Supplementary Tables S1-S4 Table S1. Previously reported
advertisement
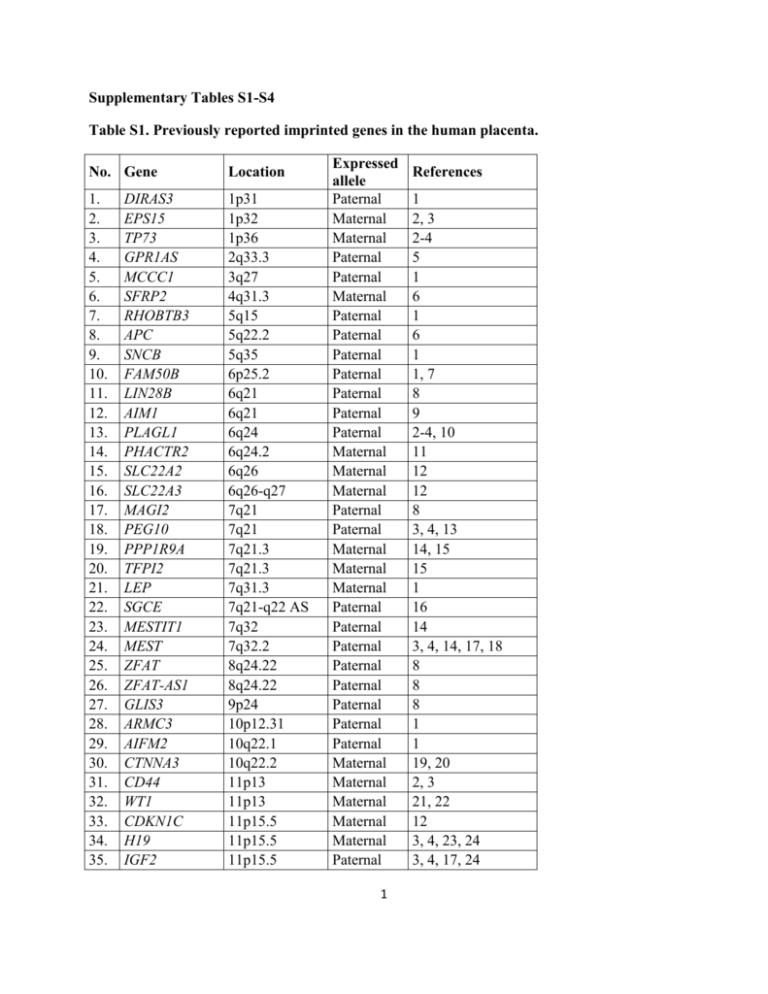
Supplementary Tables S1-S4 Table S1. Previously reported imprinted genes in the human placenta. No. Gene Location 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 1p31 1p32 1p36 2q33.3 3q27 4q31.3 5q15 5q22.2 5q35 6p25.2 6q21 6q21 6q24 6q24.2 6q26 6q26-q27 7q21 7q21 7q21.3 7q21.3 7q31.3 7q21-q22 AS 7q32 7q32.2 8q24.22 8q24.22 9p24 10p12.31 10q22.1 10q22.2 11p13 11p13 11p15.5 11p15.5 11p15.5 DIRAS3 EPS15 TP73 GPR1AS MCCC1 SFRP2 RHOBTB3 APC SNCB FAM50B LIN28B AIM1 PLAGL1 PHACTR2 SLC22A2 SLC22A3 MAGI2 PEG10 PPP1R9A TFPI2 LEP SGCE MESTIT1 MEST ZFAT ZFAT-AS1 GLIS3 ARMC3 AIFM2 CTNNA3 CD44 WT1 CDKN1C H19 IGF2 Expressed allele Paternal Maternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Paternal 1 References 1 2, 3 2-4 5 1 6 1 6 1 1, 7 8 9 2-4, 10 11 12 12 8 3, 4, 13 14, 15 15 1 16 14 3, 4, 14, 17, 18 8 8 8 1 1 19, 20 2, 3 21, 22 12 3, 4, 23, 24 3, 4, 17, 24 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. KCNQ1OT1 PHLDA2 SLC22A18 ANO1 ZC3H12C NTM ST8SIA1 WIF1 DLK1 MEG3 RTL1 SNRPN ZNF597 DNMT1 PEG3 MIR371A NLRP2 ZNF331 GNAS MOV10L1 ARHGAP4 11p15.5 11p15.5 11p15.5 11q13.3 11q22 11q25 12p12.1-p11.2 12q14.3 14q32 14q32 14q32.2 15q11.2 16p13 19p13.2 AS 19q13.4 19q13.42 19q13.42 19q13.42 20q13.3 22q13.33 Xq28 Paternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Paternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Paternal Paternal Paternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Maternal Maternal 12, 25 2, 3, 12, 17, 26, 27 2, 3, 12 28 8 8 1 6 3, 4 2-4 29 2, 3 8 1, 9 3, 4 30 31 11 1 1 1 SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES 1. Yuen RK, Jiang R, Penaherrera MS, McFadden DE, Robinson WP. Genome-wide mapping of imprinted differentially methylated regions by DNA methylation profiling of human placentas from triploidies. Epigenetics & chromatin 2011; 4:10. 2. Diplas AI, Lambertini L, Lee MJ, Sperling R, Lee YL, Wetmur J, Chen J. Differential expression of imprinted genes in normal and IUGR human placentas. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2009; 4:235-40. 3. Pozharny Y, Lambertini L, Ma Y, Ferrara L, Litton CG, Diplas A, Jacobs AR, Chen J, Stone JL, Wetmur J, et al. Genomic loss of imprinting in first-trimester human placenta. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 2010; 202:391 e1-8. 4. Lambertini L, Diplas AI, Lee MJ, Sperling R, Chen J, Wetmur J. A sensitive functional assay reveals frequent loss of genomic imprinting in human placenta. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2008; 3:261-9. 5. Kobayashi H, Yanagisawa E, Sakashita A, Sugawara N, Kumakura S, Ogawa H, Akutsu H, Hata K, Nakabayashi K, Kono T. Epigenetic and transcriptional features of the novel human imprinted lncRNA GPR1AS suggest it is a functional ortholog to mouse Zdbf2linc. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2013; 8:635-45. 6. Guilleret I, Osterheld MC, Braunschweig R, Gastineau V, Taillens S, Benhattar J. Imprinting of tumor-suppressor genes in human placenta. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2009; 4:62-8. 2 7. Zhang A, Skaar DA, Li Y, Huang D, Price TM, Murphy SK, Jirtle RL. Novel retrotransposed imprinted locus identified at human 6p25. Nucleic acids research 2011; 39:5388400. 8. Barbaux S, Gascoin-Lachambre G, Buffat C, Monnier P, Mondon F, Tonanny MB, Pinard A, Auer J, Bessieres B, Barlier A, et al. A genome-wide approach reveals novel imprinted genes expressed in the human placenta. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2012; 7:1079-90. 9. Das R, Lee YK, Strogantsev R, Jin S, Lim YC, Ng PY, Lin XM, Chng K, Yeo G, Ferguson-Smith AC, et al. DNMT1 and AIM1 Imprinting in human placenta revealed through a genome-wide screen for allele-specific DNA methylation. BMC genomics 2013; 14:685. 10. Kamiya M, Judson H, Okazaki Y, Kusakabe M, Muramatsu M, Takada S, Takagi N, Arima T, Wake N, Kamimura K, et al. The cell cycle control gene ZAC/PLAGL1 is imprinted--a strong candidate gene for transient neonatal diabetes. Human molecular genetics 2000; 9:453-60. 11. Daelemans C, Ritchie ME, Smits G, Abu-Amero S, Sudbery IM, Forrest MS, Campino S, Clark TG, Stanier P, Kwiatkowski D, et al. High-throughput analysis of candidate imprinted genes and allele-specific gene expression in the human term placenta. BMC genetics 2010; 11:25. 12. Monk D, Arnaud P, Apostolidou S, Hills FA, Kelsey G, Stanier P, Feil R, Moore GE. Limited evolutionary conservation of imprinting in the human placenta. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2006; 103:6623-8. 13. Ono R, Kobayashi S, Wagatsuma H, Aisaka K, Kohda T, Kaneko-Ishino T, Ishino F. A retrotransposon-derived gene, PEG10, is a novel imprinted gene located on human chromosome 7q21. Genomics 2001; 73:232-7. 14. Nakabayashi K, Bentley L, Hitchins MP, Mitsuya K, Meguro M, Minagawa S, Bamforth JS, Stanier P, Preece M, Weksberg R, et al. Identification and characterization of an imprinted antisense RNA (MESTIT1) in the human MEST locus on chromosome 7q32. Human molecular genetics 2002; 11:1743-56. 15. Monk D, Wagschal A, Arnaud P, Muller PS, Parker-Katiraee L, Bourc'his D, Scherer SW, Feil R, Stanier P, Moore GE. Comparative analysis of human chromosome 7q21 and mouse proximal chromosome 6 reveals a placental-specific imprinted gene, TFPI2/Tfpi2, which requires EHMT2 and EED for allelic-silencing. Genome research 2008; 18:1270-81. 16. Smallwood A, Papageorghiou A, Nicolaides K, Alley MK, Jim A, Nargund G, Ojha K, Campbell S, Banerjee S. Temporal regulation of the expression of syncytin (HERV-W), maternally imprinted PEG10, and SGCE in human placenta. Biology of reproduction 2003; 69:286-93. 17. Apostolidou S, Abu-Amero S, O'Donoghue K, Frost J, Olafsdottir O, Chavele KM, Whittaker JC, Loughna P, Stanier P, Moore GE. Elevated placental expression of the imprinted PHLDA2 gene is associated with low birth weight. Journal of molecular medicine 2007; 85:37987. 18. McMinn J, Wei M, Sadovsky Y, Thaker HM, Tycko B. Imprinting of PEG1/MEST isoform 2 in human placenta. Placenta 2006; 27:119-26. 19. Oudejans CB, Mulders J, Lachmeijer AM, van Dijk M, Konst AA, Westerman BA, van Wijk IJ, Leegwater PA, Kato HD, Matsuda T, et al. The parent-of-origin effect of 10q22 in preeclamptic females coincides with two regions clustered for genes with down-regulated expression in androgenetic placentas. Molecular human reproduction 2004; 10:589-98. 3 20. van Dijk M, Mulders J, Konst A, Janssens B, van Roy F, Blankenstein M, Oudejans C. Differential downregulation of alphaT-catenin expression in placenta: trophoblast cell typedependent imprinting of the CTNNA3 gene. Gene expression patterns : GEP 2004; 5:61-5. 21. Jinno Y, Yun K, Nishiwaki K, Kubota T, Ogawa O, Reeve AE, Niikawa N. Mosaic and polymorphic imprinting of the WT1 gene in humans. Nature genetics 1994; 6:305-9. 22. Nishiwaki K, Niikawa N, Ishikawa M. Polymorphic and tissue-specific imprinting of the human Wilms tumor gene, WT1. The Japanese journal of human genetics 1997; 42:205-11. 23. Yu L, Chen M, Zhao D, Yi P, Lu L, Han J, Zheng X, Zhou Y, Li L. The H19 gene imprinting in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Placenta 2009; 30:443-7. 24. Buckberry S, Bianco-Miotto T, Hiendleder S, Roberts CT. Quantitative allele-specific expression and DNA methylation analysis of H19, IGF2 and IGF2R in the human placenta across gestation reveals H19 imprinting plasticity. PloS one 2012; 7:e51210. 25. Guo L, Choufani S, Ferreira J, Smith A, Chitayat D, Shuman C, Uxa R, Keating S, Kingdom J, Weksberg R. Altered gene expression and methylation of the human chromosome 11 imprinted region in small for gestational age (SGA) placentae. Developmental biology 2008; 320:79-91. 26. Qian N, Frank D, O'Keefe D, Dao D, Zhao L, Yuan L, Wang Q, Keating M, Walsh C, Tycko B. The IPL gene on chromosome 11p15.5 is imprinted in humans and mice and is similar to TDAG51, implicated in Fas expression and apoptosis. Human molecular genetics 1997; 6:2021-9. 27. Lee MP, Feinberg AP. Genomic imprinting of a human apoptosis gene homologue, TSSC3. Cancer research 1998; 58:1052-6. 28. Okae H, Hiura H, Nishida Y, Funayama R, Tanaka S, Chiba H, Yaegashi N, Nakayama K, Sasaki H, Arima T. Re-investigation and RNA sequencing-based identification of genes with placenta-specific imprinted expression. Human molecular genetics 2012; 21:548-58. 29. Kagami M, Matsuoka K, Nagai T, Yamanaka M, Kurosawa K, Suzumori N, Sekita Y, Miyado M, Matsubara K, Fuke T, et al. Paternal uniparental disomy 14 and related disorders: placental gene expression analyses and histological examinations. Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society 2012; 7:1142-50. 30. Noguer-Dance M, Abu-Amero S, Al-Khtib M, Lefevre A, Coullin P, Moore GE, Cavaille J. The primate-specific microRNA gene cluster (C19MC) is imprinted in the placenta. Human molecular genetics 2010; 19:3566-82. 31. Bjornsson HT, Albert TJ, Ladd-Acosta CM, Green RD, Rongione MA, Middle CM, Irizarry RA, Broman KW, Feinberg AP. SNP-specific array-based allele-specific expression analysis. Genome research 2008; 18:771-9. 4 Table S2. Numbers of SNPs with specific properties in different trios. Family trio P001 P002 P005 P006 P007 P008 P009 P012 P013 P014 Homo Phased Hetero Mutant Indel Missing 231862 231826 232043 213532 232329 231754 231717 231927 226902 229265 8212 8339 8040 7090 7999 8294 8224 8006 7669 8319 1934 1769 1887 1784 1732 1861 2029 2095 1908 1942 14 14 18 18 10 14 14 14 18 11 135 136 135 125 135 135 136 136 131 135 744 817 778 20352 696 843 781 723 6273 3229 Homo – number of homozygous SNPs in a child (i.e., uninformative SNPs for our analysis); Phased – number of heterozygous SNPs of the child with at least one parent being a homozygote (i.e., possible to detect the parental origin of the child’s alleles. These SNPs were suitable for further analyses); Hetero – number of SNPs where mother, father and child are all heterozygotes for a particular SNP (i.e., impossible to detect the inheritance of the SNP); Mutant – number of inconsistent SNPs between the child and the parents; Indel – number of insertions and deletions; and Missing – number of SNPs where the microarray showed a missing value for mother, father or child (e.g., due to a technical problem, most likely low-quality DNA). 5 Table S3. Selected genomic intervals and primer sequences for validation. Gene Chr Start and end positions Informative SNPs Forward primer Reverse primer Product size (bp) PEG10 chr 7 94296769 94296793 rs13073 rs13226637 TGCCTGACATGAAGAGGAGT GAGCCTCTCATTCACAGCAT 283 RHOBTB3 chr 5 95131292 95131757 rs6815 rs7622 rs3184188 CATGAGCATATTCGCACCCC GTTTAGCTGTCTTGGAAGTCA 763 RHOBTB3 chr 5 95129056 95129251 rs6697 rs12351 TCTTCTGACCGAAACCAATGTG CCAAATGGCCGGCAAATTTC 413 RHOBTB3 chr 5 95091194 95091201 rs34898 rs34899 GCTGAAGCGTCACATTATAACTC ATGGCTAGCACCTGGAAATG 255 PAPPA2 chr 1 176811754 176811918 rs12137448 rs12137517 GCAGTAAGAAAGAGAGGCCG CAAGTTGGGTGGGACTGAGT 330 PAPPA2 chr 1 176659790 176660247 rs726252 TGGTCATTTGTGTCGGAGAG CAAACAAGCCCCCAAAACT 726 Chr – chromosome. 6 Table S4. Demographic and clinical data of parents and children. Family trio Maternal age (year) P001 P002 22 27 Maternal prePaternal pregnancy age (year) BMI (kg/m2) 25 20 29 20 Parity Gestational age Mode of (weeks+days) delivery Newborn gender 0 1 39+0 39+3 Male Female Apgar score 1 min/5 min after birth 9/10 8/9 P005 26 27 24 0 40+4 Male P006 P007 P008 P009 P012 P013 P014 29 24 24 41 25 23 26 27 31 26 46 27 33 35 25 24 17 35 19 20 17 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 38+1 40+6 40+5 41+0 42+0 40+2 41+1 Male Male Female Male Female Male Female VD Elective CS Emergency CS VD VD VD VD VD VD VD 3188 3628 484 575 8/9 3540 360 9/10 9/9 9/10 9/9 9/9 8/9 8/8 3750 3836 3746 4150 3128 3394 3936 552 384 408 524 369 321 472 BMI – body mass index. Parity – number of previous births. VD – vaginal delivery. CS – caesarean section. 7 Birth Placental weight (g) weight (g)