Physical Science Sequencing and Learning Targets
advertisement
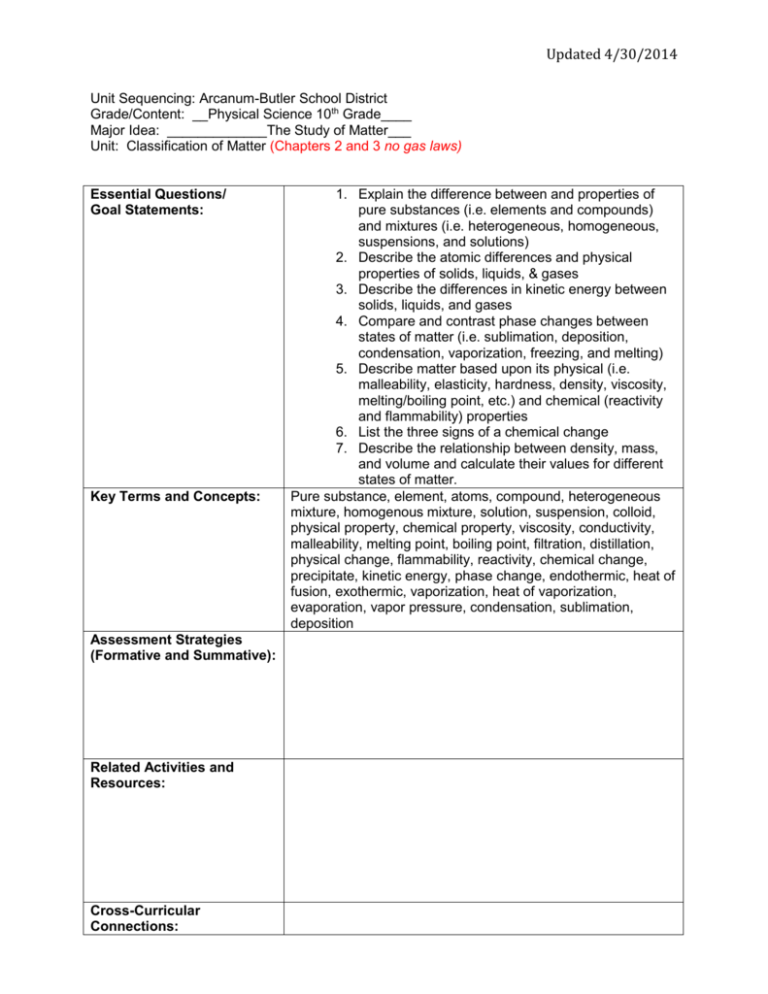
Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: __Physical Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: _____________The Study of Matter___ Unit: Classification of Matter (Chapters 2 and 3 no gas laws) Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain the difference between and properties of pure substances (i.e. elements and compounds) and mixtures (i.e. heterogeneous, homogeneous, suspensions, and solutions) 2. Describe the atomic differences and physical properties of solids, liquids, & gases 3. Describe the differences in kinetic energy between solids, liquids, and gases 4. Compare and contrast phase changes between states of matter (i.e. sublimation, deposition, condensation, vaporization, freezing, and melting) 5. Describe matter based upon its physical (i.e. malleability, elasticity, hardness, density, viscosity, melting/boiling point, etc.) and chemical (reactivity and flammability) properties 6. List the three signs of a chemical change 7. Describe the relationship between density, mass, and volume and calculate their values for different states of matter. Pure substance, element, atoms, compound, heterogeneous mixture, homogenous mixture, solution, suspension, colloid, physical property, chemical property, viscosity, conductivity, malleability, melting point, boiling point, filtration, distillation, physical change, flammability, reactivity, chemical change, precipitate, kinetic energy, phase change, endothermic, heat of fusion, exothermic, vaporization, heat of vaporization, evaporation, vapor pressure, condensation, sublimation, deposition Updated 4/30/2014 Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: ______The Study of Matter_______________ Unit: _____Atoms and the Periodic Table (Chapter 4 & 5) Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular 1. Describe the anatomy of an atom and explain the role and properties of each sub-atomic particle 2. Produce a scaled Bohr model of an atom 3. Describe the historical development of the Atomic Theory 4. Explain how the strong nuclear force holds atoms together 5. Explain the difference between atomic number and mass 6. Describe how to identify an isotope based upon atomic mass 7. Determine the correct number of electron shells and valence electrons for any element using a periodic table 8. Describe how the gain/loss of valence electrons can produce cations and anions 9. Identify and describe the physical/chemical properties of the representative groups of elements on the periodic table (i.e. metals, non-metals, transition metals, alkali metals, alkaline Earth metals, halogens, and noble gases) Proton, electron, neutron, atomic number, mass number, isotopes, valence electron, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, energy level, electron cloud, orbital, electron configuration, ground state, periodic table, period, group, periodic law, atomic mass unit, metals, transition metals, nonmetals, metalloids, valence electrons, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases Periodic Table Activity Updated 4/30/2014 Connections: Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _____Physical Science 10th Grade______ Major Idea: _____The Study of Matter________________ Unit: ___________Bonding & Compounds(Chapters 5 & 6) Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Describe how ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed 2. Describe the physical/chemical properties of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds (i.e. ionization, conductivity, bond strength, electron configurations, solubility, etc.) 3. Identify the bond type of various chemical formulas 4. Write and properly name ionic and covalent chemical formula Electron dot diagram, ion, anion, cation, chemical bond, ionic bond, chemical formula, crystals, covalent bond, molecule, polar covalent bond, polyatomic ion, metallic bond, alloy, periodic table, period, group, periodic law, atomic mass unit, metals, transition metals, nonmetals, metalloids, valence electrons, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _____Physics Science 10th Grade__ Major Idea: _____The Study of Matter____________ Unit: ____________Reactions of Matter(Chapter 7)_ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: 1. Identify the components of a chemical equation 2. Describe the role of catalysts, activation energy, and the exchange of valence electrons in a chemical reaction 3. Identify chemical reactions as either endothermic or exothermic 4. Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to properly balance chemical equations 5. Explain how an imbalance between the strong nuclear force and the repulsive electrical force of protons can produce radioisotopes 6. Describe how nuclear decay produces radiation (i.e. alpha, beta, gamma) and energy resulting in a new nucleus (daughter product) 7. Produce/analyze nuclear decay curves to calculate nuclear half-life 8. List and describe practical uses for nuclear radiation/energy (e.g. nuclear power, radiation therapy, radiometric dating) 9. Compare/contrast the process, energy production, and end products of nuclear fission and fusion 10. Describe how stellar fusion has produced all of the natural elements (i.e. stellar nucleosynthesis) Reactants, products, chemical equation, coefficients, mole, molar mass, synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, double-replacement, combustion, oxidation-reduction, chemical energy, exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction, equilibrium, reversible reaction Updated 4/30/2014 Cross-Curricular Connections: Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _____Physics Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: ______Energy & Waves_______________ Unit: ________Conservation of Energy_(Chapter 15)__ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain the first law of thermodynamics (the law of conservation of energy) 2. Explain the effects of height, mass, and velocity on potential and kinetic energy 3. Perform experiments to record and calculate the transfer/transformation of kinetic (Ek) and gravitational potential energy (Eg) in a moving system (e.g., swinging pendulum, object moving down a slope, etc.) Energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, electrical energy, electromagnetic energy, nuclear energy, energy conversion, nonrenewable energy resources, fossil fuels, renewable energy resources, hydroelectric energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, biomass energy, hydrogen fuel cell, energy conservation Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _______Physical Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: _________Energy & Waves______________ Unit: __Transfer & Transformation of Energy_(Chapter 15)_ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain the significance of Einstein's theory of relativity (E = mc2) 2. Demonstrate knowledge of the various forms of energy (i.e., nuclear, chemical, mechanical, thermal, electromagnetic, etc.) 3. Describe the energy transformations that take place in a given system Energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, electrical energy, electromagnetic energy, nuclear energy, energy conversion, nonrenewable energy resources, fossil fuels, renewable energy resources, hydroelectric energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, biomass energy, hydrogen fuel cell, energy conservation Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: _______Energy & Waves________________ Unit: ____________Waves__(Chapter 17 + some light)_ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain the structural differences between and motion of electromagnetic and mechanical waves 2. Describe how the properties of electromagnetic and mechanical waves are affected by the medium through which they travel 3. Demonstrate how reflection, refraction, diffraction, and constructive/destructive interference influence electromagnetic and mechanical waves 4. Describe the relationship between the energy of a wave and its amplitude, frequency, and wavelength 5. Organize and the divisions of the electromagnetic spectrum based upon wavelength and frequency 6. Organize the divisions of the visible spectrum based upon wavelength and frequency 7. Explain how the Doppler Effect affects electromagnetic and mechanical waves Periodic motion, period, frequency, hertz, wavelength, amplitude, reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, constructive interference, destructive interference, standing waves, node, antinode, sound waves, intensity, decibel, loudness, pitch, sonar, Doppler effect, resonance Updated 4/30/2014 Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _____Physical Science 10th Grade______ Major Idea: ________Energy & Waves________________ Unit: _____________Thermal Energy___(Chapter 16)___ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain the difference between radiation, conduction, and convection 2. Explain how thermal energy transfer influences the pressure, volume, and density of an object 3. Determine the physical factors that influence the rate of thermal conductivity (i.e., temperature, color, texture, amount of exposed surface area) 4. Describe the relationship between thermal energy absorption and emission to changes in temperature Heat, temperature, absolute zero, thermal expansion, specific heat, calorimeter, conduction, thermal conductor, thermal insulator, convection, convection current, radiation, thermodynamics, heat engine Heat Inquiry Project Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade____ Major Idea: __________Energy & Waves____________ Unit: _______________Electricity___(Chapter 20)_____ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Describe how the flow of electrons produces and electrical current 2. Compare/contrast insulators and conductors based upon the rate of electron flow 3. Describe how batteries produce an electrical current 4. Produce tangible or digital circuits to measure electric potential and voltage 5. Measure the voltage, amperage, and resistance of an electrical current through various materials Electric charge, electric force, electric field, static electricity, law of conservation of charge, induction, electric current, direct current, alternating current, electrical conductor, electrical insulator, resistance, superconductor, potential difference, voltage, batter, Ohm’s Law, electric circuit, series circuit, parallel circuit, electric power, fuse, circuit breaker, grounding Electricity Inquiry Unit Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade___ Major Idea: _________Forces & Motion_____________ Unit: ______________Motion____(Chapter 11)_______ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain how all motion is relative to the point of view of the observer 2. Describe the difference between scalar and vector quantities (i.e., speed vs. velocity and distance vs. displacement) 3. Use the appropriate formula to calculate speed, velocity, and acceleration 4. Quantify, graph, and describe the one dimensional motion of an object based upon its distance, position, displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration and time Frame of reference, relative motion, distance, vector, resultant vector, speed, average speed, instantaneous speed, velocity, acceleration, free fall, constant acceleration, linear graph, nonlinear graph Graphing Motion Activity, Vernier Probes-graphing motion Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade______ Major Idea: _________Forces & Motion________________ Unit: _______________Forces____(Chapter 12)________ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Graphically represent and calculate normal, tensional, and frictional forces on a force diagram 2. Explain how gravitational, magnetic, and electrical force fields are affected by mass and/or distance 3. Demonstrate that all objects have a free fall acceleration of 9.8 m/s/s 4. Explain how weight is influenced by both changes in gravitational acceleration and mass 5. Explain the differences between static, rolling, sliding, and fluid friction Force, newton, net force, friction, static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, fluid friction, air resistance, gravity, terminal velocity, projectile motion, inertia, mass, weight, momentum, law of conservation of momentum, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, gravitational force, centripetal force Newton’s Law Project Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: _______Physical Science 10th Grade___ Major Idea: __________Forces & Motion_____________ Unit: ________________Dynamics____(Chapter 12)___ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Describe and give examples of each of Newton's Laws of Motion 2. Utilize Newton’s Laws of Motion to predict changes in the motion of an object Force, newton, net force, friction, static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, fluid friction, air resistance, gravity, terminal velocity, projectile motion, inertia, mass, weight, momentum, law of conservation of momentum, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, gravitational force, centripetal force Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ____Physical Science 10th Grade____________ Major Idea: _______The Universe_________________________ Unit: ____________History of the Universe___(Chapters 25-26) Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Describe the current scientific evidence used to support the theory of the explosive expansion and origin of the universe, the Big Bang, over 13 billion years ago (e.g., Hubble’s Law, red and blue Doppler shifts, cosmic background radiation) 2. Research the technology used by scientists to study the origins of the universe (e.g., particle accelerators, space probes, radio, visual, and x-ray telescopes) 3. Describe the sequence of events from the Big Bang to the first hydrogen nebulae Geocentric, heliocentric, ecliptic plane, moon, astronomical unit, space probe, maria, crater, meteoroids, phases, eclipse, umbra, penumbra, tides, spring tide, neap tide, terrestrial planets, asteroids, asteroid belt, gas giants, ring, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud, solar nebula, protoplanetary disk, planetesimals, accretion, core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona, solar wind, sunspots, prominences, solar flare, star, light-year, parallax, apparent brightness, absolute brightness, absorption lines, H-R diagram, main sequence, supergiants, giants, white dwarf, nebula, protostar, planetary nebula, pulsar, black hole, constellation, star system, binary star, globular cluster, galaxy, spiral galaxies, barredspiral galaxy, elliptical galaxy, irregular galaxy, quasars, red shift, Hubble’s Law, big bang theory, dark matter Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ______Physical Science 10th Grade______ Major Idea: _________The Universe__________________ Unit: _Galaxy Formation___(Chapter 25-26)___________ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Explain how gravity contracts hydrogen nebulae into galaxies 2. Use the Doppler effect to explain the motion of galaxies 3. Describe the formation of black holes and their role in the anatomy of a galaxy 4. Explain the differences in scale between planets, stars, solar systems, and galaxies Geocentric, heliocentric, ecliptic plane, moon, astronomical unit, space probe, maria, crater, meteoroids, phases, eclipse, umbra, penumbra, tides, spring tide, neap tide, terrestrial planets, asteroids, asteroid belt, gas giants, ring, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud, solar nebula, protoplanetary disk, planetesimals, accretion, core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona, solar wind, sunspots, prominences, solar flare, star, light-year, parallax, apparent brightness, absolute brightness, absorption lines, H-R diagram, main sequence, supergiants, giants, white dwarf, nebula, protostar, planetary nebula, pulsar, black hole, constellation, star system, binary star, globular cluster, galaxy, spiral galaxies, barredspiral galaxy, elliptical galaxy, irregular galaxy, quasars, red shift, Hubble’s Law, big bang theory, dark matter Updated 4/30/2014 Updated 4/30/2014 Unit Sequencing: Arcanum-Butler School District Grade/Content: ________Physical Science 10th Grade______ Major Idea: ___________The Universe___________________ Unit: _________________Stars______(Chapter 26)_______ Essential Questions/ Goal Statements: Key Terms and Concepts: Assessment Strategies (Formative and Summative): Related Activities and Resources: Cross-Curricular Connections: 1. Describe how nebulae, under the compressional force of gravity, form into stars 2. Describe how stars, under the compressional force of gravity, initiate nuclear fusion to produce heavier elements 3. Explain how astronomers use spectral emissions to identify the contents of stars 4. Use an HR diagram to describe the life cycle of a star 5. Describe the chemical and physical changes that stars undergo prior to their collapse Geocentric, heliocentric, ecliptic plane, moon, astronomical unit, space probe, maria, crater, meteoroids, phases, eclipse, umbra, penumbra, tides, spring tide, neap tide, terrestrial planets, asteroids, asteroid belt, gas giants, ring, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud, solar nebula, protoplanetary disk, planetesimals, accretion, core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona, solar wind, sunspots, prominences, solar flare, star, light-year, parallax, apparent brightness, absolute brightness, absorption lines, H-R diagram, main sequence, supergiants, giants, white dwarf, nebula, protostar, planetary nebula, pulsar, black hole, constellation, star system, binary star, globular cluster, galaxy, spiral galaxies, barredspiral galaxy, elliptical galaxy, irregular galaxy, quasars, red shift, Hubble’s Law, big bang theory, dark matter Updated 4/30/2014