Genetics Problems
advertisement
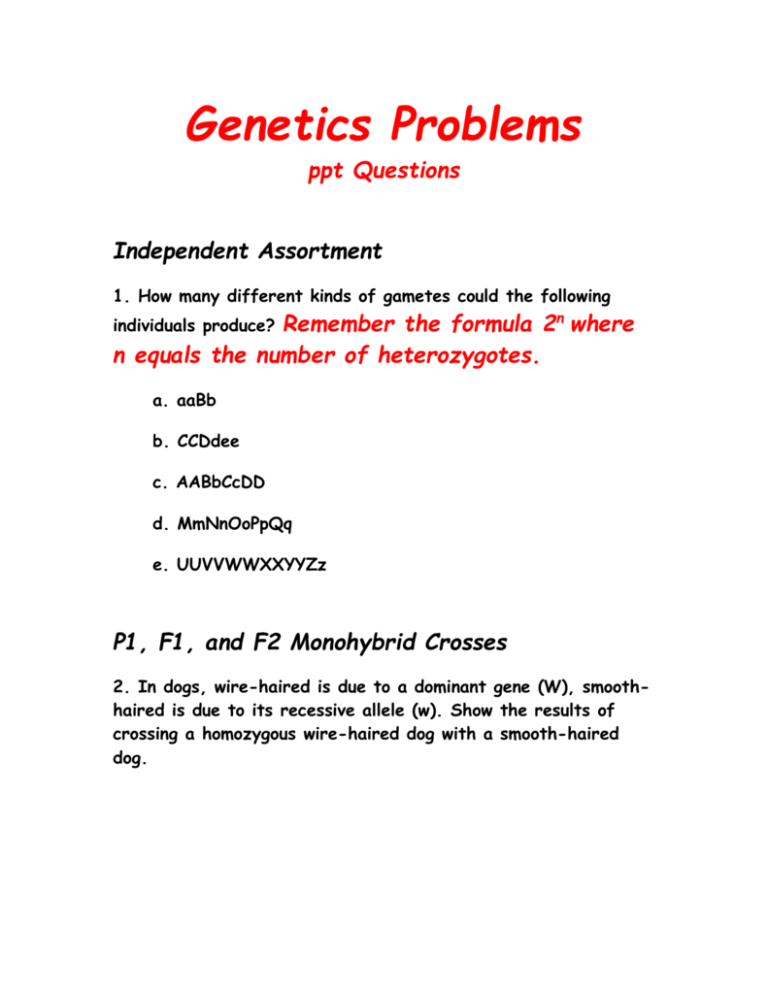
Genetics Problems ppt Questions Independent Assortment 1. How many different kinds of gametes could the following Remember the formula 2n where n equals the number of heterozygotes. individuals produce? a. aaBb b. CCDdee c. AABbCcDD d. MmNnOoPpQq e. UUVVWWXXYYZz P1, F1, and F2 Monohybrid Crosses 2. In dogs, wire-haired is due to a dominant gene (W), smoothhaired is due to its recessive allele (w). Show the results of crossing a homozygous wire-haired dog with a smooth-haired dog. 3. What kind of cross is this? 4. What was the genotype of all of the puppies? the phenotype? 5. The puppies belong to the _________ generation. 6. How would you write the F1 cross for this trait? 7. Show the results of working the F1 cross for this trait. 6. What phenotypic ratio did you get from this F1 cross? 7. What genotypic ratio did you get from this F1 cross? 8. Two wire-haired dogs are mated. Among the offspring of their first litter is a smooth-haired pup. If these two dogs mate again, what are the chances of them having another smooth-haired pup? 9. What are the chances that the pup will be wire-haired? 10. A Wire-haired male is mated with a smooth-haired female. The mother of the wire-haired male was smooth-haired. What are the phenotypes and genotypes of the pups they could produce? Show how you got your results. Incomplete Dominance 11. In snapdragons, red flower color (R) is incompletely dominant over white flower color (r). The hybrids or heterozygous plants (Rr) are pink in color. Show the genotype for a white flower and for a red flower. 12. If a red-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation plants? Show your work. 13. What is the phenotype of the flowers? what is their genotype? 14. What genotypes and phenotypes will be produced in the F2 generation? Show your work. 15. How did the genotypic and phenotypic ratio compare to each other in this incomplete dominance cross? 16. What would the phenotypic ratio have been if this had been complete dominance? 17. What kind of offspring can be produced if a red-flowered plant is crossed with a pink-flowered plant? Show your work. 18. What kind of offspring is/are produced if a pink-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant? Show your work. Sex-linked Traits 19. What is the genotype for female? for male? 20. In humans, colorblindness (Xc) is a recessive sex-linked trait. Two people with normal color vision (XC) have a colorblind son. What are the genotypes of the parents? 21. What are the genotypes and phenotypes possible among their other children? Show your work. 22. A couple has a colorblind daughter. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the parents and the daughter? Dihybrid Crosses 23. In humans, the presence of freckles is due to a dominant gene (F) and the non-freckled condition is due to its recessive allele (f). Dimpled cheeks (D) are dominant to non-dimpled cheeks (d). Two persons with freckles and dimpled cheeks have two children. One child has freckles but no dimples. The other child has dimples but no freckles. What is the genotypes of the parents? the children? 24. What are the possible phenotypes and genotypes of the children that they could produce? Show all your work. 25. What phenotypic ratio did you get? 26. What genotypic ratio did you get? 27. What are the chances that they would have a child whom lacks both freckles and dimples? What would be the child's genotype? 28. A person with freckles and dimples whose mother lacked both freckles and dimples marries a person with freckles but no dimples whose father did not have freckles or dimples. What are the chances that they would have a child whom lacks both freckles and dimples? Show the genotypes of the parents and all the offspring. 29. In dogs, the inheritance of hair color involves a gene (B) for black hair and a gene (b) for brown hair. A dominant (C) is also involved. It must be present for the color to be synthesized (made). If this gene is NOT present, a blond condition results. Complete the following table: BB or Bb bb Color Deposition gene CC or Cc CC or Cc BB or Bb bb cc cc Genotype Phenotype 30. A brown-haired male, whose father was a blond, is mated with a black-haired female ,whose mother was brown-haired and her father was blond. What is the genotype of the man and woman? Show the genotypes and phenotypes of all of their offspring. Population Genetics or Hardy-Weinberg Law Sixteen percent (16%) of the human population is known to be able to wiggle their ears. This trait is determined to be a recessive gene. Use the following equations to answer this population genetics problem: 1 = p2 + 2pq + q2 then use 1 = p + q p2 - frequency of homozygous dominants 2pq - frequency of heterozygotes q2 - frequency of homozygous recessives p - frequency of dominant allele q - frequency of recessive allele 31. What percent of the population is homozygous dominant for this trait? Show your work. 32. What percent of the population is heterozygous for this trait? Show your work. Multiple Alleles - ABO Blood Type 33. Henry Anonymous, a film star, was involved in a paternity case. The woman bringing the suit had two children. One child had blood type A and the other child had blood type B. Her blood type was O, the same as Henry's. The judge in the case awarded damages to the woman, saying that Henry had to be the father of at least one of her children. was the judge correct in his decision? Show how you got your answer.