RNA & Transcription of DNA to RNA
advertisement

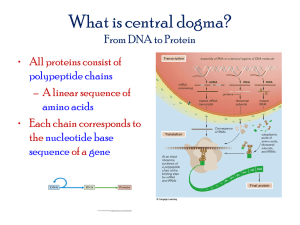
RNA & Transcription of DNA to RNA – Lesson Plan Linked to CK-12 Concepts: 1. RNA 2. Transcription from DNA to RNA Class: (Customize to your use) Date: (Customize to your use) Standard(s): (Customize to your use) Learning Activities and Timing: (Customize to your use. View this concept’s “Additional Resources” for access to even more useful materials.) Key Objective(s): Concept Objective(s): Describe the structure of RNA, and identify the three main types of RNA. Give an overview of transcription Language Objective(s): Demonstrate command of the convention of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. Use various phases and clauses to convey specific meanings and add variety and interest to writing or presentations. Exit Criteria: When students finish this lesson, they should be able to distinguish the difference between the three various RNA structures by making an acrostic poem; be able to teach transcription to another student. 1. Describe transcription. 1 2. How may mRNA be modified before it leaves the nucleus? 3. Recall today’s content and language objective. Evaluate whether you have met these objectives. Based on your own evaluation, put your paper in one of these categories; “Clueless, More practice, Sort of got it, I totally understand.” **To help the teacher gauge their student learning, you can have students evaluate themselves on the content and language objective with their completed exit tickets. Have students place in their papers into one of these four categories; “Clueless, More practice, Sort of got it, I totally understand.”** Teaching Strategies and Tips: Content Summary RNA differs from DNA in several ways. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA). Each type plays a different in role in making proteins. Introducing the Lesson: Have students chorally read out loud the Concept and Language objective two times and have them write it down in their notes. Transcription is the DNA → RNA part of the central dogma. It occurs in the nucleus. A copy of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA. The sequence of bases in DNA or RNA makes up the genetic code, which is universal, unambiguous, and redundant. Translation is the RNA → protein part of the central dogma. It occurs at a ribosome. All three types of RNA are involved in translation; mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. Take time emphasize the editing process in which RNA goes through to get mRNA. Use the video below to give students a visual idea of the transcription process. Video An animation on tRNA translating mRNA into proteins. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=41_Ne5mS2ls&feature=BFa&list=PLCA73B287977B09E9 * This was originally a clip taken from PBS production; DNA: The Secret of Life. Youtube Username: msc0328, (February 12th, 2008). Transcription and Translation. Retrieved on July 2 5ht, 2012) from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=41_Ne5mS2ls&feature=BFa&list=PLCA73B287977B09E9 Science Inquiry: This is a two step lab; translation and transcription. For this lesson use only the Transcription part. Students have a pre-lab reading before working on it. “RNATranscriptionDNAtoRNASciInq” can be found under Resources tab. Teacher preparation notes are in the teacher Version. * Waldron, Ingrid and Doherty, Jennifer. (March, 2011). From Gene to Protein. Retrieved on July 5th, 2012 from http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#dragon1 Differentiated Instruction: Tell students to create a graphic organizer, contrasting the structure and function of DNA and RNA. A sample table is shown below. RNA vs. DNA RNA DNA Full Name: Structure: Bases: Sugar: Size: Location: Common Misconceptions: None. Enrichment: Students will transcribe and translate a DNA sequence containing a mutation. Then they will perform a BLAST search to determine the protein that is encoded in the sequence. They will also infer which disease is caused by the protein. The website all the links and documents you need. http://teacherknowledge.wikispaces.com/Quist++Connecting+DNA+to+Disease+Using+BLAST 3 *Quist, Catherine. (2012). Connecting DNA to Disease Using BLAST. Retrieved on July 5th, 2012 from http://teacherknowledge.wikispaces.com/Quist++Connecting+DNA+to+Disease+Using+BLAST Review Questions: 1. What are the three main types of RNA? 2. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. Solution Guide: Answers to the Exit Criteria, and Review Questions will be available here with the Teacher version. Other answers generated from additional student handouts such as laboratory or any other introductory, differential and scientific inquiry activities will have a separate example or answer key available to the teachers. Thank you! Points to Consider: All three types of RNA are needed by cells to make proteins. - Can you develop a model in which the three types of RNA interact to make a protein? Try to elicit a range of responses. - How do you think mRNA copies the genetic instructions in DNA? How are these instructions encoded in the DNA molecule? – Sample answer: I think mRNA has a complementary sequence of bases to the DNA it copies and that the sequence of bases encodes the instructions. 4 Homework: Acrostic Poem Have students make an acrostic poem from one of the vocabulary words; messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, or transfer RNA, and translation. An example of an acrostic poem can be found here http://rebeccasatomsacrosticpoem.blogspot.com/2011/01/atoms-acrostic-poem.html * Leo, Rebecca, (January 12th, 2012). Atoms: Acrostic Poem… Retrieved on July 5th, 2012 from http://rebeccasatomsacrosticpoem.blogspot.com/2011/01/atoms-acrostic-poem.html Additional Resources: Practice I Use this resource to answer the questions that follow. http://www.hippocampus.org/Biology Function Biology for AP* Search: RNA Structure and 1. List three structural differences between DNA and RNA. 2. What is the function of mRNA? Practice II About RNA & Transcription at http://johnkyrk.com/DNAtranscription.html Practice III Use these resources to answer the questions that follow. http://www.hippocampus.org/Biology Transcription Biology for AP* Search: The Initiation of 1. What is a transcription unit? 2. Describe the importance of the template strand. 3. What enzyme is used in transcription? What does this enzyme do? 4. What are the promoter and initiation site? 5. Describe the TATA box. 6. How does RNA polymerase bind to the DNA? 5 Extra Lab In this wet lab, students will investigate how genes are regulated during development by observing differential gene expression in genetically modified plants. The Web site provides extensive pre- and post lab materials, worksheets, links, and other resources. The lab is suitable for AP biology students. http://www.moreheadplanetarium.org/files/Same_Genes_Notebook.pd Web References 1. This Web page provides many relevant links for activities, articles, online animations, quizzes, and other materials on molecular genetics. http://www.nclark.net/DNA_RNA * Clark, Nancy. (2012). DNA and RNA. Retrieved on July 5th, 2012 from http://www.nclark.net/DNA_RNA 2. This Web site from the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory provides animations, photographs, biographical sketches, problems, and links for students to learn about and explore the molecules of genetics. http://www.dnaftb.org/ * Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, (2002 – 2012). DNA from the Beginning. Retrieved on July 5th, 2012 from http://www.dnaftb.org/. 6