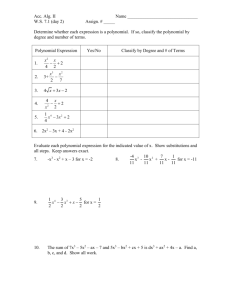
Math I Alignment to Appendix A
advertisement

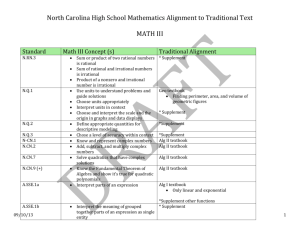
North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Traditional Text MATH I Standard N.RN.1 N.RN.2 N.Q.1 Math 1 Concept(s)/Skill N.Q.2 N.Q.3 A.SSE.1a A.SSE.1b A.SSE.2 A.SSE.3a 09/10/13 Properties of rational exponents with numerator of 1 Radicals to exponent form Exponents to radicals Using units to understand problems and guide solutions Choose units appropriately Interpret units in the context of the problem Choose and interpret scale and origin in graphs and data displays. Define appropriate quantities for descriptive modeling. Choose a level of accuracy within context Interpret parts of an expression limited to linear, quadratic and exponential (with integer exponents) Interpret the meaning of grouped together parts of an expression as a single entity Rewriting expressions by, combining like terms, expanding and factoring Factor a quadratic expression Interpret zeros of a quadratic function Traditional Alignment Integer exponents in Alg I textbook * Supplement rational exponents with numerator of 1 in Alg II textbook Alg II textbook Geometry textbook Finding the perimeter, are and volume of geometric figures * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement Alg 1 textbook Linear and exponential are found in * Supplement * Supplement Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg 1 textbook North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I within context A.APR.1 A.CED.1 A.CED.2 A.CED.3 A.CED.4 A.REI. 1 A.REI.3 A.REI.5 A.REI.6 08/03/13 Add, subtract and multiply polynomial limited to linear a quadratic expressions Create and solve equations and inequalities with one variable limited to linear and exponential. Create and graph equations with two or more variables limiting to linear, quadratic and exponential (integer inputs) Represent constraints by equations or inequalities and by systems of equations an inequalities focus on linear functions Interpret solutions Solving multivariable formulas or literal equations for a specific variable Using mathematical properties to justify each step when solving simple equations Solving one variable linear equations and inequalities, including coefficients Prove that the a system and a multiple of the same system have the same solution Combining equations maintain inequality and hence elimination work Solving systems by substitution and elimination * Supplement with other resources for contextual examples. Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks * Supplement creating quadratics with other resources. Alg II textbooks Alg I textbook Alg I textbook Alg I textbook * Supplement Alg I textbook 2 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I A.REI.10 A.REI.11 A.REI.12 F.IF.1 F.IF.3 F.IF.4 08/03/13 Graph solution to a linear inequality in two variables and recognize solutions as a half plane Graph system of inequalities and recognize the solution as the intersection of the corresponding half planes Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks * Supplement for all types of functions Alg I textbook Domain and range of a function Understand the one to one and many to one nature of a function Use function notation to write an equation Alg I and Alg II textbooks Use, evaluate and interpret statements written in function notation focusing on linear and exponential functions Alg I and Alg II textbooks Interpret key features of graphs and tables Given verbal description, sketch graphs given key features focus on but not limited to linear exponential and quadratic functions Alg I and Alg II textbook F.IF.2 Graph of an equation represent all the solutions limited to linear and exponential Solving systems using function notation focus on linear and exponential * Supplement identifying key features of a graph within context 3 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I F.IF.6 F.IF.7a F.IF.5 F.IF.7e Graph functions expressed symbolically by hand or using technology Show key features of the graph Focus on but not limited exponential functions, logarithmic and trigonometric may be explores F.IF.8a F.IF.8b F.IF.9 F.BF.1a F.BF.1b 08/03/13 Identify the domain of a function in context Relate the domain of a function to its graph Calculate average rate of change (symbolically or from a table) Interpret the rate of change in context Estimate rate of change from a graph Graph linear and quadratic functions expressed symbolically by hand or using technology Show key features of the graph Using the processes of factoring to show zeros of a function Interpret exponential functions in terms of growth or decay and percent rate of change Compare properties of two functions represented in different ways Give context, write a function using an explicit expressions, recursive process or showing steps for calculation Combine standard function types using * Supplement necessary for domain in context. Alg I textbook Alg I and Alg II text Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I textbook Alg I and Alg II textbooks * Supplement Alg II textbook * Supplement recursive process Alg II textbook 4 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I F.BF.2 F.BF.3 F.LE.1a F.LE.1b F.LE.1c F.LE.2 F.LE.3 F.LE.5 G.CO.1 08/03/13 arithmetic operations Model situations to write arithmetic and geometric sequences using informal recursive notation Identify the effect algebraic transformations to include translations, reflections and dilations. Proving when a situation can be represented using a linear or an exponential model. Recognize when a quantity changes a constant rate per unit interval relative to another Recognize when a quantity changes by a constant percent rate per unit interval relative to another Construct linear and exponential functions, including sequences, from a graph, description or two input-output pairs. Understanding that quantity increasing exponentially will eventually exceed all others. Understand and identify the practical and impractical domain in linear and exponential functions Define angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, line segment * Supplement Alg II textbook * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement Alg I textbook * Supplement * Supplement Alg I and Geometry textbooks 5 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I G.GPE.4 G.GPE.5 G.GPE.6 G.GPE.7 G.GMD.1 G.GMD.3 S.ID.1 S.ID.2 S.ID.3 S.ID.5 S.ID.6a S.ID.6b S.ID.6c 08/03/13 Using coordinates to algebraically prove simple geometric theorems Prove and use slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines Finding the midpoint Use coordinates to evaluate perimeters of areas Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri’s principle and informal limits arguments to understand formulas for circumference, area of circle and volume of cylinder, pyramid and cone Volume of cylinders, cones and spheres Represent data using dot plots, box plots and histogram Compare the center and spread of data of two or more data sets Interpret differences in shape, center and spread in the context of data Generate frequency tables Interpret relative frequencies Recognize associations and trends in data Fit functions to a data set Use functions to solve problems in context Focus on linear and exponential models Calculate and analyze residual points Use algebraic methods and technology to fit Geometry textbook Geometry textbook Alg I and Geometry textbook Geometry textbook * Supplement Geometry textbook * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement 6 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Core-Plus Mathematics MATH I S.ID.7 S.ID.8 S.ID.9 08/03/13 linear function to data Interpret slope and intercept of a linear model in context Compute and interpret correlation coefficient Distinguish between correlation and causation * Supplement * Supplement 7