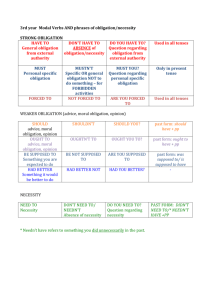
MODALS 1) ABILITY Present Ability (can/be able to) Can/be able to
advertisement

MODALS 1) ABILITY a) Present Ability (can/be able to) Can/be able to express present ability. Can is more common than be able to. Example: I can (am able to) speak English and Turkish, but I can’t speak Italian. b) Past Ability (could/was-were able to) Could/was-were able to express past ability. Example: I could/was-were able to run very fast when I was a child. Example: She was a good swimmer when she was a child. She could/was-were able to swim faster than all the children. was-were able to(managed to do) is used to express managing a difficult situation in the past. Example: The quiz on Monday was very difficult, but I was able to get a high great. (It means I managed to get a high grade although the quiz was difficult.) 2) POSSIBILITY a) Present Possibility (may/might/could) May/Might/Could express possibility in present. Example: Why is Peter at home today? - I don’t know. He may/might/could be ill today. Example: - Mum, I can’t find my mobile phone. Have you seen it? - It may/might/could be in the living room or in the kitchen. b) Past Possibility (may/might/could have + V3) May/Might/Could have + V3 expresses possibility in the past. Example: I can’t find my grammar book. I don’t where I left it. I may/might/could have left it on the bus or in the classroom. 1 Could have + V3 has also a different meaning. It means, “I had the chance to do it, but I didn’t do it. Example: I could have helped my friend with her homework, but I watched TV. (It means, I didn’t help my friend.) Example: She could have gone to the cinema. (It means, “she didn’t go to the cinema.) 3) ADVICE a) Present Advice (should/ought to/had better) Should/ought to/had better express advice in present. They all have the same meaning. Example: -I have toothache. -You should see a doctor. Had better has a stronger meaning. It means, “I should do it, if I don’t do it the results may be bad.) Example: I had better study for my math exam tonight. If I don’t I will fail the exam tomorrow. Example: You are driving too fast. You had better slow down, if you don’t you will have an accident. b) Past Advice/Criticism (should have + V3) Should have + V3 means, “There was something I had to do in the past. But, I didn’t do it and the result was bad”. Example: He didn’t study for hard enough, so he failed the exam. He should have studied harder for the exam. Shouldn’t have + V3 means, “I did something in the past and the result was bad. I shouldn’t have done it”. Example: Although I was ill, I went to work and my cold got worse. I shouldn’t have gone to work. 3) NECESSITY/OBLIGATION a) Necessity/Obligation in Present Have to/have got to/must/need to have basically the same meaning. They express the idea that something is necessary. Have got to is used in informal conversation, in daily speech. Have to is used much more frequently than in everyday speech and writing than must. 2 Example: Students must/have to/have got to study hard to pass their exams. Example: Do you have to leave now? - Yes, I do. (Yes, I have to leave now.) “Must” has a stronger meaning. You have no other choices. Example: You must stop smoking. Your lungs are getting worse. b) Necessity/Obligation in Past Had to expresses the idea that something was necessary in the past. Example: There weren’t so many toys when we were children. We had to make our own toys. Example: Did you have to wear a uniform when you were in high school? -Yes, I did. (Yes, I had to wear a uniform.) 4) LACK OF NECESSITY a) Lack of Necessity in present Don’t-doesn’t have to/don’t need to/needn’t express the idea that something is not necessary in the present(now). Example: I don’t have to go to school tomorrow because it is Saturday. Example: She doesn’t need to wash the dishes by hand because we have a dishwasher. b) Lack of Necessity in Past Didn’t have to/didn’t need to express the idea that something was not necessary in the past. Example: She didn’t have to go shopping after work. Her husband already did the shopping. Example: I didn’t need to wait long for my friends. They came only ten minutes late. ****** NEEDN’T HAVE DONE expresses the idea that there was something in the past and I thought that I had to do it. So, I did it. But, I learned that I didn’t need to do it. Example: There is plenty of food at home. You needn’t have gone shopping. (But, I already did the shopping.) 3 BE CAREFUL!!! About the difference between “NEEDN’T HAVE DONE and DIDN’T NEED TO. Look at the examples: Example 1: My friend called me and said “ We are going to go on a picnic this weekend. Everyone is going to prepare something”. I prepared some cookies for the picnic. Later, my friend called me and said, “We cancelled the picnic”. - I needn’t have prepared some cookies. Example 2: My friend called me and said “ We are going to go on a picnic this weekend. Everyone is going to prepare something”. Before I prepared some cookies for the picnic my friend called me and said, “We cancelled the picnic”. - I didn’t need to prepare cookies for the picnic. 4