notes
advertisement
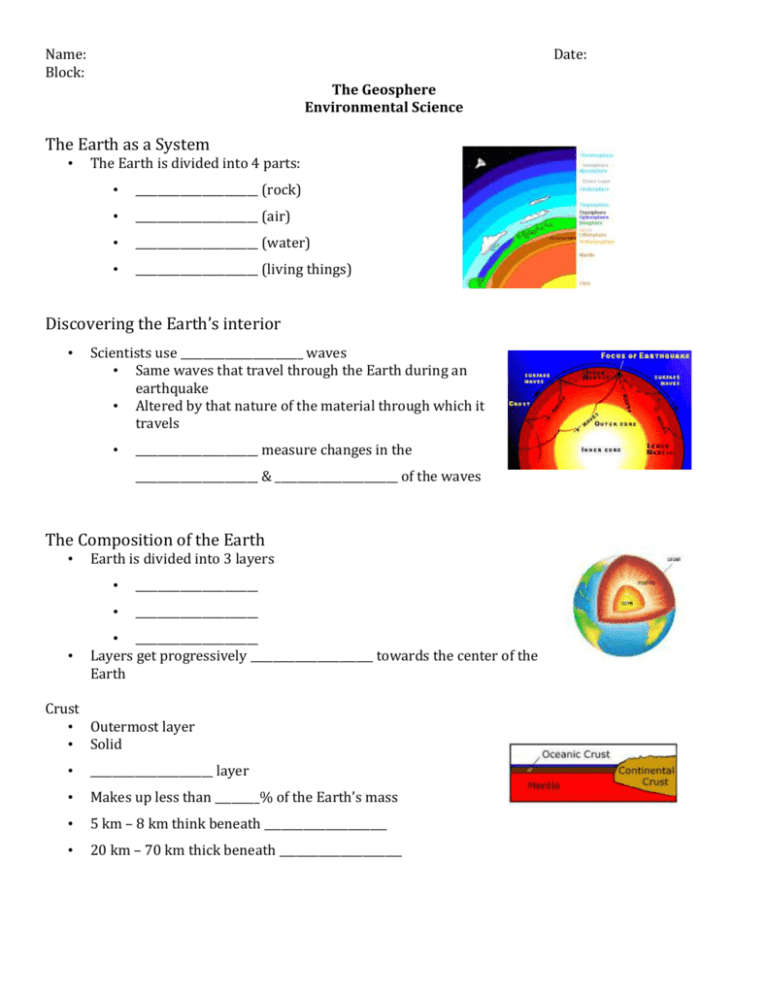
Name: Block: Date: The Geosphere Environmental Science The Earth as a System • The Earth is divided into 4 parts: • ______________________ (rock) • ______________________ (air) • ______________________ (water) • ______________________ (living things) Discovering the Earth’s interior • Scientists use ______________________ waves • Same waves that travel through the Earth during an earthquake • Altered by that nature of the material through which it travels • ______________________ measure changes in the ______________________ & ______________________ of the waves The Composition of the Earth • • Earth is divided into 3 layers • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ Layers get progressively ______________________ towards the center of the Earth Crust • Outermost layer • Solid • ______________________ layer • Makes up less than ________% of the Earth’s mass • 5 km – 8 km think beneath ______________________ • 20 km – 70 km thick beneath ______________________ Mantle • ______________________ • • Between the ______________________ & ______________________ Medium density • Makes up ________% of the mass of the Earth Core • • • ______________________ part of Earth Located below the ______________________ Composed of the densest elements The Structure of the Earth • Earth can be divided into 5 layers based on physical properties of the layers • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ • ______________________ ______________________ – solid, outer layer • Crust & upper mantle • Divided into ______________________ plates ______________________ – solid, plastic layer of the mantle • Made of ______________________ rock that flows & allows tectonic plates to move ______________________ – lower part of mantle ______________________ core – dense liquid layer ______________________ core – made of mostly ______________________ & ______________________ • Temperature estimated to be ______________________ -______________________ °C • Solid because under enormous ______________________ Both the inner core & outer core make up about ________ of the Earth’s mass Plate Tectonics • Tectonic plates – blocks of ______________________ that glide across the underlying ______________________ • Consist of the ______________________ & outermost part of ______________________ • ______________________ are located on plates & move around with them • Plates may ______________________, ______________________, or ______________________ past one another causing mountain formations, earthquakes, or volcanoes Earthquakes • ______________________ – break in the Earth’s crust • ______________________ caused when rocks under stress suddenly break along a fault causing ground vibrations • Many cannot be felt Majority take place at or near ______________________ plate boundaries • Caused by stresses generated when plates separate, collide, or slip past each other • Magnitude • Magnitude – measure of the ______________________ released by an earthquake • Smallest magnitude that can be felt = ________ • Largest magnitude recorded = ________ • • >________ magnitude = widespread damage Increase in magnitude by a whole number means __________x more energy released than the number below it Earthquake Hazard • Earthquakes cannot be predicted, but an area’s earthquake-______________________ level can be determined by past & present seismic activity • Earthquake-resistant buildings are slightly ______________________ so that they can sway with ground motion • Prevents ______________________ Volcanoes • Volcano – mountain built from ______________________ (melted rock) that rises from the Earth’s interior Located near fault lines where plates are either ______________________ or • ______________________ Most volcanoes on land surround the ______________________ Ocean in the • ____________________________________________ Effects of Volcanoes • Clouds of hot ______________________, ______________________, & ______________________ can flow down a volcano at speeds up to ____________ km/hr • Volcanic ash can mix with water & produce ______________________ • Ash can cause ______________________ buildings, buried ______________________, damaged ______________________, & ______________________ difficulties • Major volcanic eruptions can change ______________________ • Volcanic ash & sulfur can reduce the amount of ______________________ that reaches the Earth’s surface, lowering surface ______________________ Erosion • Erosion – materials of the Earth’s surface are ______________________, ______________________, or • ______________________ away & transported to another place by natural forces (wind, water, ice, gravity) Wears down rocks & makes them ______________________ over time Water Erosion • Erosion by ______________________ & ______________________ • Waves can erode ______________________ Wind Erosion • Wind can blow soil away quickly in places where few ______________________ grow • Soft rocks (______________________) erode more easily than hard rocks (______________________)











