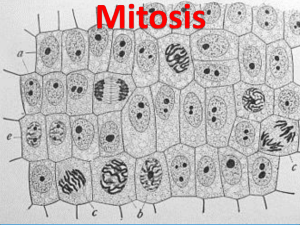
is when a cell is preparing to reproduce.
advertisement

Chapter 2: From A Cell to an Organism Lesson 2.1- The Cell Cycle and Cell Division A. The is the life cycle of the cell. 1. of the cell cycle include interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. a. is when a cell is preparing to reproduce. b. During the mitotic phase, the nucleus and cytoplasm divide producing two new cells. 2. The of a cell cycle differs for different organisms and cells. 3. A cell performs specific during interphase. a. (Each pair of similar chromosomes are called _______________ chromosomes.) b. Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. c. (Humans have ______ pairs of homologous chromosomes in each human cell). d. consists of 3 phases: G1,S, and G2. e. In the cell grows and carries out normal, cellular functions. f. Some cells such as muscle, nerve, and red blood cells, stay in G1 and never . g. In S phase, the chromosome pairs in the cell’s nucleus replicate. h. The copies of the chromosomes made during S phase are _________________________. i. The sister chromatids are held together in the region near the middle of each chromatid called the . j. The replication ensures that the new cells formed are ______________. k. In phase, the cell grows and functions, and some _____________replicate. B. is the process by which the nucleus divides; _________________is the process by which the cytoplasm divides. 1. Mitosis and cell ensure that each new cell receives all it needs to function. a. Mitosis and cell division old worn-out cells, and are the method of reproduction for some organisms. b. Mitosis and cell division produce most cells in a _____________________organism. c. A different type of cell division produces and ____________cells. 2. There are phases of mitosis in order: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. a. In , DNA in chromosomes twists into tight coils and the nucleus breaks apart. b. In , the chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and pairs of sister chromatids line up. c. In , fibers attached to the of the sister chromatids pull them apart toward opposite ends of the cell. The chromatids are then called chromosomes. d. In , a new membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two identical nuclei, and chromosomes become less tightly coiled. 3. is the final stage of cell division. a. During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm and its contents divide to form two identical cells called . b. At the start of cytokinesis, the cell membrane inward. c. In a cell with a cell wall, a forms between the two new nuclei. d. The cell plate later becomes the cell , which builds the new cell walls. 4. Cell division results in new daughter cells to replace the original parent cell. a. After mitosis and cell division, the original cell—called the ______________cell—no longer exists. b. The daughter cells’ chromosomes are identical to the parent cell’s in _____________ and type. c. Because of mitosis and cytokinesis, all the cells in your body, except sperm and cells, have identical chromosomes. Lesson 2.2- Levels of Organization A. A organism carries out all the functions it needs to survive. 1. Prokaryotes, such as , do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. a. Bacteria have with specific functions. b. Some processes that occur in in eukaryotes happen along specialized membranes in prokaryotes. 2. Each one-celled has a nucleus and organelles with specialized functions. a. One-celled eukaryotes include and some fungi. b. One-celled eukaryotes are more complex than cells in _________________eukaryotes because they are self-sufficient. c. Cells in many-celled organisms on other cells to perform different functions. d. Some protists, including Volvox, live and function in with specialized cells. B. Many-celled organisms have many cells and usually have more than one type of cell. 1. Cell is the process by which cells become different types of cells. a. Even though all cells in an organism have sets of chromosomes, cells are able to differentiate by using ___________________ parts of the instructions on the chromosomes. 2. 3. 4. 5. b. Differentiated cells often have structures and shapes to perform specific functions. c. Liver cells have ER (endoplasmic reticulum) for filtering blood; cells are highly branched for sending and receiving signals. d. Once most human cells , they cannot become any other cell type. e. are undifferentiated; they can become different types of cells. f. Some cells can differentiate into another type of cell after they have differentiated into one type. A is a group of cells, such as muscle fiber, that works together to perform a function. An is a group of similar tissues that work together to perform a function. a. Examples of human are the heart, lungs, brain, stomach, and muscles. b. have organs that store nutrients, transport substances, provide protection, and perform . c. A leaf is an example of a plant organ. An is one or more organs working together to perform one or more functions. a. The muscular, digestive, and skeletal systems are examples of organ ________________. b. The sends and receives signals to coordinate the organ systems in the body. The many-celled is the most complex unit of living things. a. Each organ system has its own but depends on other organ systems. b. The correct sequence, from least to most complex, is cell, tissue, _______________, organ system.