NON VASCLUR PLANTS
advertisement

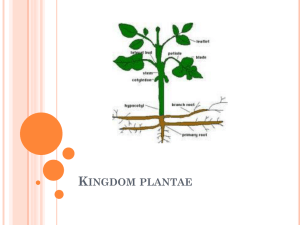
By: Shannon Havill, Emily Crosby, Liam Q Sample Organisms • • • • • Ferns Mosses Liverworts Hornworts Archegonia Habitat • Non-vascular plants grow best in damp, shaded conditions with rich soil to absorb nutrients from. • They typically grow in clusters in the coniferous forest. Principal Characteristics • The principle characteristics of non-vascular plants are: • They do not have any seed for reproduction. • They also do not have any flower. • They don’t have special tissues for nutrition movement so they use diffusion to get nutrition from the soil. Life Cycle • Vascular plants have special tissues that have cells to move food and water throughout the plant. Some examples of vascular plants are trees, shrubs and ferns. Non-vascular plants don’t have these special tissues and cells. In order to get nutrients they use diffusion to get nutrients from the soil and move them up the roots to the entire plant. • “Sporophyte" and "gametophyte" are the necessary procedures of the life cycles of non-vascular plants. • Non-vascular plants include mosses and liverworts, and a generalized moss plant makes an excellent representative for the typical non-vascular plant lifecycle. Life cycle: Sporophyte • The sporophyte is a stalk with a capsule at the tip. This is where the spores are released to reproduce. • The life cycle and reproduction of non-vascular plants called the "sporophyte". This structure makes and release spores. They are released into the environment where they can reproduce. • Since non-vascular plants are non-flowering, and don’t have seeds, spores are there only way to reproduce. The sporophyte starts out green and as they mature they turn a brownish color. Life cycle : Gametophyte • With moist conditions, the newly released spores can grow and mature. They will grow into either male or female plants. "Gamete" means reproductive cells and “Phyte" means plant. • It is the mossy green part of the moss plant that we see. Digestion • In this sense non-vascular plants are like vascular plants in that they obtain energy through photosynthesis. They obtain energy by converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy and store it as glucose or other organic compounds. As such they are autotrophy like vascular plants. The photosynthesis process normally takes place in the upper parts of the plants. Circulation • The key difference between vascular and nonvascular plants are that non-vascular plants have no circulatory system, this is the reason they do not grow to be nearly the same size. Since they lack the xylem needed to transport water throughout, they are covered in waxy cuticles that help absorb and keep water in as they have no method of transporting it. Corporal Structure • Because nonvascular plants are unable to absorb water, they almost always remain low and flat. • Consist largely of cylindrical stems, these stems that are almost certainly symmetrical, moss possessing radial symmetry while liverworts’ are bilaterally symmetrical. • They have a cell wall made of cellulose. • They are eukaryotic. • They contain chlorophyll in order to obtain energy, they are stored in appendages similar to leaves but it is worth noting that they are not truly leaves as they lack the tissues necessary to be considered as such. Nervous System • Non vascular plants do not have a nervous system to transport food and water around their body. Instead, they make their own food and they get water from the air droplets. • Non vascular plants do not move either. So they have no need for muscles or joints. • Non vascular plants do not have a nervous system so they do not respond any stimuli. Respiration • Like in vascular plants, gas exchange in plants is done through photosynthesis. This is the process by which light energy is turned into useable energy by the plant. • The equation for photosynthesis is light + 6CO2 + 12H20 --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20 • This means that water and carbon dioxide are taken into the plant (along with light) and release oxygen in it’s gaseous state (as it is found in the atmosphere. Facts • Non vascular plants are also called bryophytes. • Non vascular plants do not have roots, stems, or leaves. • Non vascular plants have no vascular tissue. • Nonvascular plants were the first to appear on earth’s soil and evolve. Their physical structure allowed them to adapt over time. • Nonvascular plants--also known as seedless or flowerless plants--are among the smaller varieties within the plant kingdom.