Background info on vaccines/herd immunity
advertisement

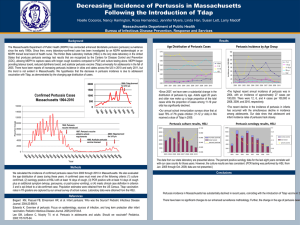
http://www.autismsciencefoundation.org/autismandvaccines.html Listing of scientific articles showing no connection between autism and vaccinations or their schedule. http://www.autismsciencefoundation.org/sites/default/files/CHOP1.pdf really nice newsletter format summary of this http://www.autismsciencefoundation.org/sites/default/files/CHOP2.pdf General vaccine info Herd Immunity Thresholds for various diseases http://commonhealth.wbur.org/2013/08/low-statevaccine-rates http://media.wbur.org/wordpress/15/files/2013/08/too-many-children-go-unvaccinated_2-620x580.jpg http://www.vaccines.gov/diseases/diphtheria/index.html info on specific vaccines, rates, risks also immune system http://www.software3d.com/Home/Vax/Immunity.php vaccination software herd immunity http://www.motherjones.com/environment/2014/02/vaccine-exemptions-states-pertussis-map http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=203593#REFJOC60132-7 Nonmedical Exemptions to School Immunization RequirementsSecular Trends and Association of State Policies With Pertussis Incidence Saad B. Omer, MBBS, MPH; William K. Y. Pan, DrPH, MS, MPH; Neal A. Halsey, MD; Shannon Stokley, MPH; Lawrence H. Moulton, PhD; Ann Marie Navar, MHS; Mathew Pierce, JD, MPH; Daniel A. Salmon, PhD, MPH [+] Author Affiliations JAMA. 2006;296(14):1757-1763. doi:10.1001/jama.296.14.1757. Figure 1. Mean Percentage and Interquartile Ranges of Nonmedical Exemptions for States That Only Permit Religious Exemptions and States That Permit Personal Belief Exemptions, 1991 Through 2004 Pertussis Incidence and Associations With State Policies The mean annual incidence of pertussis in the 50 states and the District of Columbia is presented in Figure 3. Vermont had the highest incidence at 12.8 per 100 000. In unadjusted analysis, pertussis incidence in states allowing personal belief exemptions was more than twice as high as in states that only offered religious exemptions (IRR = 2.06; 95% CI, 1.77-2.4). States with easy procedures for granting exemptions were associated with a 90% higher incidence of pertussis (IRR = 1.90; 95% CI, 1.06-2.28) and states with a medium difficulty for granting exemptions were associated with a 27% higher incidence of pertussis (IRR = 1.27; 95% CI, 1.06-1.51) compared with states with difficult procedures to obtain exemptions. Pertussis incidence was 41% higher for states that considered parental signature as sufficient proof of immunization compared with states that did not (IRR = 1.41; 95% CI, 1.12-1.77) (Table 2). From Wikipedia IRR Incidence Rate Ratio A rate ratio (sometimes called an incidence density ratio) in epidemiology, is a relative difference measure used to compare the incidence rates of events occurring at any given point in time. A common application for this measure in analytic epidemiologic studies is in the search for a causal association between a certain risk factor and an outcome.[1] [2] Where incidence rate is the occurrence of an event over person-time, for example person-years. Note the same time intervals must used for both incidence rates. Availability of personal belief exemptions and easily obtained exemptions were associated with increased pertussis incidence. The small number of states with acceptance of parental signature may have limited the power of this comparison. These study findings indicate that state exemption policies affect vaccine exemption rates as well as pertussis incidence. States should examine their exemption policies to ensure control of pertussis and other vaccine-preventable diseases. http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6230a3.htm CDC data on kindergarten immunization, by state, 2012-2013 State % surveyed Mmr alabama 100 92.8 Arkansas 96.3 85.9 Idaho 100 88.4 Indiana 83 95.4 DTAP 92.8 82.9 88.3 90 Minnesota Pennsylvania Missouri Colorado wisconsin washington National median 100 97.5 5.9 0.5% 1.8 94.7 96.3 87 96.7 85.7 92.8 91.7 94.5 96.7 90.7 96.5 82.9 96.1 91.9 95.1 FIGURE. Estimated percentage of children enrolled in kindergarten who have been exempted from receiving one or more vaccines* — United States, 2012–13 school year http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/about/faqs.html DTAP is 80-90% effective, with protection at 90% one year after all five doses. Decreases with time, : 70% fully protected after five years, with other 30% partially protected A person with pertussis can infect 12-15 other people Vaccines trigger the immune response and create Memory B cells to a specific virus. Flu, measles, mumps, chicken pox, HPV, meningitis, polio, etc. Vaccines use “dead” viruses (can’t cause disease), very weakened viruses, or simply parts of viruses with antigen to trigger the immune response. You have to have vaccines BEFORE being exposed to the disease-causing (pathogenic) virus or bacterium. Bacterial vaccines exist, using similar types of antigens. Vaccines are available against the bacterial diseases tuberculosis, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type B, cholera, typhoid, and Streptococcus pneumoniae.