Non-Vascular Plants
advertisement

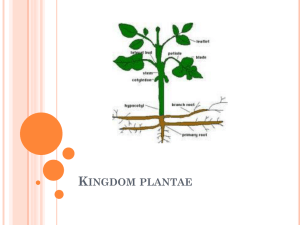
Information Sheet: Non-Vascular Plants You have probably seen plenty of moss growing around your home or school. They especially like shady, damp places. Mosses are a type of non-vascular plant that differs from vascular plants in a lot of ways. Non-vascular plants are the simplest plants found on land. The category of non-vascular plants includes Bryophyta, which includes mosses, hornworts, and liverworts. They are the successor of the green algae division of plants. Below are some more characteristics of non-vascular plants. Absence of Vascular Tissues One of the most important characteristics of non-vascular plants is the absence of vascular tissues. Non-vascular plants do not have the vascular tissues known as xylem and phloem. They do not have an internal water transport system that is found in vascular plants. Though these non-vascular plants do have stem-like and leaflike structure, they lack true roots, stems, or leaves. As they do not have any vascular tissue, they cannot retain water for a long time or transport it to other parts of the plant. Habitat Moss can be seen on moist places such as bogs and swamps as they absorb water from their surroundings. Like all plants, they need water to survive and they have to absorb it directly from the surrounding air or any other nearby resource. They distribute water to other parts by using slow means such as capillary action, diffusion, and cytoplasmic streaming. Size Non-vascular plants are always small in size. As they lack the woody tissues that are required to support a plant on land they can only reach a height of a few centimeters. Moreover, they cannot transport Information taken from: http://www.brighthubeducation.com/science-homework-help/79105-characteristics-of-nonvascular-plants/ water and food very far due to lack of vascular tissues. They transfer water, organic food, and minerals from the environment to the interior of the gametophyte through cell-to-cell osmosis. Obtaining Energy Like other plants, nonvascular plants also gain energy by the process of photosynthesis. This process takes place in the upper parts of these plants in leaf-like and stem-like appendages. Summary Do not produce seeds, flowers, or fruits Do not have the vascular tissues xylem and phloem Are multi-celled; cell walls composed of cellulose Do not have true roots, stems, and leaves. Depend on water for reproduction. Are smaller in size. Live in dark and damp places. Transport water and other nutrients through cell-to-cell osmosis Information taken from: http://www.brighthubeducation.com/science-homework-help/79105-characteristics-of-nonvascular-plants/