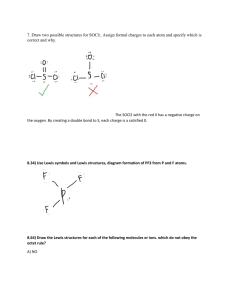
File
advertisement

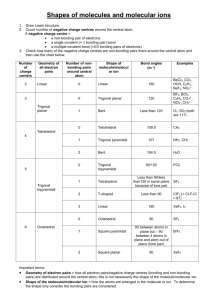
Unit 4 Worksheets 4 Molecular shapes & polarity 1. Predict the shape and bond angles of: (a) boron trichloride, BCl3 (b) phosphoryl chloride, POCl3 (c) phosphine, PH3 (d) hydrogen cyanide, HCN 2. Explain why sulfur dioxide molecules, SO2, have a bent shape whereas carbon dioxide molecules, CO2, are linear. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain why the H-N-H angle in ammonia is smaller than the H-N-H angle in the ammonium ion. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. (a) A simplified model of benzene, C6H6, shows the six carbon atoms in a ring with alternate single and double bonds between the carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is also bonded to one hydrogen atom. Based on this model predict the C-C-C bond angle in benzene. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ (b) In cyclohexane, C6H12 the six carbon atoms are also in a ring but are joined to each other only by single bonds. Each carbon atom is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Predict the C-C-C bond angle in cyclohexane. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Fluorine and oxygen are very electronegative elements. Explain why hydrogen fluoride, HF, and water, H2O, are very polar molecules but tetrafluoromethane, CF4, and carbon dioxide, CO2 are nonpolar. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ only questions 6. Predict the shape of: (a) xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4 (b) the iodine tetrachloride ion, ICl4– (c) chlorine trifluoride, ClF3 7. Predict all the F-P-F bond angles in: (a) phosphorus pentafluoride, PF5 (b) the phosphorus hexafluoride ion, PF6– Answers 1. (a) BCl3 contains 3 bonding electron pairs around the central boron atom so the shape will be trigonal planar with angles of 120o. (b) POCl3 contains 4 bonding negative charge centres so tetrahedral with angles of approximately 109.5o. In fact the Cl-P-Cl bond angle is 103o (see right) (c) PH3 contains 3 bonding & 1 non-bonding electron pairs so trigonal planar with bond angles of approximately 107o (the actual value is 93.5o) (d) HCN contains two negative charge centres around the central carbon atom so linear with bond angles of 180o. 2. The sulfur atom in SO2 contains three negative charge centres arranged to give a trigonal planar shape. The two bonding negative charge centres to the oxygen atoms give the molecule its bent shape with an angle of approximately 120o. In carbon dioxide there are only two negative charge centres (both bonding) around the central carbon atom so the molecule is linear. 3. Ammonia contains one non-bonding pair of electrons around the central nitrogen atom. This exerts a greater repulsion than the three bonding pairs so the H-N-H bond angle will be less than 109.5o. In the ammonium ion the four bonding pairs of electrons around the central nitrogen atom give the ion a regular tetrahedral shape with a bond angle of 109.5o. 4. (a) In benzene each carbon atom has three negative charge centres (all bonding) so the bond angles will all be approximately 120o. (b) In cyclohexane each carbon atom has four negative charge centres (all bonding) so the bond angles will all be approximately 109.5o. 5. HF is polar as the molecule only contains two atoms with different electronegativity values. H2O is polar as the molecule is bent and contains a dipole (see left). CF4 is tetrahedral and CO2 is linear; in both cases the bond polarities cancel out to give a zero resultant dipole. only questions 6. (a) XeF4: 6 electron pairs (4 bonding + 2 non-bonding) so square planar (b) ICl4– : 6 electron pairs (4 bonding + 2 non-bonding) so square planar (c) ClF3 : 5 electron pairs (3 bonding + 2 non-bonding) so T-shaped (see left) (the two non-bonding pairs go in the trigonal pyramid part of the trigonal bipyramid basic shape so that they are as far apart from each other as possible). 7. (a) PF5 (trigonal bipyramid shape so) 90o, 120o and 180o (b) PF6– (octahedral shape so) 90o and 180o.