usually ATP) • These carriers transfer high energy electrons to another molecule Electron transport • Electron Transport Chain (ETC)- name for the chain of electron carriers 4. NADPH (energy carrier) “Truck” that accepts and carries ___________ electrons (e-) • • • High energy electrons (analogy – hot coals) NADP • Holds 2 high energy ________ and a ____________ ion (H+) • This converts NADP into NADPH • This how we trap energy from sunlight in _________________ form NADPH- Transport electrons to serve as ______________ for chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell (for photosynthesis, to build carbs) 5. Water • Sunlight energy splits water into: • 2 __________________ (used to make NADPH & ATP) • 1 __________________ (released as a byproduct) 6. Carbon Dioxide Comes from the ______________ Burning of fossil fuels Animals/humans release during _______________ Used to make sugars II. Photosynthesis consists of 2 reactions: 1. Light ___________________ -Needs light to make ATP & NADPH 2. Light ____________________ (Calvin Cycle) -Does not need light -Uses ATP/NADPH from light reactions to convert CO2 into _______________ A. Light Reactions (Light Dependent) • Purpose: To change ___________ energy into _______________ energy of ATP & NADPH • Requires: _____________ and ___________ • Occurs in • Produces: STEPS of Light Reaction 1. Light Absorbed to Excite Electrons a. b. c. d. Light energy absorbed by ________________ in Photosystem II (PSII) __________________ = organized cluster of pigments (chlorophyll) in the membrane of thylakoids Electrons excited to _______________ energy levels Electrons passed through electron transport chain (ETC) releasing energy as they pass End with low energy electrons 2. Water Splits a. b. c. d. Sunlight splits the water to produce more ______________ for the ETC Breaks into e- (from the broken bonds), H+ ions, and O2 O2 released as _______________- moves out of thylakoid Excited electrons provide energy to pump ______________ through a carrier protein against the gradient from ______________ (low concentration) into ________________ (high concentration) e. H+ ions want to move to a lower concentration back into the ___________ 3. Formation of ATP & NADPH A. ATP Synthesis 1. Chemiosmosis o o Uses the potential energy of a concentration gradient of _________ across a membrane to create ATP through phosphorylation H+ diffuses down the concentration gradient through an enzyme called _______________ 2. Phosphorylation- adding a P to ADP to create ATP o Flowing down the gradient creates ____________________ that ATP synthase uses for phosphorylation B. NADPH Synthesis o o o Electrons move from PSII through electron transport chain into _________ Electrons AGAIN excited to higher energy state Use e- energy to add H+ & 2e- to NADP NADPH B. Dark Reactions (Light Independent or Calvin Cycle) • Purpose: • Reactants: • Products: • Does not need____________ • Takes place in ____________ • ____ cycles = 1 glucose Calvin Cycle o Breaks bonds in ATP & NADPH to create ____________ and electrons o Rearranges and adds atoms to create ______________ o ADP & NADP+ return to light reactions Location Reactants Products Light Reactions Dark Reactions V. External Impacts on Photosynthesis o o o o Word bank stroma, thylakoid, chloroplast, light dependent reactions, calvin cycle, sunlight, Water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sugar, ATP, ADP + P, NADP+, NADPH Photosynthesis Light Reactions Dark Reactions Purpose: Purpose: Location: Location: Step 1: Uses from the air and Location: From light rxns Electrons are Breaks to make Then passed through the Needs CO2 for 1 Step 2: Sunlight splits Sends & to light reactions A. From bonds: B. C. Replaces Pumped against gradient from Byproduct In PSII back Released into air Causes To to move into thylakoid Step 3: ATP Synthesis Chemiosmosis Step 3: NADPH Synthesis Electrons from Movement of go through to Through enzyme called At , electrons excited by sun. Provides energy for: Phosphorylation: + + + Photosynthesis Review sheet - Honors 1. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? Give examples for each. 2. What is a food web? Create a food web using grass, grasshopper, bunny, deer, mouse, cow, human, toad, and hawk. a. Producers b. Primary consumers c. Secondary consumers 3. What is an ecological pyramid? What happens to energy and # of organisms as you move up the pyramid? Explain the 10% rule. 4. Definition and give the equation for photosynthesis. 5. What are the 6 requirements for photosynthesis? 6. Why does something red appear red? White? In terms of the visible spectrum (what’s absorbed/reflected?) 7. What is ATP? How does it work? How is it similar/different from ADP? 8. What is a pigment? What are some examples – what color do they appear? What is primary pigment in plants? 9. Given the absorbance graph for chlorophyll a and b – be able to analyze and answer questions for example: 10. For chlorophyll B (the red line): a. b. c. d. e. f. Which color is the least visible? What percent of this color is being absorbed? What is the approximate wavelength for this color? Would this color of light speed up or slow down the rate of photosynthesis? Why? Which color is most reflected? What percent of this color is absorbed? Reflected? Chlorophyll B Chlorophyll A 11. Draw and label the parts of a chloroplast. 12. Label and describe the parts of a plant: mesophyll, stomata, chloroplast , thylakoid, grana 13. How many reactions are there in the process of photosynthesis? a. What are they? b. Where in the chloroplast does each take place? c. What are the reactants/products of each step? Briefly describe what happens. 14. What is NADPH? (what does it carry?) When is it created? When is it used? How is it different from NADP+? 15. What splits water? What does it split into? Describe what happens to each of these after water is split? (i.e. released …or helps create….) 16. What 2 things are made in the light reaction that are used in the dark reaction? 17. Where does carbon dioxide come from? What is it used to help make? a. Which reaction is carbon dioxide used? 18. Which reaction is being shown in this picture to the right? 19. What are the three major steps that are happening? 20. What is chemiosmosis? Phosphorylation? C. B. A. E. D. F. G. H. I. 21. Label the boxes with the following words: sunlight, light reaction, calvin cycle (dark reaction), carbon dioxide, ATP, NADPH, oxygen, glucose, and water. (hint this picture is in your notes packet, and it is a really good summary for all of photosynthesis – be familiar with this .) 22. What are 2 other names for the dark reaction? 23. What is the purpose of the dark reaction? 24. Why are there 6 cycles of the dark reaction? 25. What are the 4 things that impact the rate of photosynthesis?










