Rhythm card - WordPress.com
advertisement
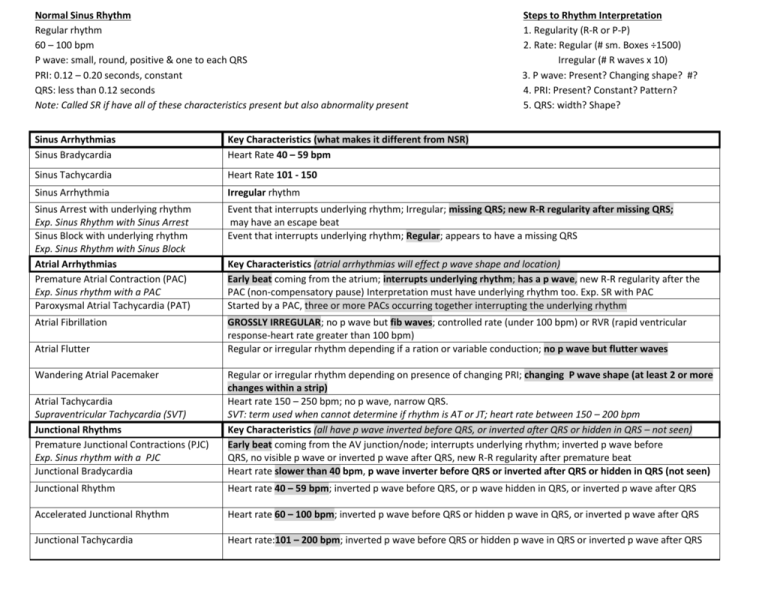
Normal Sinus Rhythm Regular rhythm 60 – 100 bpm P wave: small, round, positive & one to each QRS PRI: 0.12 – 0.20 seconds, constant QRS: less than 0.12 seconds Note: Called SR if have all of these characteristics present but also abnormality present Steps to Rhythm Interpretation 1. Regularity (R-R or P-P) 2. Rate: Regular (# sm. Boxes ÷1500) Irregular (# R waves x 10) 3. P wave: Present? Changing shape? #? 4. PRI: Present? Constant? Pattern? 5. QRS: width? Shape? Sinus Arrhythmias Sinus Bradycardia Key Characteristics (what makes it different from NSR) Heart Rate 40 – 59 bpm Sinus Tachycardia Heart Rate 101 - 150 Sinus Arrhythmia Irregular rhythm Sinus Arrest with underlying rhythm Exp. Sinus Rhythm with Sinus Arrest Sinus Block with underlying rhythm Exp. Sinus Rhythm with Sinus Block Atrial Arrhythmias Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) Exp. Sinus rhythm with a PAC Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia (PAT) Event that interrupts underlying rhythm; Irregular; missing QRS; new R-R regularity after missing QRS; may have an escape beat Event that interrupts underlying rhythm; Regular; appears to have a missing QRS Atrial Fibrillation GROSSLY IRREGULAR; no p wave but fib waves; controlled rate (under 100 bpm) or RVR (rapid ventricular response-heart rate greater than 100 bpm) Regular or irregular rhythm depending if a ration or variable conduction; no p wave but flutter waves Atrial Flutter Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Key Characteristics (atrial arrhythmias will effect p wave shape and location) Early beat coming from the atrium; interrupts underlying rhythm; has a p wave, new R-R regularity after the PAC (non-compensatory pause) Interpretation must have underlying rhythm too. Exp. SR with PAC Started by a PAC, three or more PACs occurring together interrupting the underlying rhythm Atrial Tachycardia Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Junctional Rhythms Premature Junctional Contractions (PJC) Exp. Sinus rhythm with a PJC Junctional Bradycardia Regular or irregular rhythm depending on presence of changing PRI; changing P wave shape (at least 2 or more changes within a strip) Heart rate 150 – 250 bpm; no p wave, narrow QRS. SVT: term used when cannot determine if rhythm is AT or JT; heart rate between 150 – 200 bpm Key Characteristics (all have p wave inverted before QRS, or inverted after QRS or hidden in QRS – not seen) Early beat coming from the AV junction/node; interrupts underlying rhythm; inverted p wave before QRS, no visible p wave or inverted p wave after QRS, new R-R regularity after premature beat Heart rate slower than 40 bpm, p wave inverter before QRS or inverted after QRS or hidden in QRS (not seen) Junctional Rhythm Heart rate 40 – 59 bpm; inverted p wave before QRS, or p wave hidden in QRS, or inverted p wave after QRS Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Heart rate 60 – 100 bpm; inverted p wave before QRS or hidden p wave in QRS, or inverted p wave after QRS Junctional Tachycardia Heart rate:101 – 200 bpm; inverted p wave before QRS or hidden p wave in QRS or inverted p wave after QRS AV BLOCKS A rhythm with 1st degree AVB Exp. Sinus Rhythm with 1st degree AVB 2nd degree AV Block, Type I (little boy late for school bus) 2nd degree AV Block, Type II (how many phone calls to get gossip) 3rd degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block- CHB) (divorced couple) Ventricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) Exp. Sinus rhythm with a PVC Ventricular or Idoventricular Rhythm Key Characteristics (conduction delays; altered PRI and number of p waves) Regular; long PRI (greater than .20 sec) and constant; state underlying rhythm Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm Regular rhythm: 50 – 100 bpm; no p wave; wide QRS Ventricular Tachycardia Regular rhythm: 150 – 250 bpm; no p wave; wide QRS Torsades de pointes (polymorphic VT) Regularly irregular; greater 200 bpm; no p wave; changing QRS width and amplitude of QRS Ventricular Fibrillation Chaotic waves without form, no QRS, no heart rate but movement in isoelectric line indicates fast activity. Ventricular Standstill Regular p waves only (no QRS complexes) Ventricular Asystole Asystole Pulseless Electrical Activity Wide QRS complex to no wave forms (isoelectric line) No waveforms; isoelectric line Looks like Normal Sinus Rhythm or Sinus Bradycardia but the patient does not have a pulse Pacemaker Rhythm Pacer spike either replacing or beginning of the p wave or the QRS complex or both Number of Small Boxes 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Rate per Minute 300 250 214 188 167 150 136 125 115 107 Irregular; more p waves than QRS complexes, progressively lengthening PRI until missing QRS and then it is shorter after missing QRS than previous PRI Regular or irregular depending on the conduction; ratio conduction if same number of p waves between QRS or irregular if changing number of p waves between QRS; more p waves; constant PRI Regular: more p waves than QRS; no constant PRI ; p waves may be hidden in other wave forms. Can march out p waves. Both p waves and R waves are regular. Key Characteristics (all rhythms have wide QRS and no p wave) Early beat from the ventricles; rhythm regular or irregular; no p wave; wide QRS; R-R regularity is not reset after the premature beat (compensatory pause); state underlying rhythm; T wave opposite direction of QRS Regular rhythm: 20 – 40 bpm; no p wave; wide QRS; Heart Rate Card Number of Small Boxes 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Rate per Minute 100 94 88 84 79 75 72 68 65 63 (1500 divided by number of small boxes counted between R waves) Number of Rate per Number of Rate per Number of Small Boxes minute Small Boxes Minute Small Boxes 25 60 35 43 45 26 58 36 42 46 27 56 37 41 47 28 54 38 40 48 29 52 39 39 49 30 50 40 38 50 31 48 41 37 32 47 42 36 33 45 43 35 34 44 44 34 Rate per Minute 33 33 32 31 31 30