observations study sheet 110216
advertisement
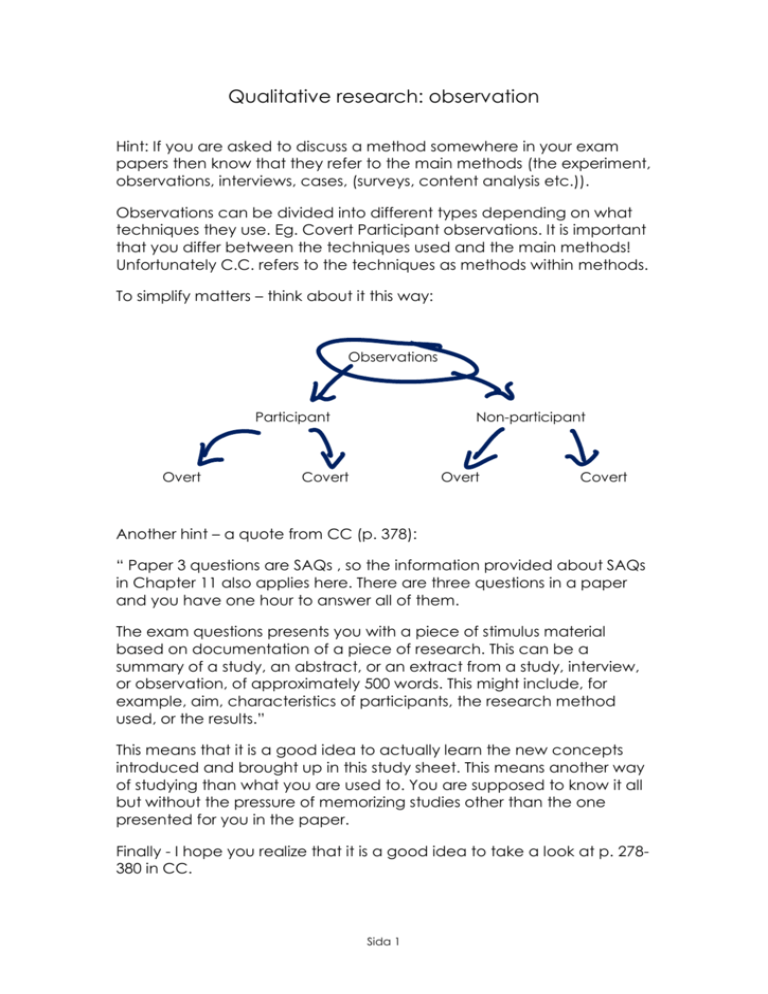
Qualitative research: observation Hint: If you are asked to discuss a method somewhere in your exam papers then know that they refer to the main methods (the experiment, observations, interviews, cases, (surveys, content analysis etc.)). Observations can be divided into different types depending on what techniques they use. Eg. Covert Participant observations. It is important that you differ between the techniques used and the main methods! Unfortunately C.C. refers to the techniques as methods within methods. To simplify matters – think about it this way: Observations Participant Overt Non-participant Covert Overt Covert Another hint – a quote from CC (p. 378): “ Paper 3 questions are SAQs , so the information provided about SAQs in Chapter 11 also applies here. There are three questions in a paper and you have one hour to answer all of them. The exam questions presents you with a piece of stimulus material based on documentation of a piece of research. This can be a summary of a study, an abstract, or an extract from a study, interview, or observation, of approximately 500 words. This might include, for example, aim, characteristics of participants, the research method used, or the results.” This means that it is a good idea to actually learn the new concepts introduced and brought up in this study sheet. This means another way of studying than what you are used to. You are supposed to know it all but without the pressure of memorizing studies other than the one presented for you in the paper. Finally - I hope you realize that it is a good idea to take a look at p. 278380 in CC. Sida 1 1. Explain the main characteristics of the method observation 2. Fill in the table below to be able to evaluate the two basic methods (techniques) of observations: PARTICIPANT OBSERVATION NON-PARTICIPANT OBSERVATION (including naturalistic observations) General characteristics: General characteristics: One research example: One research example Strenghts: Weaknesse: Strenghts: 3. Briefly explain the difference between: a) Unstructured observations b) Semi structured observations c) Structured observations Sida 2 Weaknesses: 4. Participant and non-participant observations can be overt or covert. It is important that you know how to evaluate each one in a balanced way. Therefore, fill in the table below: OVERT OBSERVATION COVERT OBSERVATION General characteristics: General characteristics: One research example: One research example 5. Strenghts: 6. Weaknesse: 7. Strenghts: 8. Weaknesses: 3. Summarize ethical challenges that might be relevant in different types of observations. Sida 3 4. The Festinger study is very useful when discussing observation. It is also used in the Sociocultural Level of Analysis as an example of typical research done in this level (p. 102-102 in CC). Outline the following SAQ: Explain the use of one research method at the sociocultural level of analysis There are some hints on how to attack a question like this on p. 103. Know that you could choose another method as well in your exam – eg. the Experiment. Also – make sure when writing an answer to a question like this to make everything you write relevant to the level you are writing about (SLOA) 5. About considerations involved in setting up and carrying out an observation: In bullet form - outline important features when: a) Preparing an observation b) Conducting the observation c) After the observation 6. What is an inductive approach to data? 7. About how researchers analyse data obtained - Describe what is included in the three parts of grounded theory analysis: a) Description b) Coding and connecting themes c) Produce an account. Remember, chapter 10.1 (about qualitative research methods will be covered later so don’t worry too much about triangulation and inferential and theoretical generalizations. Sida 4