Exam Review - Prairie Spirit Blogs
advertisement

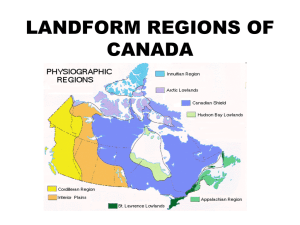
Geography Test Review 1. Continents, Oceans, and Hemispheres a. Be able to label the 7 continents b. Be able to label the 5 oceans c. Be able to locate and label the Prime Meridian, International Date Line, and Equator d. Know which hemispheres you live in e. Know the purpose of the International Date Line 2. Physical and Human Geography a. Be able to sort the topics into either the physical or human geography column 3. Map of Canada a. Be able to label all 10 provinces and all 3 territories b. Be able to label their capitals in APPROXIMATELY THE CORRECT LOCATION c. Be able to label the capital city of Canada d. Be able to label the Great Lakes e. Be able to label Hudson’s Bay and the Gulf of the St. Lawrence f. Be able to label the United States, Greenland, and Iceland 4. Time Zones a. Be able to label the different time zones on a map b. Be able to define daylight savings time c. Know that the time zones start at the Prime Meridian 5. Regions of Canada a. Know the highlighted information on the next page (in the form of multiple choice questions) b. Be able to label the regions on a map of Canada 6. Current Events a. Wi-Fi – What is Wi-Fi? Why are people worried about it being in schools? b. Egypt in Turmoil – NO MAP – What is happening in Egypt? i. People revolted in 2011 ii. Got rid of the leader, who was a dictator iii. They elected a new leader, but he was corrupt iv. There was more fighting v. Now the army is in control until elections c. Syria at Centre Stage – What is happening in Syria? i. The government attacked their own people with chemical weapons ii. The UN couldn’t agree about what to do because China and Russia side with Syria iii. Eventually they made Syria give up its chemical weapons and close chemical weapon factories Innuitian Mountains Definition: The Innuitian Mountains are a mountain range in Canada's Arctic territories of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories. They are part of the Arctic Cordillera and are largely unexplored, due to the hostile climate. They are named after the northern indigenous people, who live in the region. What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because the climate is a lot more hostile, and because it is composed of a series of islands, which is really a mountain range that is mostly submerged in the ocean. High/Low Temperatures: +3 to -40 on average Climate: The climate in this region is very harsh. Summers are short, and the temperatures get barely above freezing, with very little precipitation. In the winter, this area gets bitterly cold temperatures, with high winds, and often doesn’t receive much snowfall. When it does snow, it is often in the form of a blizzard, with high winds and freezing temperatures. Vegetation: This area is covered by glaciers, and does not have vegetation for the most part. In the summer, when he ground thaws somewhat, you will occasionally get grasses and lichens. Hudson Bay and Arctic Lowlands Definition: The Hudson Bay Lowlands are a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is an area of low-lying land which is surrounded by the Canadian Shield. High/Low Temperatures: +12 to -40 on average Climate: Wet, windy, cold Vegetation: consists largely of tundra (very flat lowlands). Trees cannot withstand the tundra’s low precipitation, harsh temperatures, and nutrient-poor soil, frozen with permafrost. Instead, short plants such shrubs, lichens, grasses, and 400 flower varieties sprout during this area’s 50-60 day growing season. Arctic plants are adapted to cold temperatures and a very short growing season. They grow rapidly in spring and remain short and clustered, sheltering each other, to survive harsh winds. Canadian Shield Definition: a large plateau that occupies almost 50% of the land area of Canada; it extends from the Great Lakes northward to the Arctic Ocean What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is a section of shield rock (part of the Earth’s crust) with very little soil. It is NOT part of a mountain range, but is mostly comprised of rock. High/Low Temperatures: +20 to -20 on average Climate: In the North there are long, cold winters, and short, cool summers. In the South, the weather is milder and summers are longer and warmer. It gets 200-300 mm of rain in summer and 1250-1500 mm of snow in winter. Vegetation: Consists mainly of birch, aspen, tamarack, spruce, willow, hemlock, and pine trees. You can find nearly any colour of leaves, and the vegetation is different from the rest of Canada. LA RONGE Interior Plains Definition: a relatively flat region that extends from the Arctic Ocean to the US border between the Rocky Mountains and the Canadian Shield. What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is a flat, fertile region between two rocky areas. High/Low Temperatures: +30 to -35 on average Climate: The climate of the Interior Plains is very diverse. Weather is very extreme; up north, long winters and summers are short and cool, and down south, summers are long and hot and winters are cold, however there is very little precipitation. Air from the Gulf of Mexico flows north, colliding into air from Canada, creating sudden and violent weather, such as tornadoes, blizzards, and hailstorms. Vegetation: Much diversity as with climate; up North is Tundra, which is treeless area where the ground is always frozen, and down south there are deciduous and evergreen trees. In the Prairies there are tall grasses and even some that can grow to the height of a person. SASKATOON YELLOWKNIFE NORTH POLE/ALERT BAY Cordillera Definition: An extensive chain of mountains or mountain ranges, especially the mountain system of North America What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is made up of mountains as opposed to prairie. High/Low Temperatures: +10/+20 to -10/-30 on average depending on how far north you are Climate: Along the coast, this area has cool, wet winters with lots of rain, and warm fairly dry summers. In the interior, this area has cooler winters with lots of snowfall, and hot dry summers. Vegetation: The area is covered mostly by coniferous forests in the upper elevations, coniferous forests with a few deciduous trees in the mid-elevations, and trees with grasslands along the valleys. Appalachian Mountains Definition: A mountain range in the eastern United States extending from Quebec to the Gulf of Mexico. What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is a mountain range that runs from north to south alongside the St. Lawrence Lowlands and Shield. High/Low Temperatures: +20 to -10 on average Climate: The climate is controlled by two ocean currents, which makes the winters cold with lots of precipitation, and the summers more mild, but humid. This area is sometimes hit by tropical storms and hurricanes. Vegetation: The mountains are covered mostly by deciduous forests in the low-lying areas, although there are some coniferous trees further up the mountains. Large hard-wood trees such as maple, walnut, and hemlock are commonly found in this area. VANCOUVER/ BANFF QUEBEC CITY St. Lawrence and Great Lakes Lowlands Definition: It includes the St. Lawrence seaway and the Great Lakes. What makes it different: It is different from the surrounding regions because it is a low-lying area between the Appalachian Mountains and Canadian Shield. High/Low Temperatures: +30 to -30 on average Climate: The great lakes region is very humid because of the Great Lakes. This climate allows for good growing season for crops. On average, around 100 cm of rain or snow is received every year. Vegetation: The Great Lakes are home to a broad leaf forest, and the Lowland has a mixed forest of conifers and deciduous trees. Grass is also plentiful. The soil is very fertile, so a lot of farming is done here. Interesting Facts: This Is one of the most populated regions in Canada, and contains half of Canada’s population. This region is one of the smallest geographical regions in Canada. TORONTO Definitions Climate: The weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. Natural Resources: Materials or substances occurring in nature which can be used for economic gain. Non-renewable Resources: A non-renewable resource (also known as a finite resource) is a resource that does not renew itself at a sufficient rate for sustainable economic extraction in meaningful human timeframes. An example is carbon-based, organically-derived fuel. Renewable Resources: any natural resource (such as wood or solar energy) that can be replenished naturally with the passage of time