File
advertisement

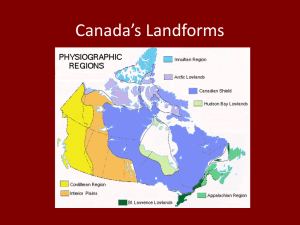
LANDFORM REGIONS OF CANADA Rock Types in Canada Profile of Canada The Western Cordillera • The Western Cordillera region covers most of British Columbia and the Yukon Territory. The great height and rugged appearance of the mountains tell us they are very young. The collision of the North American and the Pacific plates uplifted the region into several mountain ranges. • From West to East, the Western Cordillera is composed of three subregions, each one running from north to south • The West Coast Mountains on the Pacific coast • The Interior Plateau in the middle • The Rockies, bordering and crossing in to Alberta See Fig. 11-13 on p. 113* Google Earth - Vancouver Island Coastal Mountains The West Coast Mountains • • • • • VERY TALL PEAKS VOLCANIC MANY FIORDS (narrow inlets) IN SOME AREAS, THE SEA OFFERS THE BEST WAY TO GET AROUND COMMUNITIES IN VALLEYS ON SHORELINES WEST COAST MOUNTAINS • Subduction zone • Oceanic plate sliding under continental plate • Prone to earthquakes WEST COAST MOUNTAINS • SOME VOLCANOES MORE RECENT THAN OTHERS • MOUNTAINS COVERED IN LUSH FORESTS WEST COAST MOUNTAINS • • INDUSTRIES TAKE ADVANTAGE OF THE RESOURCES AND LANDFORMS OF THE AREA WHISTLER ATTRACTS A SIGNIFICANT NUMBER OF …. WEST COAST EXTREME • WHY WOULD EARLY SETTLERS HAVE FOUND THIS REGION DIFFICULT TO CROSS? • WHAT WOULD DISCOURAGE SETTLERS FROM REMAINING IN THIS REGION? THE INTERIOR PLATEAU • A HIGHLAND FLAT AREA • THE INTERIOR OF BRITISH COLUMBIA IS A MIXTURE OF SMALL MOUNTAIN RANGES AND HIGH FLATLAND AREAS (hence, “plateau”) • LOADED WITH VALUABLE METALLIC MINERALS • DUE TO GLACIAL AND RIVER DEPOSITS = EXCELLENT FARMLAND! INTERIOR PLATEAUS • DESCRIBE TWO THINGS ABOUT THIS LANDSCAPE USING THE IMAGE TO THE LEFT The Interior Plateau • EVEN THOUGH IT IS IN THE MOUNTAINS, THERE ARE A NUMBER OF WELL KNOWN COMMUNITIES WHERE PEOPLE FARM AND RANCH • PLACES SUCH AS PENTICTON, KELOWNA, OKANAGAN VALLEY AND GOLDEN ARE IMPORTANT COMMUNITIES The Interior Plateau • Tourism is a big industry • What types of tourist activities would take place here? (record your answer) The Rockies THE ROCKIES • CANADA’S LARGEST AND YOUNGEST MOUNTAINS • WHAT WOULD YOU TELL A FRIEND ABOUT ROCKIES’ VEGETATION AND CLIMATE? (record your answer) • IF THE CAMERA POINTS NORTH, WHAT TIME OF DAY IS IT IN THE 2nd PICTURE? (6am, 9am, 5pm or 7pm?) Lake Louise • This is one of Canada’s most favoured tourist spots - Chateau Lake Louise • What is the flat surface in the foreground? • What are the almost straight lines on the mountain slopes? Unlike flat regions, mountains are known for fastflowing rivers which gouge/cut steep valleys in the landscape In what ways do the climate and vegetation change as you go up the mountainside? The Rockies are home to many alpine glaciers • A narrow channel of ice which slides down a mountain. • Snow accumulates at the top of the glacier/ melts at the bottom • What season is shown in this image? Interior Plains The Interior Plains (Prairies) • Once the bed of a huge sea between the Canadian Shield and the Rockies = mineral deposits • Glaciation = deposits • Mostly flat • Composed of sedimentary rocks • Highly suitable for farming where climate offers the right conditions The Interior Plains A typical huge prairie farm. The Prairies • Known for its relatively dry climate Vegetation on the Interior Plains • Is this ‘parkland’ or ‘grassland’? • What type of vegetation would you expect to see farther north where it is colder and damper? (record your answer) The Interior Plains Economy • Agriculture is one of the most important activities in the Interior Plains • What other major resource activity takes place there? (record your answer) Transport on the Prairies Canada’s wheat basket requires many kilometers of rail lines to deliver wheat to Vancouver, Hudson Bay and Thunder Bay Canadian Shield The Canadian Shield • Largest region in Canada and the geographic foundation of Canada • Among the oldest known rocks on the planet • Formed by volcanic activity, therefore mostly igneous rock (but lots of metamorphic rock too) = valuable metallic minerals • Cold winters, warm summers, precipitation all year give it a distinctive type of vegetation CANADIAN SHIELD • Stretches from Arctic to Great Lakes, from Mackenzie delta to Atlantic • Soils are thin - a poor choice for agriculture/farming in most places • But the drainage of the Shield = winding rivers, lakes, and wetlands. Great for tourism! TYPICAL FEATURES OF THE CANADIAN SHIELD • What does the vegetation tell you of the location of this part of the Shield? • Name two typical features of the Shield shown by this picture Canadian Shield Wildlife Vegetation on the Shield • White patches reveal the extraction of resources on the Shield. • What resource is being extracted? Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands Great Lakes St. Lawrence Lowlands • Most southerly and smallest landform region of Canada • Newest landform region • Formed by the action of glaciers scraping away and re-depositing material on the landscape • Consists of lakes, valleys and rolling hills Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands • Why would landforms of this region favour large scale settlement? Comment on: soil, climate, flat land for transportation • Densely populated • Many of Canada’s largest cities “Canada’s industrial and urban heartland” • What is meant by the term ‘high density’? People/KM Gt. Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands Southern Ontario Farming • Much of this region is taken up with dairy farming • What products are created in dairy farming? • Why is dairy farming important to this area? Other features of this region • The image shows a popular part of Southern Ontario. • Why is southern Ontario a popular tourist destination? (record your answer) The Appalachians APPALACHIANS • How would you describe to a friend the land in this image? (record your answer) • This is part of the Cabot Trail on Cape Breton Island • Oldest highland region in Canada made mostly of sedimentary rock = nonmetallic minerals like coal • Land sank and “Drowned coastline” after last Ice Age = deep harbours The Maritimes • While the Atlantic provinces have relatively poor economies, still many people want to live there. • What features of Atlantic life would encourage people to live there? (record your answer) Nova Scotia • The flatter land next to the sea reveals the location of the old shoreline New Brunswick • Compare this landscape to southern Ontario • What is similar and what is different? ARCTIC AND HUDSON BAY LOWLANDS • Usual to think the Arctic has few if any plants • When would you expect to see the most Arctic growth? • But ground remains frozen for most of the year • Deposits = coal, oil and natural gas The Arctic - the most varied Canadian region • This is the Brodeur peninsula of Baffin Island NT • Describe the shape of the land, the amount and type of vegetation, the amount of water present Brodeur Peninsula Baffin Island NT • These are called Hoodoos • What kind of erosion do you think formed them? Baffin Island Greenshield Glacier • Continental glaciers or icefields Shark Fjord • This valley was carved out by a narrow band of glacial ice cutting into the plateau on either side Labrador - Torngat Mountains NL Ayr Lake - Baffin Island NU • Very remote to most Canadians • Some mining industries are leaving a permanent mark on the landscape District of Mackenzie NT District of Mackenzie • What season is this? • What evidence is there that this area experiences warm summers? • Describe the nature of soil in this region District of Mackenzie • Why would these features be called ‘kettles’? • Where do these ‘kettles’ drain out? • Formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters.