Test Plan and Test for 8th grade
advertisement

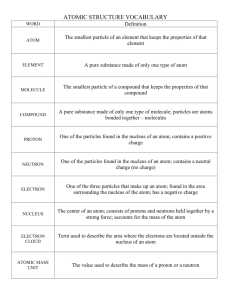
Test Plan Learning Targets Atomic Structure (1) I can identify the parts of an atom which made up its structure. (nucleus, electron cloud, neutron, electron, proton) (2) I can distinguish the parts of an atom based upon mass and charge. (proton, electron, neutron) (3) I can demonstrate, in words and pictures, how the size of an atom compares to a visible object. (4) I know what holds an atom together. Periodic Table (5) I can define an element. (single type of atom) (5) I can classify atoms into element categories. (9) I can classify substances using reactivities into like groups (families). (6) I can describe patterns from periods and families from the periodic table. (8) I can predict missing elements based upon existing pattern. (6) I can identify chemical trends using atomic numbers and data in tables/graphs (flammability, and reactivity). (6) I can identify physical trends using atomic numbers and data in tables/graphs (density, boiling point, and solubility). (7) I can identify groups of elements with similar properties (metals, non-metals and non-reactive). (9) I can use reactivities to classify substances into like reactivity groups. (9) I can rank order reactivity based upon data patterns. Biogeochemical (10) I can compare the elements essential for life to those found in the Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. – no questions related to this target (11) I can make inferences about the source of these elements. (12) I can identify processes that produce and consume organic forms of carbon molecules and CO2 molecules. (13) I can explain how a plant uses CO2. (14) I can explain a plant’s role in carbon cycling. (15) I can describe how matter and energy are transformed in a food chain and ecosystems. (16) I can describe how matter and energy are transformed during decomposition. (17) I can describe interactions between the bio- and atmosphere in terms of carbon cycling. (18) I can describe how plants store Carbon. (19) I can explain how land use decisions can cause imbalance in the amount of Carbon released or stored. (20) I can describe how soils store Carbon. (21) I can explain how different variables affect decomposition by soil organisms. 1 Conservation of Matter (22) I can modify the definition of matter (to include the concepts of atom and element). (23) I can explain the relationship between atoms and the conservation of matter. (23) I can use the existence of atoms to demonstrate the conservation of matter. (23) I can interpret evidence which supports the conservation of matter. Modeling I can explain how models are predictive. I can use a model to explain the effect of increasing and decreasing scale (in 2-D and 3D). I understand that even the best representation of an atom does not exactly depict what an atom is like. I can distinguish between different forms of models. I can analyze multiple, basic atomic structure models for advantages and limitations. I can identify the form of model to use. I can explain that the type of model you use is based upon the model’s purpose. 2 8th Grade Structure and Transformation of Matter Directions: Selection the best answer to the question and mark your answer on the scantron using a number 2 pencil. 1. Which of these conclusions can be drawn from Rutherford’s experiment as diagramed below? Polonium in lead box Gold foil > 90 occasional Alpha particles Fluorescent screen 0˚-many <90-few a. b. c. d. e. Each atom contains electrons. The nucleus of an atom can be split. Each atom contains protons. Atoms are mostly empty space. Neutrons are found in the center of the atom. 2. What is in between the electrons and nucleus of an atom? a. Nothing b. Air c. Water vapor d. Smaller atoms e. No one knows. 3. The mass of a proton is _______ the mass of an electron. a. equal to b. greater than c. smaller than d. cannot compare the mass of a proton and electron 3 4. An electron has a charge of ___. a. -1 b. +1 c. -0.5 d. 0 5. If an electron is removed from a neutral atom, the result is __. a. b. c. d. a large reduction of mass and no charge change nearly no change in mass and no change in charge a large reduction in mass and a change in charge nearly no change in mass and a change in charge 6. Select the best relationship between the electron cloud and the nucleus a. b. c. d. Ping -pong ball (nucleus) and tennis ball (electron cloud) BB (nucleus) and ping pong ball (electron cloud) BB (nucleus) and plastic beach ball (electron cloud) Beach ball (nucleus) and tennis ball (electron cloud) 7. The reason why the electron cloud and the nucleus stay together is __. a. b. c. d. because it is the way nature intended it to work that they are melted together that they are chemically bonded together an electromagnetic attraction 8. Atoms of the same element must contain ___. a. equal numbers of protons and neutrons b. the same number of protons c. the same number of neutrons d. the same numbers of electrons 9. From the choices below, which is the most active alkali metal (group 1 metal)? a. b. c. d. Li Na K Rb 4 10. In the periodic table, the elements are organized ____. a. b. c. d. e. by discovery date by volume by color by the similarity of properties None of the above. 11. According to the periodic table, which of the following series of elements is ordered from most to least reactive? a. He, Cs, Si, Mg b. Ca, Mg, Si, He c. Si, He, Cs, Mg d. Mg, Si, Cs, He e. none of the above 12. Which element is most likely to display both metallic and non-metallic qualities? H He c a b e d a. (a) b. (b) c. (c) d. (d) e. (e) 5 13. Which of the following must be the same before and after a chemical reaction? a. b. c. d. e. The sum of the masses of all substances involved. The number of molecules of all substances involved. The number of atoms of each type involved. Both (a) and (c) must be the same. Each of the answers (a), (b), and (c) must be the same. 14. Which statement about matter is TRUE? a. Atoms are not matter but they are contained in matter. b. Matter exists only when you can see it. c. Living things are not matter. d. Matter is made up of atoms. 15. A student places some baking soda and a jar of lemon juice in a plastic bag and seals the bag. She weighs the bag and everything in it. She shakes the bag so that the lemon juice spills out of the jar and mixes with the baking soda inside the bag. The student observes that bubbles form and the bag expands. If the student weighs the bag and everything in it after the bubbling stops and compares the final weight to the starting weight, what will she find out? a. The final weight will be greater than the starting weight because new atoms are produced during the experiment. b. The final weight will be less than the starting weight because some of the atoms are destroyed during the experiment. c. The final weight will be the same as the starting weight because the number of each kind of atom does not change during the experiment. d. The final weight will be the same as the starting weight because some atoms are destroyed, but new ones are created during the experiment. 6 16. Iron combines with oxygen and water from the air to form rust. If an iron nail were allowed to rust completely, one should find that the rust weighs: a. less than the nail it came from. b. the same as the nail it came from. c. more than the nail it came from. d. it is impossible to predict about the weight. 17. Which is bigger, an atom or a blood cell? a. The atom is bigger. b. The blood cell is bigger. c. They are both the same size. d. It depends on the kind of atom. 7 Name ____________________________ Class _________________ Teacher ____________ Open Response Questions Directions: Write your answer to this question below. Be as complete as possible. A. What is the definition of a scientific model? B. Provide 2 examples and 2 non-examples of a scientific model. Explain why the examples are or are not a scientific model. 8 Biogeochemical Cycles 18. In order for a biogeochemical cycle to function properly: a. The amount of energy must exceed the amount of matter in the system. b. The amount of matter must exceed the amount of energy in the system. c. Matter must be recycled continually. d. There must be a perfect balance of matter and energy. 19. The chemical reaction of photosynthesis naturally occurs in the presence of sunlight because the light: a. is one of the reactants. b. helps oxygen to “see” carbon dioxide. c. vaporizes water. d. provides the energy to start the reaction. e. brings the oxygen into the plant. 20. Predict what would happen to the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide if a large percentage of earth's animal life was killed by a disease. a. It would decrease because there would be more oxygen released and recombined into carbon dioxide. b. It would decrease because there would be less glucose broken down and recombined into carbon dioxide. c. It would increase because there would be less oxygen released and recombined into carbon dioxide. d. It would increase because there would be more glucose broken down and recombined into carbon dioxide. 21. Planting more trees would mean: a. More carbon dioxide in the air b. Less carbon dioxide in the air c. Less oxygen in the air d. No change Use the following graph for questions 22 – 9 22. Which of the following might account for the increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) over the past 50 years as measured at Mauna Loa, Hawaii? a. Increased planting of trees worldwide b. Increased deforestation worldwide c. Increased burning of fossil fuels d. Both a and c e. Both b and c 23. Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the atmosphere fluctuates with a predictable pattern annually. Seasonal changes in rate for which of the following processes is the best explanation? a. Respiration b. Photosynthesis c. Combustion d. Decomposition 10 Name ____________________________ Class _________________ Teacher ____________ Open Response Questions Directions: Write your answer to this question below. Be as complete as possible. 2. A small oak tree was planted in a meadow. After 20 years, it has grown into a big tree, weighing 500 kg more than when it was planted. Do you think the tree will need any of the following things to grow and gain weight? Please circle Yes or No and explain your choice. Things Does the tree need it to grow bigger? Sunlight Yes No Soil Yes No Water Yes No Carbon Dioxide Yes No Explain your choice. 11 3. A tree falls in the forest. After many years, the tree will appear as a long, soft lump on the forest floor. The lump on the forest floor weighs less than the original tree. a. Explain what processes caused the weight to become less. b. Where would you find the matter that used to be in the tree? c. Explain how energy is involved for the tree to decay. 12 Test Plan Analysis Sheet Name _____________________ Target 1 1 2 2 2 3 4 5 6 or 9 6 6 or 9 7 22 22 23 23 scale 11 12 12, 15, 17 13, 14 12, 17 12, 13 Question Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Right/Wrong Simple Mistake Do not know What targets did I do well on? ___________________________________ Which targets do I still need to work on? _____________________________________ 13 Test Plan Analysis and Answer Sheet Name _____________________ Target 1 1 2 2 2 3 4 5 6 or 9 6 6 or 9 7 22 22 23 23 scale 11 12 12, 15, 17 13, 14 12, 17 12, 13 Question Number 1 D 2 A 3 B 4 A 5 D 6 D 7 D 8 B 9 D 10 D 11 B 12 C 13 D 14 D 15 C 16 C 17 B 18 C 19 D 20 D 21 B 22 E 23 B Right/Wrong Simple Mistake Do not know What targets did I do well on? ___________________________________ Which targets do I still need to work on? _____________________________________ 14