Activity 2 Composition of Matter Practice Problems pt 2
advertisement
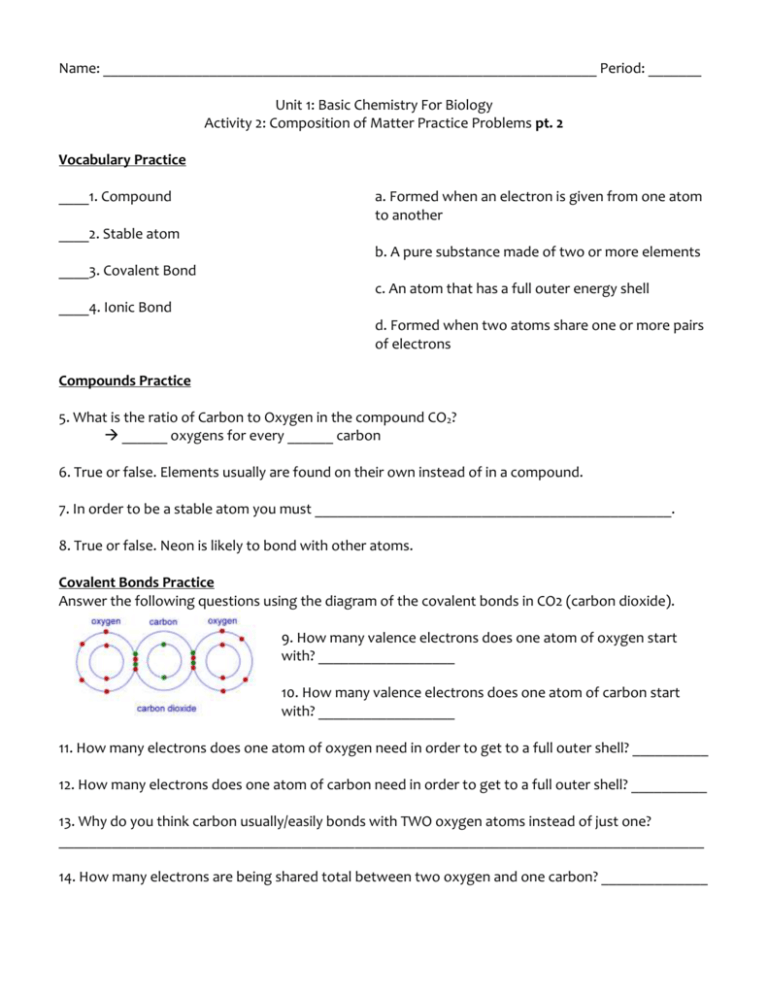
Name: _________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ Unit 1: Basic Chemistry For Biology Activity 2: Composition of Matter Practice Problems pt. 2 Vocabulary Practice ____1. Compound a. Formed when an electron is given from one atom to another ____2. Stable atom b. A pure substance made of two or more elements ____3. Covalent Bond c. An atom that has a full outer energy shell ____4. Ionic Bond d. Formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons Compounds Practice 5. What is the ratio of Carbon to Oxygen in the compound CO2? ______ oxygens for every ______ carbon 6. True or false. Elements usually are found on their own instead of in a compound. 7. In order to be a stable atom you must _______________________________________________. 8. True or false. Neon is likely to bond with other atoms. Covalent Bonds Practice Answer the following questions using the diagram of the covalent bonds in CO2 (carbon dioxide). 9. How many valence electrons does one atom of oxygen start with? __________________ 10. How many valence electrons does one atom of carbon start with? __________________ 11. How many electrons does one atom of oxygen need in order to get to a full outer shell? __________ 12. How many electrons does one atom of carbon need in order to get to a full outer shell? __________ 13. Why do you think carbon usually/easily bonds with TWO oxygen atoms instead of just one? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. How many electrons are being shared total between two oxygen and one carbon? ______________ Ionic Bonds Practice Answer the following questions using the diagram of the ionic bond between lithium and fluorine. 15. How many valence electrons does lithium start with? ________ 16. How many valence electrons does fluorine start with? _______ 17. What would be easier for lithium to do in order to get a full outer energy level? a. bond with 7 other atoms in order to have 8 valence electrons b. give away its 1 valence electron, and leave itself with a full 1st energy level. 18. Originally, lithium has 3 electrons and 3 protons. The 3 negatively charged electrons cancel out the 3 positively charged protons. By giving away one electron, lithium now has ______ electrons and ______ protons. This means that lithium now has more ______________(choose one: protons OR electrons) and becomes ________________ (choose one: positively OR negatively) charged. 19. Originally, fluorine has 9 electrons and 9 protons. The 9 negatively charged electrons cancel out the 9 positively charged protons. By accepting one electron, fluorine now has ______ electrons and ______ protons. This means that fluorine now has more ______________ (choose one: Protons OR Electrons) and becomes _________________ (choose one: Positively OR Negatively) charged. ____20. Lithium ____21. Flourine a. positive ion b. negative ion 22. After electrons have been transferred, why are the ions attracted to each other to form a bond? ___________________________________________________________________________________





