Disorders of the Integumentary system
advertisement
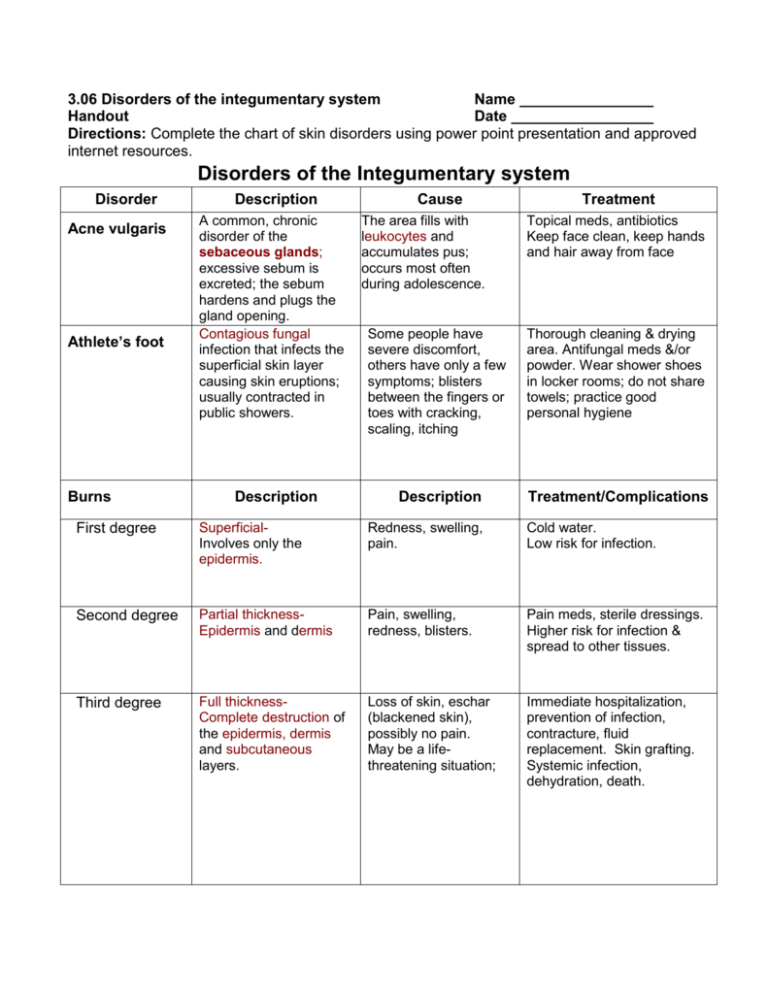
3.06 Disorders of the integumentary system Name ________________ Handout Date _________________ Directions: Complete the chart of skin disorders using power point presentation and approved internet resources. Disorders of the Integumentary system Disorder Acne vulgaris Athlete’s foot Burns Description A common, chronic disorder of the sebaceous glands; excessive sebum is excreted; the sebum hardens and plugs the gland opening. Contagious fungal infection that infects the superficial skin layer causing skin eruptions; usually contracted in public showers. Description Cause The area fills with leukocytes and accumulates pus; occurs most often during adolescence. Treatment Topical meds, antibiotics Keep face clean, keep hands and hair away from face Some people have severe discomfort, others have only a few symptoms; blisters between the fingers or toes with cracking, scaling, itching Thorough cleaning & drying area. Antifungal meds &/or powder. Wear shower shoes in locker rooms; do not share towels; practice good personal hygiene Description Treatment/Complications First degree SuperficialInvolves only the epidermis. Redness, swelling, pain. Cold water. Low risk for infection. Second degree Partial thicknessEpidermis and dermis Pain, swelling, redness, blisters. Pain meds, sterile dressings. Higher risk for infection & spread to other tissues. Third degree Full thicknessComplete destruction of the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layers. Loss of skin, eschar (blackened skin), possibly no pain. May be a lifethreatening situation; Immediate hospitalization, prevention of infection, contracture, fluid replacement. Skin grafting. Systemic infection, dehydration, death. Disorder Dermatitis Eczema Herpes Description Inflammation of the skin. Non-contagious rash. Psoriasis Ringworm Treatment The cause may be non-specific (allergic reaction, stress, exposure to chemicals). Same Remove the causative agent; topical ointments to alleviate the symptoms. Painful blisters that rupture and leave sores. Spread by oral secretions, sexual contact. If a pregnant woman has symptoms when the delivery date arrives, the baby may become infected when passing through the vagina. A c-section may be performed. No cure; treat with Acyclovir a anti-viral medication. Acute, inflammatory and contagious skin disease seen in babies and young children. Two bacteria cause impetigo- vesicles that rupture and develop yellow crustsStaphylococcus or streptococcus organism. Topical antibacterial cream or oral antibiotics. Don’t share toys, bedding, towels, etc. Chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by the development of dry reddish patches covered with silvery-white scales; affects skin over elbows, knees, shins, scalp, lower back. More common in adults. Unknown. No definite treatment at present. Moisturizers. Highly contagious fungal infection; raised, itchy, circular patches with crusts. Fungus (tinea). It spreads Skin-to-skin contact with a person or animal, sharing Antifungal meds & creams. Acute (< 6 months), chronic (>6 months), non-contagious inflammatory skin disease. Viral infection that is usually seen as a blister. Two types of HSV: HSV type 1-causes sores around the mouth and lips (cold sores/fever blisters). HSV type 2- Genital Herpes -sores around the genitals or rectum. Impetigo Cause Same towels, sports equipment Scabies Shingles Skin Cancer A condition of very itchy skin caused by tiny mites that burrow into your skin. It is highly contagious, spread by close, physical contact, sexual contact, sharing towels, bed sheets. It will not go away on its own, special Scabies med is needed Painful skin eruptions due to a virus infection of the nerve endings. People most at risk are those who have had chicken pox, 50 or older, weakened immune system. Caused by the same virus that causes chicken pox (herpes zoster). It is contagious. But it can be spread to people who have not had chicken pox. Anti-viral creams & meds. Vaccine for prevention. Description Cause Treatment/Possible Complications (Primary causesunlight!) Basil Cell The most common and least malignant type of skin cancer. Usually occurs on the face. Start in the epidermis & spread. Squamous Cell Arises from the epidermis Arises from epidermis Malignant Melanoma and occurs most often on the scalp and lower lip, & grows rapidly and metastasizes to the lymph nodes. Occurs in melanocytes and metastasizes to other areas quickly; may appear as a brown or black irregular patch which occurs suddenly; a color or size change in a pre-existing mole or wart. Exposure to ultraviolent light from the sun and tanning beds. Surgical removal, radiation, cryosurgery (Freezing). Limit exposure to direct sunlight. Surgical removal or radiation. Limit exposure to direct sunlight. Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation. Limit exposure to direct sunlight. Skin Lesions Macule Abnormal area on the skin. Solid, elevation, <1cm = elevated nevi Pustule Small blister filled with pus, < 0.5cm = acne, impetigo Decubitus ulcer Vesicle Warts = Nodule = solid elevation varies Flat local change in skin color = freckle Papule Ulcer varies Depressed lesion of epidermis & upper dermis = stage 2 pressure ulcer Bedsore: a deep loss of skin surface that may extend into the dermis; occur when a person is constantly sitting or lying in the same position. Turning, repositioning frequently, relief of pressure on bony areas. Remove damaged tissue, dressings, pain meds. Virus Ex: Human papilloma virus (there are over 100 kinds of HPV); YES, they are contagious! Medications, Cryosurgery (freezing), Laser treatment, Duct tape =) There are solutions to treat the warts but *they can recur after they are removed. Preventiondon’t share towels, wear shoes in public showers. Infection, even ultimately death. Small blister filled with serous fluid, = Herpes, chicken pox Small, rough, hard growth on the skin.