Linear Algebra Course Handbook - University of Lahore
advertisement

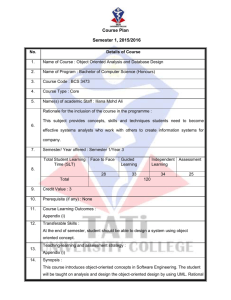
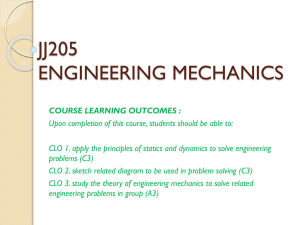
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING The University of Lahore 1 - KM Defence Road, Lahore Course Hand Book Course Title Linear Algebra 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Course Code Credit Hours Pre Requisite Lecture days Contact Hours (Theory) Contact Hours (Lab) Section Instructor MA2320 10 11 12 13 14 Office Telephone/Email Website Visiting Hours Course Introduction CE03 3 NIL Thursday , Friday 3 hours/ week A Engr. Obaid Ur Rehman Tuesday (11:00-14:00), Wednesday (13:30-16:30) In this course, Expertise of the students will be developed in the field of Linear Algebra and analysis of vector spaces through matrix operations. The main topics that will be covered in this subject are, Vector algebra, Matrix algebra, Properties of Matrices and its Determinants, Vector Spaces, Solution of linear equations, Orthogonality principle, Eigen-analysis, and the application of Matrices in Engineering. 15 Learning Objectives 1. CLO:1. Acquire knowledge related to basic concepts, and understanding of vectors and Matrices. 2. CLO:2. Understanding Vector spaces and subspaces. 3. CLO:3. Understanding the Solution of linear equations. 4. CLO:4. Understanding the basics of Eigen analysis. 5. CLO:5. Develop rational thinking patterns in terms of problem solving skills through logical reasoning. 16 Course Contents Vectors, Vector Spaces, Matrices & Determinants, Cofactor and Inverse, Rank, Linear Independence, Solution of System of Linear systems, Positive Definite matrix, Linear Transformations, Operations of Matrices, Inner products, Orthogonality and least squares, Eigenvalue and Eigen Vectors, Applications to System of Equations and to geometry, and Singular Value Decomposition. 17 Lecture Break Up Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 19 Topic of Lecture Vectors and Linear Combinations Linear Dependence and Independence Assignment 1 Length and Dot Products Quiz 1 Vectors and Linear Equations Elimination using Matrices Rules for Matrix Operations Inverse Matrices Transpose and Permutations Assignment 2 Spaces of Vectors The Nullspace of A: Solving Ax= 0 Quiz 2 The Rank and the Row Reduced Form The Complete Solution to Ax = b Independence, Basis and Dimension Dimensions of the Four Subspaces Orthogonality of the Four Subspaces Orthogonal Bases and Gram-Schmidt The Properties of Determinants Permutations and Cofactors Cramer’s Rule, Inverse, and Volumes Assignment 3 Introduction to Eigenvalues Diagonalizing a Matrix Applications to Differential Equations Quiz 3 Symmetric Matrices Positive Definite Matrices Similar Matrices Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) The idea of a Linear Transformation The matrix of a Linear Transformation Assignment 4 Change of Basis Diagonalization and the Pseudoinverse Quiz 4 Matrices in Engineering Graphs and Networks Course Assessment Policy and Grading The total hours should equal the learning hours for the module and is made up of the teaching contact hours as well as the students' private study hours. THEORY (100%) Type Hours Teaching Contact Hours Instructors Office Hours 3 hours/ week 5 hours/ week Percentage Break Up Theory (Total Weightage = 100 %) Exam Quantity Weightage 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 1 4 4 30 50 10 10 MidTerm Final Exam Quiz Assignments 20. Text Book/s Gilbert Strang, " Introduction to Linear Algebra ", WellesleyCambridge Press, (Latest Edition) 21. Reference Books Howard Anton / Chris Rorres, “Elementary Linear Algebra” 10 th Edition. 22. Plagiarism Policy Plagiarism involves the unacknowledged use of someone else’s work, usually in coursework, and passing it off as if it were one’s own. Many students who submit apparently plagiarised work probably do so inadvertently without realising it because of poorly developed study skills, including note taking, referencing and citations; this is poor academic practice rather than malpractice. Study skills education within programmes of study should minimise the number of students submitting poorly referenced work. However, some students plagiarise deliberately, with the intent to deceive. This intentional malpractice is a conscious, pre-mediated form of cheating and is regarded as a particularly serious breach of the core values of academic integrity. The Computer Engineering Programme has zero tolerance for intentional plagiarism. 23. Attendance Policy Every student must attend 80% of the lectures/seminars delivered in each course and 80% of the practical/laboratory work prescribed for the respective courses. The students having short of required percentage of attendance of lectures/seminars/practical/laboratory work, etc., shall not be allowed to appear in the terminal examination of this course and shall be treated as having failed this course. 24. Project / Report / Simulation 25. Field Trips/Case Studies/Seminars/Workshop 26. Mapping of Course Learning Objective to Program Learning Objective CLOs/PLOs CLO:1 PLO:1 (Knowledge Base) √ PLO:2 (Application) √ CLO:2 CLO:3 CLO:4 CLO:5 √ PLO:3 (Designing Skills) √ PLO:4 (Problem Solving) √ PLO:5 (Analysis and Critical Thinking) √ √ √ √ √ √ PLO:6 (Industrial Tools) PLO:7 (Engineering Management Skills) PLO:8 (Professionalism and Ethics) PLO:9 (Professional Development and Selflearning) √ √ PLO:10 (Team Work) √ √ PLO:11 (Communication Skills) √ √ 27. Mapping of CLOs to Assessment Modules Assessment Modules CLO1 CLO2 CLO3 CLO4 CLO5 CLOs/Assessment Modules CLO:1 CLO:2 CLO:3 CLO:4 CLO:5 Assignments √ √ √ √ √ Quizzes √ √ Midterm Exam √ √ Final Exam √ √ Project √ √ √ √ √