Genetics Study Guide: Mendel, Heredity, and Punnett Squares
advertisement

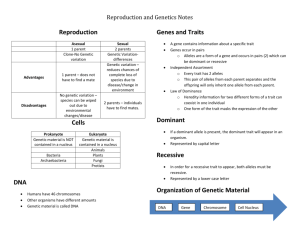
Study Guide for Genetics Test Gregor Mendel - The father of genetics, who studied inheritance in the late 1800s Heredity- The passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics- The scientific study of inheritance or heredity Gene – A part of a chromosome that codes for a trait Alleles - An allele is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. They are usually represented with a letter and combine to form the genotype for each gene. Homozygous - The two alleles are the same, RR (pure dominant) or rr (recessive) Heterozygous or Hybrid- a genotype that is a combination of a dominant and a recessive allele – Rr – Dd Dominant gene- Strong form of a gene, which is expressed even if a recessive gene is present – represented by a capital letter in the genotype (RR, Rr) Recessive gene- The weak form of a gene, which is not expressed when the dominant gene is also present – only expressed when both genes are recessive – represented by a lower case letter in the genotype (rr) Phenotype- A genetic trait that an individual actually shows, (photo) – the words that describe the trait. Eg. Purple flower – Blue eyes – Short arms Genotype- The gene combination that determines the phenotype. Eg. Kk – Rr - VV Incomplete Dominance- A condition that results when genes produce a trait somewhere in between the traits of the parents , skin color on a mixed race child. Somatic cell - is almost any cell forming the body of an organism other than a gamete. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes Gametes- Sex cells; egg and sperm in organisms that reproduce sexually. Human sex cells have 23 chromosomes or 1 from each of the parent chromosome pairs. Egg cells – female sex cell. All of the 400,000 egg cells a woman will ever produce are already present in her ovaries when she is born Sperm cells – male sex cell, In Humans formed through meiosis beginning at puberty and continuing for the rest of the male’s life. Study Guide for Genetics Test Mitosis – Cell division that produces 2 daughter cells identical to the 1 parent cell – occurs for growth and to replace dead cells Meiosis- Cell division that produces gametes (sex cells: eggs and sperm) or spores having one set of unpaired chromosomes – 1 cell creates 4 gametes using Meiosis Chromosomes – The normal human cell contains 46 chromosomes organized in 23 pairs. Karotype – a picture of a person’s chromosomes X chromosome-The longer sex chromosome; females have two X chromosomes, Y chromosome-The shorter sex chromosome, males have one X and one Y chromosome Mutation- A sudden, unexpected change in the structure of the DNA or the chromosomes; mutations can occur in body or sex cells; most are not harmful Replication- The copying process in which new DNA is created DNA Replication - adenine (A) always is paired with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) -- Punnant Square For example, let's say that for the red-throated bird , red throat is the dominant trait and white throat is recessive. Since the "red-throat code" and the" white-throat code" are alleles (two forms of the same gene), we abbreviate them with two forms of the same letter. So we use "R" for the dominant allele/trait (red throat) and "r" for the recessive allele/trait (white throat). R r r R R R r Rr Rr r Rr Rr One more note: A very very helpful thing to memorize is that the ONLY way for a recessive trait to show up in an organism is if that organism's genotype is recessive (two little letters, like "rr"). Study Guide for Genetics Test